Paul Lensch
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Kahnawake Gaming Commision adalah sebuah badan komite yang berfungsi untuk mengatur dan juga mengawasi segala aktivitas para agen judi daring serta dipercayai memiliki otoritas penuh untuk mengeluarkan lisensi bagi situs penyedia layanan judi daring. K...
Ellenberg Lambang kebesaranLetak Ellenberg NegaraJermanNegara bagianBaden-WürttembergWilayahStuttgartKreisOstalbkreisPemerintahan • MayorRainer Knecht (CDU)Luas • Total30,17 km2 (1,165 sq mi)Ketinggian574 m (1,883 ft)Populasi (2021-12-31)[1] • Total1.775 • Kepadatan0,59/km2 (1,5/sq mi)Zona waktuWET/WMPET (UTC+1/+2)Kode pos73488Kode area telepon07962, 07961, 07965, 07966Pelat kendaraanAASitus webwww.ell...

Keuskupan KotorDioecesis CatharensisKatolik Katedral Santo Trifon, KotorLokasiNegara MontenegroProvinsi gerejawiSplit-MakarskaStatistikLuas674 km2 (260 sq mi)Populasi- Total- Katolik(per 2013)111.00010,030 (9%)InformasiDenominasiKatolik RomaGereja sui iurisGereja LatinRitusRitus RomaPendirianAbad ke-10KatedralKatedral Santo TrifonKepemimpinan kiniPausFransiskusUskupIlija JanjicUskup agungMarin BarišićPetaPeta Montenegro Keuskupan Kotor - Bi...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Jaringan komputer. Artikel ini sudah memiliki daftar referensi, bacaan terkait, atau pranala luar, tetapi sumbernya belum jelas karena belum menyertakan kutipan pada kalimat. Mohon tingkatkan kualitas artikel ini dengan memasukkan rujukan yang lebih mendetail bila perlu. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Potongan sklerenkim, jaringan dasar pada tumbuhan Tampilan mikroskopik spesimen jaringan paru-paru manusia yang diwarnai dengan he...

Gatot Subroto Informasi pribadiLahir24 November 1960 (umur 63)Jember, Jawa TimurAlma materAkademi Kepolisian (1983)Karier militerPihak IndonesiaDinas/cabang Kepolisian Republik IndonesiaMasa dinas1983—2018Pangkat Brigadir Jenderal PolisiSatuanLantasSunting kotak info • L • B Brigjen. Pol. (Purn.) Drs. Gatot Subroto (lahir 24 November 1960) adalah seorang Purnawirawan perwira tinggi Polri yang sebelumnya menjabat sebagai Analis Kebijakan Utama bidang Jemen Sarpra...

This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (September 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Velòdrom d'HortaThe banking of the Velòdrom d'HortaLocationBarcelona, Catalonia, SpainCoordinates41°26′17″N 2°08′56″E / 41.43813°N 2.148861°E / 41.43813; 2.148861Capacity3...

Andrej Plenković Perdana Menteri KroasiaPetahanaMulai menjabat 19 Oktober 2016PresidenKolinda Grabar-KitarovićZoran MilanovićWakil Lihat daftar Ivan Kovačić (2016–2017)Davor Ivo Stier (2016–2017)Damir Krstičević (2016–2020)Martina Dalić (2016–2018)Predrag Štromar (2017–2020)Marija Pejčinović Burić (2017–2019)Tomislav Tolušić (2018–2019)Zdravko Marić (2019–sekarang)Davor Božinović (2019–sekarang)Tomo Medved (2020–sekarang)Boris Milošević (2020–sekar...

Sporting event delegationLatvia at the2000 Summer OlympicsIOC codeLATNOCLatvian Olympic CommitteeWebsitewww.olimpiade.lv (in Latvian and English)in SydneyCompetitors45 (30 men, 15 women) in 13 sportsFlag bearer Voldemārs LūsisMedalsRanked 44th Gold 1 Silver 1 Bronze 1 Total 3 Summer Olympics appearances (overview)19241928193219361948–1988199219962000200420082012201620202024Other related appearances Russian Empire (1908–1912) Soviet Union (1952–1988) Latvia compete...

Lihat pula: Terminal Kenjeran dan Shelter Bulak Terminal Kedung CowekTerminal Penumpang Tipe BPapan Nama Terminal Kedung CowekNama lainTerminal Tambak WediLokasiJalan Tambak Wedi Nomor 2, Kelurahan Kedung Cowek, Kecamatan Bulak, Kota Surabaya, Provinsi Jawa Timur, Kodepos 60125Kawasan Utara Surabaya IndonesiaKoordinat7°12′47″S 112°46′45″E / 7.213027°S 112.779302°E / -7.213027; 112.779302Koordinat: 7°12′47″S 112°46′45″E / 7.213...

