List of defunct Canadian railways
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini perlu dikembangkan agar dapat memenuhi kriteria sebagai entri Wikipedia.Bantulah untuk mengembangkan artikel ini. Jika tidak dikembangkan, artikel ini akan dihapus. Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: DualShock – berita · surat kabar · bu...

Two athletes. Tondo of a bowl, circa 400/375 BC. Paris, Louvre The Meleager Painter was an ancient Greek vase painter of the Attic red-figure style. He was active in the first third of the 4th century BC. The Meleager Painter followed a tradition started by a group of slightly earlier artists, such as the Mikion Painter. He is probably the most important painter of his generation. He painted a wide variety of vase shapes, including even kylikes, a rarity among his contemporaries. The Calydoni...

Species of plant Roscheria Conservation status Near Threatened (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae Clade: Tracheophytes Clade: Angiosperms Clade: Monocots Clade: Commelinids Order: Arecales Family: Arecaceae Subfamily: Arecoideae Tribe: Areceae Subtribe: Verschaffeltiinae Genus: RoscheriaH.Wendl. ex Balf.f.[2][3] Species: R. melanochaetes Binomial name Roscheria melanochaetesH.Wendl. Roscheria is an endangered, monotypic genus of flowerin...

Sur une sphère les géodésiques sont les grands cercles. La géodésique tracée en rouge réalise la plus petite distance possible entre les points P et Q. Pour u et v qui sont antipodaux, plusieurs géodésiques réalisent la distance minimale.En géométrie, une géodésique est la généralisation d'une ligne droite du plan ou de l'espace euclidien, au cadre des surfaces, ou plus généralement des variétés ou des espaces métriques. Elles sont étroitement liées à la notion de plus...
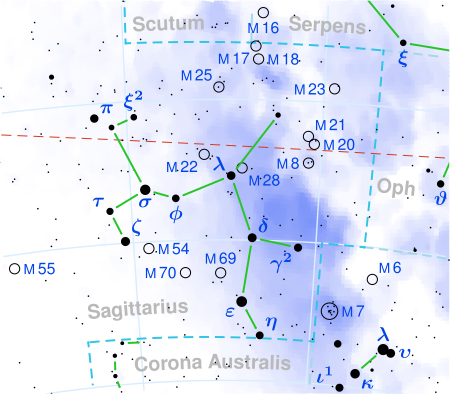
KW Sagittarii Peta rasi bintang Sagitarius Data pengamatan Epos J2000.0 Ekuinoks J2000.0 (ICRS) Rasi bintang Sagitarius Asensio rekta 17j 52m 00.72665d[1] Deklinasi −28° 01′ 20.5622″[1] Magnitudo tampak (V) 11,0[2] Ciri-ciri Kelas spektrum M1.5Iab[3] (M0I - M4Ia[4]) Magnitudo semu (K) 1,43[2] Indeks warna U−B 3,21[3] Indeks warna B−V 2...

مارسيل بانيولMarcel Pagnol (بالفرنسية: Marcel Pagnol) معلومات شخصية اسم الولادة (بالفرنسية: Marcel Paul Pagnol) الميلاد 28 فبراير 1895(1895-02-28)أوباني , فرنسا الوفاة 18 أبريل 1974 (79 سنة)باريس , فرنسا سبب الوفاة سرطان الجنسية فرنسي عضو في الأكاديمية الفرنسية[1] الزوجة جوزيت داي [�...

† Человек прямоходящий Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:Синапсиды�...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir La Rochefoucauld. Edmée de La RochefoucauldPortrait d'Edmée de La Rochefoucauld.FonctionPrésidenteUnion nationale pour le vote des femmes (d)BiographieNaissance 28 avril 189517e arrondissement de ParisDécès 20 septembre 1991 (à 96 ans)16e arrondissement de ParisSépulture MontmirailNom de naissance Edmée Christiane Marie Frisch de FelsNationalité françaiseDomicile Hôtel de La Rochefoucauld (d)Activités Écrivaine, biographePère Edm...

