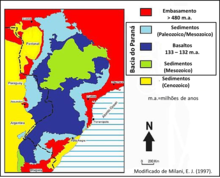
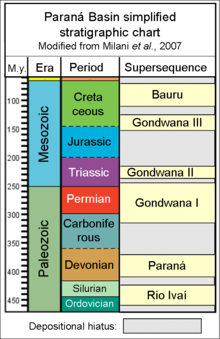
Paraná Basin
|
Read other articles:

Canadian children's animated television series This article is about the TV series. For the 2021 film, see PAW Patrol: The Movie. For 2023 sequel film, see PAW Patrol: The Mighty Movie. PAW PatrolGenre Action Adventure Comedy Created byKeith ChapmanDeveloped byScott KraftDirected by Jamie Whitney (episodes 1–58) Charles E. Bastien (episode 59–present) Voices of Owen Mason Elijha Hammill Jaxon Mercey Joey Nijem Beckett Hipkiss Kai Harris Tristan Samuel Max Calinescu Justin Paul Kelly Luke ...

An Bukid han mga Olibo (Hebreo: הַר הַזֵּיתִים, Har ha-Zeitim; Arabo: جبل الزيتون, الطور, Jabal al-Zaytun, Al-Tur) in uska bukid ha syudad han Jerusalem ha nasod han Israel. Usa ka turók ini nga barasahon. Dako it imo maibubulig ha Wikipedia pinaagi han pagparabong hini.

O filme estrelou Alice Joyce. The Cub Reporter's Temptation é um filme curto de drama mudo norte-americano de 1913.[1] O filme estrelou Earle Foxe, Alice Joyse e Tom Moore nos papéis principais. Elenco Tom Moore Alice Joyce Earle Foxe Matt Snyder (como Matt B. Snyder) Charles M. King Richard Purdon Referências ↑ The Cub Reporter's Temptation / IMDb Portal do cinema Este artigo sobre um curta-metragem é um esboço. Você pode ajudar a Wikipédia expandindo-o.vde

Erinnerung an die Schlacht bei Ampfing, Glasfenster im Münchner Rathaus 700 Jahre Schlacht bei Mühldorf – Ausstellung in München und Mühldorf Am 28. September 1322 standen sich in der Schlacht bei Mühldorf in Oberbayern (früher auch Schlacht bei Ampfing genannt) der Wittelsbacher Ludwig IV. der Bayer (Herzog von Oberbayern) und der Habsburger Friedrich der Schöne (Herzog von Österreich) gegenüber. Die seit 1314 anhaltenden Streitigkeiten um die Nachfolge des verstorbenen Heinrich V...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Neopost web-enabled stamps – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2009) (Learn how and when to ...

Coronaviridae CoronavirusKomposisi genom virus ICTVpositive-sense single-stranded RNA virus (en) TaksonomiSuperdomainBiotaDomainVirusDuniaRiboviriaKerajaanOrthornaviraeFilumPisuviricotaKelasPisoniviricetesOrdoNidoviralesFamiliCoronaviridae Subfamili dan genus Letovirinae Alphaletovirus Orthocoronavirinae Alphacoronavirus Betacoronavirus Deltacoronavirus Gammacoronavirus lbs Coronaviridae adalah keluarga dari virus RNA dengan untaian tunggal, amplop virus, dan sense-positif. Genom virus ini pa...

Lendra Symphurus Symphurus arawakSymphurus ommaspilusTaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumChordataKelasActinopteriOrdoPleuronectiformesFamiliCynoglossidaeGenusSymphurus Rafinesque, 1810 Tata namaSinonim takson Ammopleurops Günther, 1862 Glossichthys Gill, 1861 lbs Symphurus adalah genus ikan dalam keluarga Cynoglossidae yang terdapat di Samudera Atlantik, Hindia, dan Pasifik. Sebagian besar spesies terutama hidup di perairan yang relatif dangkal, termasuk muara . Di Indonesia, ikan ini lebih dikena...

Comic books House of XCover of House of X #1Publication informationPublisherMarvel ComicsFormatLimited seriesGenre Superhero Publication dateJuly – October 2019No. of issues6Main character(s)X-MenCreative teamWritten byJonathan HickmanPenciller(s)Pepe LarrazInker(s)Pepe LarrazLetterer(s)Clayton CowlesColorist(s)Marte GraciaEditor(s)Jordan D. White Annalise Bissa Powers of XPowers of X #1Publication informationPublisherMarvel ComicsFormatLimited seriesGenre Superhero Publication dateJul...