Principal Union army unit in the Western Theater of the American Civil War Army of the CumberlandBattle of Missionary RidgeActiveOctober 24, 1862 – August 1, 1865Country United StatesBranch United States ArmyTypeField armyEngagementsAmerican Civil War Battle of Stones River Tullahoma Campaign Battle of Chickamauga Chattanooga Campaign Atlanta Campaign Franklin–Nashville Campaign CommandersNotablecommandersWilliam S. RosecransGeorge H. ThomasRobert AndersonMilitary unit The Army o...

Flavio Cotti Presiden Konfederasi Swiss Ke-143Masa jabatan1 Januari 1991 – 31 Desember 1991PendahuluArnold KollerPenggantiRené FelberPresiden Konfederasi Swiss Ke-150Masa jabatan1 Januari 1998 – 31 Desember 1998PendahuluArnold KollerPenggantiRuth DreifussAnggota Dewan Federal SwissMasa jabatan10 Desember 1986 – 13 Januari 1999PendahuluAlphons EgliPenggantiJoseph Deiss Informasi pribadiLahir(1939-10-18)18 Oktober 1939Prato-Sornico, SwissMeninggal16 Desember 20...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

English idiomatic expression Sea change or sea-change is an English idiomatic expression that denotes a substantial change in perspective, especially one that affects a group or society at large, on a particular issue. It is similar in usage and meaning to a paradigm shift, and may be viewed as a change to a society or community's zeitgeist, with regard to a specific issue. The phrase evolved from an older and more literal usage when the term referred to an actual change wrought by the sea,&#...

American electrical engineer (1835–1901) Elisha GrayBorn(1835-08-02)August 2, 1835Barnesville, Ohio, U.S.DiedJanuary 21, 1901(1901-01-21) (aged 65)Newtonville, Massachusetts, U.S.OccupationEngineer/InventorAwardsElliott Cresson Medal (1897)Signature Elisha Gray (August 2, 1835 – January 21, 1901) was an American electrical engineer who co-founded the Western Electric Manufacturing Company. Gray is best known for his development of a telephone prototype in 1876 in Highland Park, Illin...
Hildburghausen Lambang kebesaranLetak Hildburghausen di Hildburghausen NegaraJermanNegara bagianThüringenKreisHildburghausenSubdivisions10Pemerintahan • MayorSteffen Harzer (Kiri)Luas • Total72,94 km2 (2,816 sq mi)Ketinggian380 m (1,250 ft)Populasi (2013-12-31)[1] • Total11.746 • Kepadatan1,6/km2 (4,2/sq mi)Zona waktuWET/WMPET (UTC+1/+2)Kode pos98641–98646Kode area telepon03685Pelat kendaraanHBNSitus...

Former radio station in London Melody FM redirects here. For the Malaysian station of this name, see Melody (radio station). This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Melody 105.4 FM – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Melody Radio/Melody FMBroadcast area...

Chinese state-owned banking corporation This article reads like a press release or a news article and may be largely based on routine coverage. Please help improve this article and add independent sources. (April 2018) China CITIC BankChina CITIC Bank in HangzhouNative name中信银行Company typePublicTraded asSSE: 601998 (A share)SEHK: 998 (H share)SSE Composite ComponentIndustryBankingFoundedApril 1987HeadquartersBeijing, Hong Kong, ChinaArea servedPeople's Republic of ChinaKey people...

Jyutping Naam (taalvarianten) Vereenvoudigd 粤拼 Traditioneel 粵拼 Pinyin yuèpīn Jyutping (Standaardkantonees) jyut6 jyu5 ping3 jam1 Standaardkantonees IPA: [jyːt̚˨ pʰɪŋ˧ ] Yale (Standaardkantonees) yuht ping Dapenghua IPA: [jiːt̚˨ pʰɐŋ˧ ] Hongkong-Hakka jet8 pin6 Meixianhua jat8 bin5 Peng'im (Chaozhouhua) uak8 peng1 Letterlijke vertaling Kantonese dialecten spelling Andere benamingen 香港語言學學會粵語拼音方案 Jyutping is een vorm van romanisatie o...
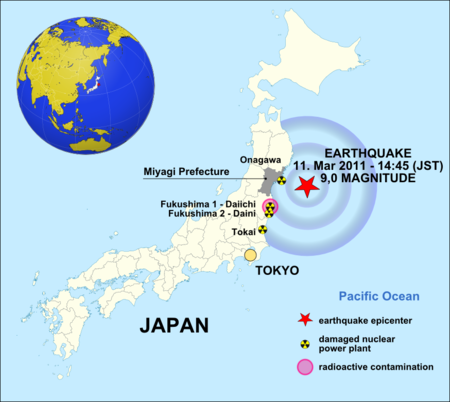
Centrale nucléaire de Fukushima DainiFukushima Daini 福島第二原子力発電所(ou Fukushima II)AdministrationPays JaponBourgs Naraha et Tomioka, Préfecture de FukushimaCoordonnées 37° 18′ 58″ N, 141° 01′ 32″ EPropriétaire Compagnie d'électricité de TokyoOpérateur Compagnie d'électricité de Tokyo (TEPCO)Construction 1982Mise en service De 1981 à 1986Mise à l’arrêt définitif 30 septembre 2019Statut En cours de déclassement (2019)Réac...