Former railway station on the Chester and Birkenhead railway in Birkenhead, Wirral, England Rock LaneGeneral informationLocationRock Ferry, WirralEnglandCoordinates53°22′03″N 3°00′28″W / 53.3676°N 3.0079°W / 53.3676; -3.0079Grid referenceSJ330860PlatformsTwoOther informationStatusDisusedHistoryOpenedJune 1846 (1846-06)Closed1 November 1862 (1862-11-01)Original companyChester and Birkenhead RailwayPre-groupingBirkenhead Joint Railway...

Классификация Карнеги учреждений высшего образования — базовая основа для классификации (группировки) колледжей и университетов США, предназначенная для дальнейших образовательных исследований и анализов, для которых часто имеет значение идентификация групп несрав�...

أم المؤمنين جويرية بنت الحارث جويرية بنت الحارث بن أبي ضرار بن حبيب بن عائذ بن مالك بن المصطلق معلومات شخصية اسم الولادة بَرَّة بنت الحارث بن أبي ضرار[1] الميلاد 15 ق.هـ / 608مالمدينة المنورة الوفاة ربيع الأول 56 هـ / فبرایر 676مالمدينة المنورة مكان الدفن البقيع اللقب أم ا�...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...

SatanophanyGambar sampul manga volume pertamaサタノファニ(Satanofani)GenreCerita seru[1] MangaPengarangYoshinobu YamadaPenerbitKodanshaMajalahWeekly Young MagazineDemografiSeinenTerbit13 Maret 2017 – sekarangVolume12 (Daftar volume) Portal anime dan manga Satanophany (Jepang: サタノファニcode: ja is deprecated , Hepburn: Satanofani) adalah sebuah seri manga seinen Jepang yang ditulis dan diilustrasikan oleh Yoshinobu Yamada. Manga ini dimuat berseri dalam majal...

Americans of Croatian birth or descent Croatian Americans Američki HrvatiTotal population414,714[1]–1.2 million+ (est.)[2]Regions with significant populationsPennsylvania, Illinois, Ohio, California, North Carolina, Pacific Northwest, New York, Wisconsin, Indiana, Michigan, Florida, Tennessee, Louisiana, Missouri, Colorado and MinnesotaLanguagesAmerican English and CroatianReligionPredominantly Roman CatholicismRelated ethnic groupsSlavic Americans, Croatian Canadians, Euro...

لاغازيتا ديلو سبورتLa Gazzetta dello Sport (بالإيطالية) الشعارمعلومات عامةتصدر كل 1 يوم بلد المنشأ إيطاليا التأسيس 3 أبريل 1896 القطع تابلويد موقع الويب gazzetta.it[1] شخصيات هامةالمالك Sonzogno (en) (1913 – ) المؤسس Eugenio Camillo Costamagna (en) التحريراللغة الإيطالية الإدارةالمقر الرئيسي ميلانو الناش�...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. Koordinat: 48°23′14″N 15°31′13″E / 48.38722°N 15.52028°E / 48.38722; 15.52028 Pertempuran Dürenstein (atau Dürnstein)Bagian dari Perang Koalisi KetigaPertempuran Dürenstein pada malam hari.Tanggal11 November 1805...

American Spanish-language telenovela This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Dame Chocolate – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January ...

India-related events during the year of 1875 This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: 1875 in India – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) ← 1874 1873 1872 1875 in India → 1876 1877 1878 Centuries: 17th 18th 19th 20th 21st ...

Overview of transport industry in Taiwan The Taipei Metro The Ministry of Transportation and Communications governs transportation in Taiwan. Land transport Taiwan High Speed Rail (THSR) 700T Series Shinkansen train. Roads Main article: Highway system in Taiwan Total length: 41,475 km (2009) National highway: 901 km Provincial highway: 4,680 km Highways: 20,947 km (including 872 km of freeways) Urban roads: 16,395, km Rail Main article: Rail transport in Taiwan Railwa...

Planeta Corporación, S.R.L.Kantor pusat PlanetaJenisSociedad de Responsabilidad LimitadaIndustriMedia massaPendiriJosé Manuel Lara Hernández [es]KantorpusatMadrid, SpanyolTokohkunciJosé Creuheras [es] (Presiden)ProdukPenerbitan, penyiaran, produksi televisi, produksi filmSitus webwww.planeta.es Planeta Corporación, S.R.L. (berbisnis dengan nama Grupo Planeta) adalah sebuah konglomerat media massa asal Spanyol yang beroperasi di Spanyol, Portugal, Prancis, dan Am...