Potassium arsenite
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Kodama Gentaro, Gubernur-Jenderal Taiwan dari 1898 sampai 1906 Posisi Gubernur–Jenderal Taiwan Taiwan Sōtoku (臺灣總督code: ja is deprecated ) ada ketika Taiwan (dikenal dalam Bahasa Inggris sebagai Formosa) dan Pescadores adalah bagian dari Kekaisaran Jepang, dari 1895 sampai 1945. Gubernur-Jenderal Jepang adalah anggota pimpinan sipil, jenderal atau orang terkenal asal Jepang. Referensi Pranala luar Arsip Gubernur Jenderal Taiwan Jepang Diarsipkan 2004-07-27 di Wayback Machine. (Mand...

For the penny fiction weekly, see The London Journal. James Boswell James Boswell's London Journal is a published version of the daily journal he kept between the years 1762 and 1763 while in London. Along with many more of his private papers, it was found in the 1920s at Malahide Castle in Ireland, and was first published in 1950, in an edition by Frederick A. Pottle. In it, Boswell, then a young Scotsman of 22, visits London for his second time. One of the most notable events in the journal...

AliImam Taqiyuddin As-SubkiKun-yahAbul HasanNamaAliNasabBin Abdul Kafi bin Ali bin Tamam bin Yusuf bin MusaNisbahAs-SubkiWilayah aktifMesir, SyamFirkahSunni Dipengaruhi oleh Hafizh Al-Iraqi Mempengaruhi Tajuddin as-Subki Masjid Agung Umayyah saat ini Taqiyuddin as-Subki (Arab: تقي الدين السبكيcode: ar is deprecated ) adalah seorang ulama ahli hadits, tafsir, ushul fiqih, nahwu, sharaf dan sastra dari mazhab Syafi'i.[1] Hakim Agung ini dijuluki sebagai Syaikhul Isla...

Longest Beethoven piano sonata, composed in 1818 Beethoven in 1818–19; portrait by Ferdinand Schimon [de] (1797–1852); source: the Library of Congress Ludwig van Beethoven's Piano Sonata No. 29 in B♭ major, Op. 106 (known as the Große Sonate für das Hammerklavier, or more simply as the Hammerklavier) is a piano sonata that is widely viewed as one of the most important works of the composer's third period and among the greatest piano sonatas of all time. Completed in ...

Warner Bros. theatrical cartoon character Tazmanian Devil redirects here. For other uses, see Tasmanian Devil (disambiguation). Fictional character Tasmanian Devil (Taz)Looney Tunes/Merrie Melodies characterFirst appearanceDevil May Hare (June 19, 1954; 69 years ago (1954-06-19))Created byRobert McKimsonSid Marcus[1]Voiced byMel Blanc (1954–1989)Jeff Bergman (1990–1994, 1997, 2004, 2014)Noel Blanc (1990)Maurice LaMarche (1990)Greg Burson (1990–1995, 1997)Jim Cu...

Starting grid for the Coppa Fiera di Milano. In the foreground are two Diatto cars. The 1st Coppa Fiera di Milano was an automobile race held in 1925 in the Autodromo di Monza. During the International Milan Trade Fair, held from 12 to 27 April 1925, which included the International Motor Show, an international speed trial, with a fuel limit of 18 litres,[1] was organized on the Monza circuit on Sunday, April 19. In the spirit of the Milan Trade Fair, the competition was intended to d...

The Oxfordshire MuseumThe entrance to the museumShown within OxfordshireLocationFletcher's House, Park Street, Woodstock, Oxfordshire, EnglandCoordinates51°50′54″N 1°21′26″W / 51.8483°N 1.3572°W / 51.8483; -1.3572Websitewww.oxfordshire.gov.uk/the_oxfordshire_museum The Oxfordshire Museum (also known as Oxfordshire County Museum) is in Woodstock, Oxfordshire, England, located in Fletcher's House, Park Street, opposite the Bear Hotel.[1] It is a regi...

Norman PaechPaech in 2010Member of the Bundestag for HamburgIn office2002–2009 Personal detailsBorn (1938-04-12) 12 April 1938 (age 86)Bremerhaven, Bremen, GermanyPolitical partyThe LeftOther politicalaffiliationsSPD (1969–2001) Norman Paech (born 12 April 1938, Bremerhaven) is a retired German professor and member of the political party The Left. Career This section of a biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. SMK Wikrama 1 JeparaLogo SMK Wikrama 1 JeparaInformasiDidirikanJuni 2011JenisSekolah Mengengah KejuruanKepala SekolahSholikhin, S.AgJurusan atau peminatanTeknik Komputer dan Jaringan & Rekayasa Perangkat LunakStatusSwastaAlamatLokasiJl. Kelet...

