List of high-speed railway lines
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Radio station in Mission, Texas (1957-2023) KIRTMission, TexasUnited StatesBroadcast areaRio Grande ValleyFrequency1580 kHzBrandingLa RadicalProgrammingFormatSpanish ReligiousOwnershipOwnerIglesia del Pueblo(Bravo Broadcasting Company, Inc.)HistoryFirst air date1957 (1957)Last air dateNovember 21, 2023 (2023-11-21)Technical information[1]Licensing authorityFCCFacility ID56474ClassBPower1,000 watts day302 watts nightTransmitter coordinates26°17′34.8″N 98°19′...

French footballer (born 1981) Wilfried Niflore Niflore with Litex Lovech in 2009Personal informationDate of birth (1981-04-29) 29 April 1981 (age 42)Place of birth Toulouse, FranceHeight 1.86 m (6 ft 1 in)Position(s) ForwardSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2001–2002 Toulouse 23 (3)2002–2004 Cannes 52 (18)2004–2005 Tours 30 (9)2005–2007 Gueugnon 72 (23)2008–2011 Litex Lovech 75 (39)2011–2013 Nîmes 18 (1)2013 → Paris FC (loan) 12 (2)2013–2014 Muret 19 (4)T...

Chronologie de la France ◄◄ 1780 1781 1782 1783 1784 1785 1786 1787 1788 ►► Chronologies Le Serment des Horaces de Jacques Louis David.Données clés 1781 1782 1783 1784 1785 1786 1787Décennies :1750 1760 1770 1780 1790 1800 1810Siècles :XVIe XVIIe XVIIIe XIXe XXeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies géographiques Afrique Afrique du Sud, Algérie, Angola, Bénin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroun, Cap-Ve...

Basilika Bunda dari KortenbosBasilika Minor Bunda dari KortenbosBelanda: Basiliek Onze-Lieve-Vrouw-Hemelvaartcode: nl is deprecated Basilika Bunda dari KortenbosLokasiSint-TruidenNegaraBelgiaDenominasiGereja Katolik RomaArsitekturStatusBasilika minorStatus fungsionalAktif Basilika Bunda dari Kortenbos (Belanda: Basiliek Onze-Lieve-Vrouw-Hemelvaartcode: nl is deprecated ) adalah sebuah gereja basilika minor Katolik yang terletak di Sint-Truiden, Belgia. Basilika ini ditetapkan statusnya pada 1...

Eyalet di RumeliaEyalet di Rumelia - LocalizzazioneL'eyalet di Rumelia nel 1609 Dati amministrativiNome completoEyalet-i Rumili Lingue ufficialiturco ottomano Lingue parlateturco ottomano, albanese, bulgaro, greco, macedone, serbo, albanese CapitaleEdirneSofiaMonastir Dipendente daImpero ottomano PoliticaForma di StatoEyalet Forma di governoEyalet elettivo dell'Impero ottomano Capo di StatoSultani ottomani Nascita1362 Fine1826 Territorio e popolazioneBacino geograficoAlbaniaBulgariaGreciaMace...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) 2007 في الهندمعلومات عامةالسنة 2007 2006 في الهند 2008 في الهند تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات سنوات 2005: 200...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Послание к Коринфянам. Второе послание к Коринфянам Раздел Новый завет Название на других языках: греч. Β΄ Ἐπιστολὴ πρὸς Κορινθίους; лат. Epistula II ad Corinthios; Язык оригинала древнегреческий (койне) Автор (церковное предание) ...

Untuk menara markah tanah yang kadang dikenal sebagai Canary Wharf, lihat One Canada Square. Koordinat: 51°30′13″N 0°01′06″W / 51.503611°N 0.018333°W / 51.503611; -0.018333 Canary Wharf Kaki langit Canary Wharf Canary Wharf Letak Canary Wharf di London Raya Ref. grid OS TQ375802 Borough London Tower Hamlets County seremonial London Raya Region London Negara konstituen Inggris Negara berdaulat Britania Raya Kota pos LONDON Distr...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: WOCN-FM – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Radio station in Massachusetts, United StatesWOCN-FMOrleans, MassachusettsUnited StatesBroadcast areaCape CodFrequency104.7 MHzBrandingOcean 104.7P...

National Highway in India National Highway 513Map of National Highway 513 in redRoute informationAuxiliary route of NH 13Length140 km (87 mi)Major junctionsSouth endPasighatNorth endYingkiong LocationCountryIndiaStatesArunachal Pradesh Highway system Roads in India Expressways National State Asian ← NH 13→ NH 513 National Highway 513 (NH 513) is a National Highway in North East India that connects Pasighat and Yingkiong in Arunachal Pradesh.[1] It is a sec...