Um depilador elétrico. Um depilador elétrico é um aparelho utilizado para remoção de pelos do corpo. O processo de depilação através deste aparelho consiste inicialmente no contato do mesmo com a superfície da pele, e em seguida na extração mecânica de vários cabelos simultaneamente utilizando-se discos giratórios. Esta extração mecânica consiste em agarrar e puxar os cabelos para fora. História O primeiro depilador elétrico da história foi o Epilady, que foi lançado pela...

American politician This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (March 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Willis AllenMember of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom Illinois's 9th districtIn officeMarch 4, 1853 – March 3, 1855Preceded byDistrict createdSucceeded bySamuel S. MarshallMember of the U.S. Hous...

Pinky gets ready to pounce Pinky the Cat is a video that aired on several American reality television programs in the 1990s before it achieved additional fame on the internet as a viral video in the 2000s. The video clip shows a cat attacking an animal control officer during a promotional message for pet adoption for an animal shelter in Placer County, California. Background External videos An episode of World's Most Amazing Videos features the video clip The video footage was taped by Placer...

Animals with embryonic bilateral symmetry BilateriansTemporal range: Ediacaran–Present, 560–0 Ma[1] PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N Diversity of bilaterians. Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Subkingdom: Eumetazoa Clade: ParaHoxozoa Clade: BilateriaHatschek, 1888 Phyla Proarticulata? † Xenacoelomorpha? Nephrozoa: Ikaria † Superphylum Deuterostomia Chordata Xenacoelomorpha? Ambulacraria (unranked) Hemichordata Echinodermata Cambroernida † Prot...

Canadian politician (1898–1985) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Gordon Churchill – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) The HonourableGordon Minto ChurchillPC DSOChurchill, c. 1940sMinister of National DefenceIn...

Choral anthem by Henry Purcell Hear my prayer, O LordAnthem by Henry PurcellPortrait of the composer by John Closterman, 1695KeyC minorCatalogueZ. 15GenreSacred choral musicTextExcerpt from the Litany from Book of Common PrayerLanguageEnglishComposedc. 1682ScoringSSAATTBB choir, optional continuo Hear my prayer, O Lord, Z. 15,[1] is an eight-part choral anthem by the English composer Henry Purcell (1659–1695).[2] The anthem is a setting of the first verse of Psalm 102&...

This article is about the district. For its eponymous headquarters, see Pudukkottai. District in Tamil Nadu, IndiaPudukkottai District புதுக்கோட்டை மாவட்டம்DistrictClockwise from top-left: Pudukkottai District Court, Avudayar Kovil, Thirumayam Fort, Moovar Kovil, Sittanavasal Cave TempleLocation in Tamil NaduPudukkottai districtCoordinates: 10°23′N 78°49′E / 10.38°N 78.82°E / 10.38; 78.82Country IndiaState Tamil Nadu...

Watsons BaySydney, New South WalesPantai Camp Cove di Watsons BayJumlah penduduk691[1] • KepadatanGalat Lua: Tidak dapat mengkonversi populasi "691'"`UNIQ--ref-00000000-QINU`"'" menjadi bilangan.Kode pos2030Luas0,6 km2 (0,2 sq mi)Letak11 km (7 mi) sebelah north-east Sydney CBDLGAWoollahraDaerah pemilihan negara bagianVaucluseDivisi FederalWentworth Suburban di sekitar Watsons Bay: Clifton Gardens Manly Mosman Watsons Bay Vaucl...

Human settlement in EnglandLittle HorwoodSt Nicholas' parish churchLittle HorwoodLocation within BuckinghamshirePopulation434 (2011 Census)[1]OS grid referenceSP7930Civil parishLittle HorwoodUnitary authorityBuckinghamshireCeremonial countyBuckinghamshireRegionSouth EastCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townMILTON KEYNESPostcode districtMK17Dialling code01296PoliceThames ValleyFireBuckinghamshireAmbulanceSouth Central UK Parli...

Australian singer (born 1995) Troye SivanSivan in 2018BornTroye Sivan Mellet (1995-06-05) 5 June 1995 (age 28)Johannesburg, South AfricaCitizenship Australia South Africa OccupationsSinger-songwriteractorYouTuberYears active2006–presentAwardsFull listMusical careerOriginPerth, Western Australia, AustraliaGenresPop[1]synth-pop[2]electropop[3]dance-pop[4]Instrument(s)VocalsDiscographyTroye Sivan discographyLabelsEMI Australia[5]Capitol Musical...

この項目には性的な表現や記述が含まれます。免責事項もお読みください。 女性化セッションを行うフェムドムと、調教を受ける男性。 女性化(じょせいか、Feminization)、または強制女性化(きょうせいじょせいか)[1][2]、もしくはシシフィケーション(sissification)[3] とは、BDSMや変態行為(英語版)などにおいて行われるプレイのひとつで、従順な...

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...