Pernambucan revolt
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Keuskupan Agung NanningArchidioecesis Nannimensis天主教南宁总教区Katedral Bunda dari TiongkokLokasiNegaraChinaProvinsi gerejawiNanningStatistikPopulasi- Total- Katolik(per 1950)6.000.0007,584 (0.7%)InformasiRitusRitus LatinKatedralKatedral Bunda dari Tiongkok di NanningKepemimpinan kiniPausFransiskusUskup agungJoseph Tan Yan-quan Keuskupan Agung Nanning (Latin: Nannimen(sis)code: la is deprecated , Hanzi: 南寧) adalah sebuah keuskupan agung yang terletak di k...

Canadian actress Sarah GadonGadon in 2012BornSarah Lynn Gadon (1987-04-04) April 4, 1987 (age 37)Toronto, Ontario, CanadaAlma materUniversity of TorontoOccupationActressYears active1998–presentSpouse Max Fine (m. 2022)Children1 Sarah Lynn Gadon[1] (born April 4, 1987[2]) is a Canadian actress. She began her acting career guest-starring in a number of television series, such as Are You Afraid of the Dark? (1999), Mutant X (2002),...

Shida Kartli შიდა ქართლიMkhareShida Kartli dan sebagian wilayahnya yang berada di bawah otoritas Republik Ossetia SelatanCountry GeorgiaIbu kotaGori[1]Subdivisions1 kota dan 5 distrikPemerintahan • GubernurGiorgi Khojevanishvili[2]Luas • Total5.729 km2 (2,212 sq mi)Populasi (Sensus 2014[3]) • Total263.382[a]Zona waktuUTC+4 (Waktu Georgia)Kode ISO 3166GE-SKIPM (2017)0.741[4]high · ...

إنريكو بومبيري (بالإيطالية: Enrico Bombieri) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 26 نوفمبر 1940 (العمر 83 سنة)ميلانو مواطنة إيطاليا الجنسية إيطالي عضو في الأكاديمية الفرنسية للعلوم، وأكاديمية لينسيان، والأكاديمية الوطنية للعلوم، وأكاديمية أوروبيا[1]، والأكاديمية الأمريكية...

Second brightest star in the constellation Lepus β Leporis Location of β Leporis (circled) Observation dataEpoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) Constellation Lepus Right ascension 05h 28m 14.72316s[1] Declination −20° 45′ 33.9878″[1] Apparent magnitude (V) 2.84[2] Characteristics Spectral type G5 II[3] U−B color index +0.47[2] B−V color index +0.82[2] R−I...

Village in FloridaRoyal Palm Beach, FloridaVillageVillage of Royal Palm BeachLocation of Royal Palm Beach in Palm Beach County, FloridaCoordinates: 26°42′21″N 80°13′36″W / 26.70583°N 80.22667°W / 26.70583; -80.22667Country United States of AmericaState FloridaCounty Palm BeachIncorporatedJune 18, 1959Government • TypeMayor-Council • MayorFred Pinto (D)[1][2] • Vice MayorJeff Hmara • ...

بطولة كاريوكا 1943 تفاصيل الموسم بطولة كاريوكا البلد البرازيل البطل نادي فلامينغو بطولة كاريوكا 1942 بطولة كاريوكا 1944 تعديل مصدري - تعديل بطولة كاريوكا 1943 هو موسم من بطولة كاريوكا. فاز فيه نادي فلامنغو.[1][2] نتائج الموسم مراجع ^ Futebolnacional.com.br – Championship...

Non-fiction film genre Part of a series on theAnthropology of art,media, music, dance and film Basic concepts Color symbolism Visual culture Body culture Material culture New media Case studies Art Art of the Americas Indigenous Australian art Oceanic art Film Nanook of the North The Ax Fight Nǃai, the Story of a ǃKung Woman Incidents of Travel in Chichen Itza The Doon School Quintet Museums National Anthropological Archives Centro Cultural Mexiquense Museum of Anthropology at UBC Museum of...

Stuart Beattie Información personalNacimiento 1972 Melbourne (Australia) Nacionalidad AustralianaEducaciónEducado en Knox Grammar SchoolCharles Sturt University Información profesionalOcupación Guionista y director de cine [editar datos en Wikidata] Stuart Beattie (n. 1972) es un escritor o guionista de Hollywood. Su más importante creación ha sido para la película del 2003: Pirates of the Caribbean: The Curse of the Black Pearl como escritor de la historia. Stuart fue a la K...

University in Sweden This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Linnaeus University – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2013) (Learn ...

This article is about the unreleased video game developed by Bandai Namco. For the 2012 Capcom game, see Street Fighter X Tekken. Video gameTekken X Street FighterPromotional image from Gamescom 2010Developer(s)Bandai Namco StudiosPublisher(s)Bandai Namco EntertainmentProducer(s)Katsuhiro HaradaComposer(s)Akitaka TohyamaNobuyoshi SanoKeiichi OkabeSeriesTekkenStreet FighterReleaseUnreleasedGenre(s)FightingMode(s)Single-player, multiplayer Tekken X Street Fighter[a] (pronounced Tekken C...