Disambiguazione – Anni '60 rimanda qui. Se stai cercando la serie televisiva, vedi Anni '60 (miniserie televisiva). XIX secolo · XX secolo · XXI secolo Anni 1940 · Anni 1950 · Anni 1960 · Anni 1970 · Anni 1980 1960 · 1961 · 1962 · 1963 · 1964 · 1965 · 1966 · 1967 · 1968 · 1969 Gli anni 1960, comunemente chiamati anni Sessanta, sono il decennio che comprende gli anni dal 1960 al 19...
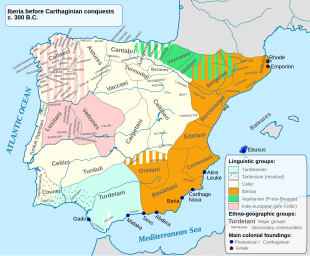
Disambiguazione – Hispania rimanda qui. Se stai cercando l'omonimo comune della Colombia, vedi Hispania (Colombia). SpagnaInformazioni generaliNome ufficiale(LA) Hispania CapoluogoTarraco (Hispania Citerior), eCorduba (Hispania Ulterior);poi Emerita Augusta (Merida) Dipendente daRepubblica romana Impero romano Suddiviso inSpagna citeriore, Spagna ulteriore AmministrazioneForma amministrativaProvincia romana GovernatoriGovernatori romani della Hispania Evoluzione storicaInizio206 a....

City in Michigan, United StatesEast LansingCityCity of East LansingDowntown East Lansing c. 2022Location within Clinton County (top) and Ingham County (bottom)East LansingLocation within the state of MichiganShow map of MichiganEast LansingLocation within the United StatesShow map of the United StatesEast LansingEast Lansing (North America)Show map of North AmericaCoordinates: 42°44′53″N 84°29′01″W / 42.74806°N 84.48361°W / 42.74806; -84.48361Country...

A 1946 stamp of the Falkland Islands Dependencies. Stamp of the Falkland Islands overprinted for Graham Land, 1944.Stamp of the Falkland Islands overprinted for South Georgia, 1944. Stamp of the Falkland Islands overprinted for the South Orkneys.Stamp of the Falkland Islands overprinted for the South Shetlands. First issues The first stamps specifically for the Falkland Islands Dependencies were issued in 1944 and consisted of overprints on stamps of the Falkland Islands for Graham Land, Sou...

Scottish Whig politician, journalist, lawyer and political economist Francis HornerFrancis Horner by Henry Raeburn.Member of Parliament for St MawesIn office1813–1817Member of Parliament for WendoverIn office1807–1812Member of Parliament for St IvesIn office1806–1807 Personal detailsBorn(1778-08-12)12 August 1778Edinburgh, Scotland.Died8 February 1817(1817-02-08) (aged 38)Pisa, Italy.Resting placeOld English Cemetery, Livorno, Italy.CitizenshipUnited Kingdom of Great Britain and Ir...

American mountain range This article is about the northernmost extent of the greater Sangre de Cristo mountain range. For the full extent of the mountain range, see Sangre de Cristo Mountains. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Sangre de Cristo Range – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR...
بنك التنمية الآسيوي (بالإنجليزية: Asian Development Bank)[1] بنك التنمية الآسيوي الاختصار (بالإنجليزية: ADB)[2] البلد الفلبين[3] المقر الرئيسي مانداليونغ سيتي، مترو مانيلا، الفلبين تاريخ التأسيس 22 أغسطس 1966 النوع منظمة إقليمية منطقة الخدمة آسيا والمحيط الهادئ ...

2003 compilation album by Grace JonesThe Universal Masters CollectionCompilation album by Grace JonesReleasedDecember 2, 2003Recorded1977–1982Genre Reggae soul new wave LabelUniversalGrace Jones chronology Private Life: The Compass Point Sessions(1998) The Universal Masters Collection(2003) The Grace Jones Story(2006) Alternative cover2006 Colour Collection re-release Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRatingAllMusic[1] The Universal Masters Collection is a mid-price gre...

Academic journalL'Enseignement mathématiqueDisciplineMathematicsLanguageEnglish and FrenchPublication detailsHistory1899 to present with suspension due to WW IIPublisherEuropean Mathematical Society Publishing House (Switzerland)FrequencyBiannualStandard abbreviationsISO 4 (alt) · Bluebook (alt1 · alt2)NLM (alt) · MathSciNet (alt )ISO 4Enseign. Math.IndexingCODEN (alt · alt2) · JSTOR (alt) · LCCN (alt)M...

Chronologies Données clés 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992Décennies :1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010Siècles :XVIIIe XIXe XXe XXIe XXIIeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies géographiques Afrique Afrique du Sud, Algérie, Angola, Bénin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroun, Cap-Vert, République centrafricaine, Comores, République du Congo, République démocratique du Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Djibouti, Égyp...







