Pebble-mound mouse
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Cette chronologie est une ébauche concernant la science. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Chronologies Données clés 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013Décennies :1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 2030 2040Siècles :XIXe XXe XXIe XXIIe XXIIIeMillénaires :Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies géographiques Afrique Afrique du Sud, Algérie, Angola, Béni...

1938 day of protest by Indigenous Australians against British invasion 150 years earlier Proclamation of the Day of Mourning. The Day of Mourning was a protest held by Aboriginal Australians on 26 January 1938, the 150th anniversary of the arrival of the First Fleet, which marked the beginning of the colonisation of Australia. It was declared to be a protest of 150 years of callous treatment and purposefully coincided with Australia Day celebrations. Day of Mourning protests have been held on...

Federico Cesicardinale di Santa Romana ChiesaMedaglia raffigurante il cardinale Cesi Incarichi ricoperti Vescovo di Todi (1523-1545) Cardinale presbitero di San Pancrazio fuori le mura (1545-1550) Amministratore apostolico di Caserta (1549-1552) Cardinale presbitero di Santa Prisca (1550-1557) Amministratore apostolico di Vulturara e Montecorvino (1550-1551) Amministratore apostolico di Cremona (1551-1560) Camerlengo del Collegio Cardinalizio (1555-1556) Cardinale vescovo di Palestrina ...

Type of ecosystem The three primary zones of a lake A lake ecosystem or lacustrine ecosystem includes biotic (living) plants, animals and micro-organisms, as well as abiotic (non-living) physical and chemical interactions.[1] Lake ecosystems are a prime example of lentic ecosystems (lentic refers to stationary or relatively still freshwater, from the Latin lentus, which means sluggish), which include ponds, lakes and wetlands, and much of this article applies to lentic ecosystems in g...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Mariage (homonymie). Sculpture représentant un couple marié dans la Rome antique.Les Époux Arnolfini de Jan van Eyck.Mariage de Willem-Alexander et Máxima, 2002. Le mariage est une union conjugale contractuelle et/ou rituelle, à durée illimitée, déterminée ou indéterminée, reconnue et encadrée par une institution juridique ou religieuse qui en détermine les modalités. Le terme désigne à la fois la cérémonie rituelle, l'union qui en est issu...

Rifugio Dante Livio BiancoIl rifugio Dante Livio BiancoUbicazioneStato Italia Altitudine1 910 m s.l.m. LocalitàValdieri CatenaAlpi Marittime Coordinate44°14′46″N 7°14′52.6″E / 44.246111°N 7.247944°E44.246111; 7.247944Coordinate: 44°14′46″N 7°14′52.6″E / 44.246111°N 7.247944°E44.246111; 7.247944 Dati generaliInaugurazione7 luglio 1963 ProprietàC.A.I. sez. Cuneo GestioneLivio Bertaina Periodo di aperturaDal 15 giugno al 15...

Group of West Slavic dialects You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (March 2009) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the German article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated ...

PhilippinesFINA codePHIAssociationPhilippine Swimming, Inc.ConfederationAASF (Asia)Head coachReynaldo GalangAsst coachRicardo DilapdilapDale EvangelistaCaptainTani Gomez Jr.Home venueRizal Memorial Sports ComplexAsian GamesAppearances3 (first in 1954)Best result5th place (1958)Southeast Asian GamesAppearances7 (first in 2005)Best result (2005, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2019) The Philippines men's national water polo team represents the Philippines in international men's water polo competitions and f...

Ця стаття містить правописні, лексичні, граматичні, стилістичні або інші мовні помилки, які треба виправити. Ви можете допомогти вдосконалити цю статтю, погодивши її із чинними мовними стандартами. (листопад 2018) Ця стаття є сирим перекладом з іншої мови. Можливо, вона с�...

Local board of Auckland Council in New ZealandWaitākere Ranges Local BoardLocal board of Auckland CouncilCountryNew ZealandRegionAucklandTerritorial authorityAuckland CouncilWardWaitākere WardLegislated2010Government • Board chairGreg PreslandArea[1] • Land305.73 km2 (118.04 sq mi)Population (June 2023)[2] • Total55,600 Local Board Members[3]StructureFuture West4 / 6WestWards/WestWards-Independent2 / 6Elections...