State park in Kentucky, United States My Old Kentucky Home State ParkFederal Hill MansionLocation in KentuckyShow map of KentuckyMy Old Kentucky Home State Park (the United States)Show map of the United StatesLocationBardstown, Nelson, Kentucky, United StatesCoordinates37°48′23″N 85°27′25″W / 37.80639°N 85.45694°W / 37.80639; -85.45694Elevation643 ft (196 m)[1]Established1936[2]Governing bodyKentucky Department of ParksWebsite...

Iranian banking establishment Keshavarzi BankCompany typeState-owned enterpriseIndustryBanking , Financial servicesFounded1933; 91 years ago (1933)HeadquartersTehran, IranArea servedIranKey peopleVahab Mottaghinia,(Acting) CEOProductsFinance and insuranceConsumer BankingCorporate BankingInvestment BankingInvestment ManagementGlobal Wealth ManagementPrivate EquityMortgagesCredit CardsRevenue US$2.91 billion (2016)[1]Net income US$1.3 million (2007)Total assets$18.29 m...

2013 2019 Élections législatives autrichiennes de 2017 183 sièges du Conseil national(Majorité absolue : 92 sièges) 15 octobre 2017 Type d’élection Élections législatives Corps électoral et résultats Population 8 772 865 Inscrits 6 400 998 Votants 5 120 879 80,00 % 5,1 Votes exprimés 5 069 929 Blancs et nuls 50 950 ÖVP - Liste Sebastian Kurz – Sebastian Kurz Voix 1 595 526 31,4...

Geological formation The western section of the Lauterbrunnen Wall, with the north faces of the Grosshorn (left) and the Breithorn (right) The Lauterbrunnen Wall is a term used in the English-speaking mountaineering world[1] to refer to a north-west-facing mountain wall in the Bernese Alps in Switzerland. It runs for 8 kilometres from the Gletscherhorn (3,983 m) in the east, through the Ebnefluh, (3,962 m), the Mittaghorn (3,897m) and the Grosshorn (3,754 m), to the Breithorn (3,785 m...

Колониеобразующая единица (сокр. КОЕ) — величина, показывающая количество микробных клеток (бактерий, грибов и т. д.) или неклеточных форм жизни (вирусов и вирионов) в образце, которые являются жизнеспособными и/или способными размножаться путём деления в контролируем�...

Philosophy derived from the works of Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels Part of a series onMarxism Theoretical works Economic and Philosophic Manuscripts of 1844 The Condition of the Working Class in England The German Ideology The Communist Manifesto The Eighteenth Brumaire of Louis Bonaparte Grundrisse Capital Critique of the Gotha Programme Dialectics of Nature The Origin of the Family, Private Property and the State What Is to Be Done? The Accumulation of Capital Philosophical Notebooks Terro...

Property of two varying quantities with a constant ratio For other uses, see Proportionality. This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (August 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) The variable y is directly proportional to the variable x with proportionality constant ~0.6. The variable y is inversely proportional to the variable x with prop...

Oahu Facula Géographie et géologie Coordonnées 5° 00′ N, 166° 42′ O Type de relief Facula Diamètre 465 km Éponyme Oahu, Hawaii Localisation sur Titan modifier Oahu Facula est une zone brillante sur Titan, satellite naturel de Saturne. Caractéristiques Oahu Facula est centrée sur 5,0° de latitude nord et 166,7 de longitude ouest, et mesure 465 km dans sa plus grande dimension[1]. Observation Oahu Facula a été découverte par les images transmises...
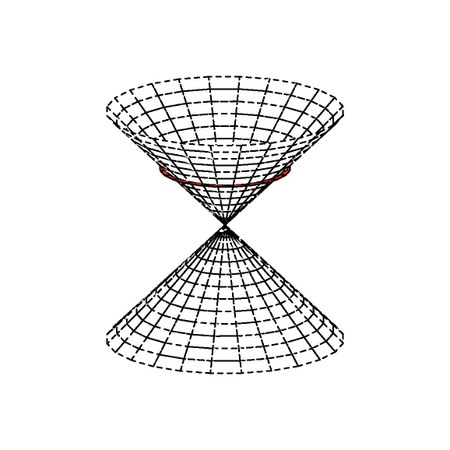
Vector on which a quadratic form is zero This article is about zeros of a quadratic form. For the zero element in a vector space, see Zero vector. For null vectors in Minkowski space, see Minkowski space § Causal structure. A null cone where q ( x , y , z ) = x 2 + y 2 − z 2 . {\displaystyle q(x,y,z)=x^{2}+y^{2}-z^{2}.} In mathematics, given a vector space X with an associated quadratic form q, written (X, q), a null vector or isotropic vector is a non-zero element x of X for whi...




