SMS Rover
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

湖南省 Provinsi Hunan Singkatan: 湘 (pinyin: Xiāng) Asal nama 湖 hú - danau 南 nán - selatan selatan Danau Dongting Tipe administrasi Provinsi Ibu kota Changsha Kota terbesar Changsha Sekretaris PKT Du Jiahao [1] Gubernur Xu Dazhe [2] Wilayah 211.800 km² (ke-10) Populasi (Tahun) - Kepadatan 66.630.000 (ke-7) 315/km² (ke-13) PDB (2003) - per kapita CNY 463,9 miliar (ke-12) CNY 6960 (ke-21) Suku-suku utama (2000) Suku Han - 90%Suku Tujia - 4%Suku Miao - 3%Suku Don...

Museum Daerah Deli SerdangMuseum Deli Serdang, Januari 2020Didirikan8 September 2018LokasiJalan Negara, Petapahan Kawasan Olahraga, Seni dan Budaya, Lubuk Pakam, Deli Serdang, Sumatera UtaraJenisMuseum sejarah dan budayaSitus webMuseum Daerah Deli Serdang Museum Daerah Deli Serdang atau Museum Deli Serdang adalah museum sejarah dan budaya yang terletak di lokasi kompleks perkantoran pemerintahan, yaitu di Tanjung Garbus I, Lubuk Pakam, Deli Serdang. Museum ini didirikan dengan tujuan mencatat...

Species of lizard For the genus, see Podarcis. Common wall lizardTemporal range: 0.01170–0 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N ↓ Early Holocene – Recent[1] Wall lizard near the Entella river, northwestern Italy Conservation status Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[2] Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Reptilia Order: Squamata Family: Lacertidae Genus: Podarcis Species: P. muralis Binomial name Podarcis muralis(...

Salib pektoral emas dari Italia atau daerah subalpine, akhir abad ke-6 – abad ke-7 Salib pektoral Paus Paulus VI Salib pektoral atau pectorale (dari Latin pectoralis, dari dada) adalah salib yang dikenakan di dada, biasanya digantung di leher dengan tali atau rantai. Pada masa kuno dan abad pertengahan, salib pektoral dikenakan oleh pastor dan awam, namun pada akhir Abad Pertengahan salib pektoral menjadi indikator khusus mengenai kedudukan yang dikenakan oleh para uskup. Di Gereja Katolik ...

Char kway teow Hanzi tradisional: 炒粿條 Hanzi sederhana: 炒粿条 Makna harfiah: kwetiau goreng Alih aksara Mandarin - Hanyu Pinyin: cháo guǒ tiáo Min Nan - Romanisasi POJ: chhá-kóe-tiâu Yue (Kantonis) - Jyutping: caau2 gwo2 tiu4 Nama alternatif dikawasan berbahasa Kanton Hanzi tradisional: 炒貴刁 Hanzi sederhana: 炒贵刁 Makna literal: tidak ada Alih aksara Mandarin - Hanyu Pinyin: cháo guì diāo Yue (Kantonis) - Jyutping: caau2 gwai3 diu1 Char kway teowJenisShahe fenTempa...

Questa voce sull'argomento stadi di calcio dell'Ungheria è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Sóstói Stadion Informazioni generaliStato Ungheria UbicazioneSzékesfehérvár Inizio lavori1963 Inaugurazione1967 Chiusura2015 Demolizione2016 Ristrutturazione2002-2004 Informazioni tecnichePosti a sedere14900 Coperturatribuna centrale Mat. del terrenoerba Dim. del terreno105 × 68 m Uso e beneficiariCalcio Vadásztölténygyári(...

Irish nationalist and author (1870–1922) Erskine ChildersDSCChilders in uniform of the CIV, 1899Teachta DálaIn officeMay 1921 – June 1922ConstituencyKildare–Wicklow Personal detailsBornRobert Erskine Childers(1870-06-25)25 June 1870Mayfair, London, EnglandDied24 November 1922(1922-11-24) (aged 52)Beggars Bush Barracks, Dublin, IrelandCause of deathExecution by firing squadResting placeGlasnevin Cemetery, DublinNationalityIrishPolitical partySinn FéinSpouse Mary...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Kick-Ass. Kick-Ass Données clés Titre original Kick-Ass Réalisation Matthew Vaughn Scénario Matthew Vaughn Jane Goldman Acteurs principaux Aaron Johnson Christopher Mintz-Plasse Chloë Grace Moretz Nicolas Cage Mark Strong Sociétés de production Marv Films Plan B Entertainment DMG Entertainment Pays de production Royaume-Uni États-Unis Chine Genre Action Super-héros Comédie noire Durée 117 minutes Sortie 2010 Série Kick-Ass Kick-Ass 2(2013) P...
Artikel ini perlu diterjemahkan dari bahasa Inggris ke bahasa Indonesia. Artikel ini ditulis atau diterjemahkan secara buruk dari Wikipedia bahasa Inggris. Jika halaman ini ditujukan untuk komunitas bahasa Inggris, halaman itu harus dikontribusikan ke Wikipedia bahasa Inggris. Lihat daftar bahasa Wikipedia. Artikel yang tidak diterjemahkan dapat dihapus secara cepat sesuai kriteria A2. Jika Anda ingin memeriksa artikel ini, Anda boleh menggunakan mesin penerjemah. Namun ingat, mohon tidak men...