Japanese footballer Tsubasa Endoh Endoh playing for Toronto FC in 2020Personal informationDate of birth (1993-08-20) 20 August 1993 (age 30)Place of birth Tokyo, JapanHeight 1.70 m (5 ft 7 in)Position(s) Winger, Second StrikerYouth career2005–2012 JFA Academy FukushimaCollege careerYears Team Apps (Gls)2012–2015 Maryland Terrapins 85 (12)Senior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2016–2017 Toronto FC 25 (2)2017 → Toronto FC II (loan) 14 (3)2018 Toronto FC II 14 (8)2019–2...
1997–98 World CupWinnersOverall Primož PeterkaSki Jumping (NH, LH) Primož PeterkaSki Flying Sven HannawaldFour Hills Tournament Kazuyoshi FunakiNordic Tournament Andreas WidhölzlNations Cup JapanCompetitionsVenues20Individual27Cancelled1← 1996–97 1998–99 → The 1997–98 FIS Ski Jumping World Cup was the 19th World Cup season in ski jumping and the 8th official World Cup season in ski flying. It began in Lillehammer, Norway on 29 November 1997 and finished i...

Men's pommel horse at the 2014 Asian GamesVenueNamdong GymnasiumDate21–24 September 2014Competitors60 from 16 nationsMedalists Masayoshi Yamamoto Japan Abdulla Azimov Uzbekistan Park Min-soo South Korea← 20102018 → Gymnastics at the2014 Asian GamesArtisticTeammenwomenIndividual all-aroundmenwomenBalance beamwomenFloormenwomenHorizontal barmenParallel barsmenPommel horsemenRingsmenUneven barswomenV...

Barakuda besar Barakuda besar mengarungi arus di Arrecife Paraiso, Cozumel, Meksiko Status konservasi Risiko Rendah (IUCN 3.1) Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Kelas: Actinopterygii Ordo: Istiophoriformes Famili: Sphyraenidae Genus: Sphyraena Spesies: S. barracuda Nama binomial Sphyraena barracuda(Edwards dalam Catesby, 1771) Sinonim Daftar Sphyraena barracuda Walbaum, 1792 Agrioposphyraena barracuda (Walbaum, 1792) Esox barracuda Walbaum, 1792 Esox barracuda ...
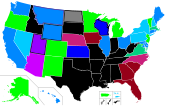
Overview of the legality and prevalence of abortions in the U.S. state of Alaska Abortion in Alaska is legal on demand at all stages of pregnancy, as long as a licensed physician performs the procedure. As of 2016, Alaska does not require a minor to notify a parent or guardian in order to obtain an abortion. 63% of adults said in a poll by the Pew Research Center that abortion should be legal in all or most cases. Alaska was one of only four states to make abortion legal between 1967 and 197...

Protected wilderness area in California, United States This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Dinkey Lakes Wilderness – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Dinkey Lakes WildernessIUCN category Ib (wilderness area)Aerial view looking sou...

Computer component that stores information for immediate use DDR4 SDRAM module. As of 2021[update], over 90 percent of computer memory used in PCs and servers was of this type.[1] Computer memory and Computer data storage types General Memory cell Memory coherence Cache coherence Memory hierarchy Memory access pattern Memory map Secondary storage MOS memory floating-gate Continuous availability Areal density (computer storage) Block (data storage) Object storage Direct-attache...

Este artículo o sección tiene referencias, pero necesita más para complementar su verificabilidad. Busca fuentes: «Constantino Nicoláyevich de Rusia» – noticias · libros · académico · imágenesEste aviso fue puesto el 22 de abril de 2015. Constantino Nikoláyevich de Rusia Gran príncipe de Rusia El gran duque Constantino de Rusia.Información personalNombre completo Constantino Nikoláyevich Románov (en ruso: Константи́н Никола́евич Poм...
كأس الأمم الإفريقية تحت 20 سنة معلومات عامة الرياضة كرة القدم المنظم CAF المنطقة أفريقيا التواتر كل عامين عدد المشاركين 16 الموقع الرسمي الموقع الرسمي قائمة الفائزين آخر بطل السنغال (اللقب الأول) الأكثر تتويجًا نيجيريا (7 ألقاب) التسلسل الزمني للمنافسة [[2023]] [[2025]] تعديل �...

هذه المقالة بحاجة لصندوق معلومات. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة صندوق معلومات مخصص إليها. يعود تاريخ الفن المغربي إلى الحقبة ما قبل التاريخ عبر النقوش الصخرية.[1] حواف من الكتان الطبيعي مطرزة بالحرير الأحمر بتصميم هندسي من خيطين متشابكين، القرن 19 عينة تطريز من ...