1989 American filmRude AwakeningTheatrical release posterDirected byDavid GreenwaltAaron RussoScreenplay byNeil LevyRichard LaGraveneseStory byNeil LevyProduced byAaron RussoStarring Cheech Marin Eric Roberts Julie Hagerty Robert Carradine Buck Henry Louise Lasser Cindy Williams Andrea Martin Cliff DeYoung CinematographyNewton Thomas SigelEdited byPaul FriedMusic byJonathan EliasProductioncompanyAaron Russo ProductionsDistributed byOrion PicturesRelease date August 16, 1989 (1...

Western music created during the Middle Ages Part of a series onMedieval music Overview Composers / Instruments / Theory (Theorists) Movements and schools Saint Gall Saint Martial Goliard Ars antiqua Notre-Dame school Troubadour Trouvère Minnesang Ars nova Trecento Ars subtilior Major figures Notker Guido Hildegard Bernart Walther Pérotin Adam de la Halle Franco Vitry Machaut Landini Ciconia Dunstaple Major forms Canso Conductus Formes fixes Ballade Rondeau Virelai Geissl...
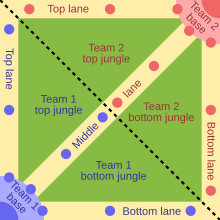
Video game genre MOBA redirects here. For other uses, see Moba. Part of a series onStrategy video games Subgenres 4X Auto battler Multiplayer online battle arena Real-time strategy Time management Real-time tactics Tactical RPG Tower defense Turn-based strategy Turn-based tactics Artillery Wargame Lists List of 4X video games List of artillery video games List of grand strategy video games List of massively multiplayer online real-time strategy games List of massively multiplayer online turn-...

Post-secondary school in Paris Lycée Saint-LouisLocation44 Boulevard Saint-Michel75006 ParisFranceCoordinates48°50′58″N 2°20′29″E / 48.84944°N 2.34139°E / 48.84944; 2.34139InformationFormer namesCollège d'Harcourt (1280-1820)Lycée Saint-Louis (1820-present)TypePublic funded classes préparatoiresEstablished1280 - 742 years agoSchool districtLatin QuarterNumber of students1,416LanguageFrenchMascotSaint LouisNicknameSancto-LudovicienWebsitelycee-saintlouis...
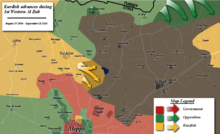
ميّز عن هجوم شمال الباب (سبتمبر 2016). هجوم غرب الباب (سبتمبر 2016) جزء من التدخل بقيادة الولايات المتحدة في سوريا (الحرب الأهلية السورية) مقاتلي قوات سوريا الديمقراطية على مقربة من قرية حربل معلومات عامة التاريخ 30 أغسطس - 6 سبتمبر 2016 الموقع محافظة حلب النتيجة سيطرة قوات سو�...
U.S. Republican gerrymandering plan This article is part of a series on thePolitics of the United States Federal government Constitution of the United States Law Taxation Policy Legislature United States Congress House of Representatives Speaker Mike Johnson (R) Majority Leader Steve Scalise (R) Minority Leader Hakeem Jeffries (D) Congressional districts (list) Non-voting members Senate President Kamala Harris (D) President Pro Tempore Patty Murray (D) Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (D) Minor...

Campionati europei di ciclismo su pista 2022 Competizione Campionati europei di ciclismo su pista Sport Ciclismo su pista Edizione 13ª Organizzatore UEC Date 11-16 agosto Luogo Monaco di Baviera Impianto/i Messe München Statistiche Gare 22 Cronologia della competizione Grenchen 2021 Grenchen 2023 Manuale I Campionati europei di ciclismo su pista 2022 si sono svolti a Monaco di Baviera, in Germania, dall'11 al 16 agosto 2022 all'interno della seconda edizione multisportiva dei Campionati eu...

Civil war in Spain from 1833 to 1840 First Carlist WarPart of the Carlist WarsThe Battle of Irún, 17 May 1837.Date29 September 1833 – 6 July 1840 (6 years, 9 months and 7 days)LocationSpainResult Liberal victory Lord Eliot Convention Convention of VergaraBelligerents Carlists Supported by: Portugal (until 1834) Liberals Supported by: France United Kingdom Portugal (from 1834)Commanders and leaders See list Carlos V Tomás Zumalacárregui Ramón Cabrera Rafael Maroto Gonzále...

200 метрів на спині (чоловіки)на XXXII Олімпійських іграх Піктограма плаванняМісце проведенняОлімпійський центр з водних видів спортуДати28 липня 2021 (попередні запливи)29 липня 2021 (півфінали)30 липня 2021 (фінал)Учасників29 з 23 країнПризери Євген Рилов Олімпійс�...

「けんか」はこの項目へ転送されています。化学反応の「けん化」については「鹸化」をご覧ください。 この記事には複数の問題があります。改善やノートページでの議論にご協力ください。 出典がまったく示されていないか不十分です。内容に関する文献や情報源が必要です。(2013年2月) 独自研究が含まれているおそれがあります。(2020年1月)出典検索?: 喧�...