Библейские рукописи:Папирусы • Унциалы • Минускулы • ЛекционарииУнциал 01 Синайский кодекс, Книга Эсфирь (фрагмент)НазваниеСинайский кодексТекстВетхий (частично) и Новый Завет (полностью)Языкгреческий языкДатаIV векКем найденаКонстантин ТишендорфСейчас вБританская �...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

2022年肯塔基州聯邦參議員選舉 ← 2016年 2022年11月8日 (2022-11-08) 2028年 → 获提名人 蘭德·保羅 查爾斯·布克 政党 共和黨 民主党 民選得票 913,326 564,311 得票率 61.8% 38.2% 各縣結果保羅: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90%布克: 50–60% 60–70% 选前聯邦參議...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Malcolm. Malcolm Ier d'ÉcosseMalcolm Ier, portait imaginaire du XVIIIe siècle.FonctionRoi d'Écosse943-954Constantin II d'ÉcosseIndulf Ier d'ÉcosseBiographieNaissance 897Décès 954Sépulture Abbaye d'IonaNom dans la langue maternelle Máel Coluim An Bodhbhdercc ou Malcolm I the Dangerous RedActivité Homme politiqueFamille Maison d'AlpinPère Donald II d'ÉcosseEnfants Kenneth II d'ÉcosseDubh Ier d'ÉcosseBlasonm...

Forest fire in northern British Columbia and Alberta in 1950 Chinchaga FireDate(s)June - October 1950LocationBritish Columbia and Alberta, CanadaStatisticsTotal area1,400,000–1,700,000 hectares (3,500,000–4,200,000 acres)MapMap The Chinchaga fire, also known as the Wisp fire, Chinchaga River fire and Fire 19,[1] was a forest fire that burned in northern British Columbia and Alberta in the summer and early fall of 1950. With a final size of between 1,400,000 hectares (3,500,000 acr...

Pattern that has no predecessors A Garden of Eden in Conway's Game of Life, discovered by R. Banks in 1971.[1] The cells outside the image are all dead (white). An orphan in Life found by Achim Flammenkamp. Black squares are required live cells; blue x's are required dead cells. In a cellular automaton, a Garden of Eden is a configuration that has no predecessor. It can be the initial configuration of the automaton but cannot arise in any other way. John Tukey named these configuratio...

1787 American organic legislation creating Northwest Territory Northwest Territory (1787) This article is part of a series on theUnited StatesContinental CongressIndependence Hall in Philadelphia Predecessors Albany Congress Stamp Act Congress First Continental Congress Declaration and Resolves Continental Association Petition to the King Second Continental Congress United Colonies Olive Branch Petition Committee of Secret Correspondence Necessity of Taking Up Arms Lee Resolution Declaration ...

Questa voce sull'argomento sali è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Bisolfato di potassio Nomi alternativiidrogenosolfato di potassio Caratteristiche generaliFormula bruta o molecolareKHSO4 Massa molecolare (u)136,17 g/mol Aspettosolido incolore Numero CAS7646-93-7 Numero EINECS231-594-1 PubChem516920 e 18674734 SMILESOS(=O)(=O)[O-].[K+] Proprietà chimico-fisicheDensità (g/cm3, in c.s.)2,32 (20 °C) Solubilità in acqua490 g/l (20 °C) (...

1966 film by Michelangelo Antonioni This article is about the 1966 film. For the mathematical operation, see Blowing up. For other uses, see Blow up. Blow-UpTheatrical release posterDirected byMichelangelo AntonioniScreenplay by Michelangelo Antonioni Tonino Guerra Dialogue byEdward Bond Story byMichelangelo AntonioniBased onLas babas del diabloby Julio CortázarProduced byCarlo PontiStarring David Hemmings Vanessa Redgrave Sarah Miles CinematographyCarlo Di PalmaEdited byFrank ClarkeMusic by...
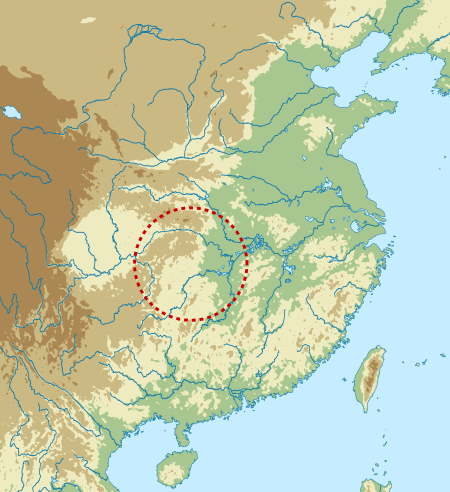
Daxi cultureGeographical rangemiddle YangtzePeriodNeolithicDatesc. 5000 – c. 3300 BCFollowed byQujialing cultureChinese nameChinese大溪文化TranscriptionsStandard MandarinHanyu PinyinDàxī wénhuà The Daxi culture (5000–3300 BC) was a Neolithic culture centered in the Three Gorges region around the middle Yangtze, China. The culture ranged from western Hubei to eastern Sichuan and the Pearl River Delta. The site at Daxi, located in the Qutang Gorge around Wushan, Chongqing, was disco...

Pier in Hong Kong This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Tuen Mun Ferry Pier – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Tuen Mun Ferry PierThe Tuen Mun Ferry Pier during its expansionTypePassenger Boarding PierCarriesPublic Passenger Fer...
