L-gulonolactone oxidase
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Gallimard (homonymie). Repères historiques Création 1911 (il y a 113 ans) Fondée par Gaston Gallimard, André Gide, Jean Schlumberger Fiche d’identité Forme juridique SA à conseil d'administration[1] Statut groupe d'édition Siège social Paris (France) Dirigée par Antoine Gallimard depuis 2005 Spécialités littérature Collections Blanche[2] (1911), Bibliothèque des idées (1927), Du monde entier (1931), Bibliothèque de la Pléiade (1931/1933), S...

Pemerintahan Revolusioner Republik Indonesia1958–1961Operasi militer TNI Angkatan Laut terhadap PRRI di Sumatera Tengah tahun 1958StatusPemerintah revolusioner yang tidak diakuiIbu kotaPadangBahasaIndonesiaPemerintahanRepublik parlementerPerdana Menteri • 1958–1961 Sjafruddin Prawiranegara Era SejarahPerang Dingin• Didirikan 17 Februari 1958• Dibubarkan 28 September 1961 Didahului oleh Masa demokrasi liberal di Indonesia Sekarang bagian dariIndonesia Sunting kota...

العلاقات الإسبانية السريلانكية إسبانيا سريلانكا إسبانيا سريلانكا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الإسبانية السريلانكية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين إسبانيا وسريلانكا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتي�...

Jersey Post International LimitedCompany typeLimited Liability CompanyIndustryMailPredecessorCommittee for Postal AdministrationFounded1 July 2006 (2006-07-01)HeadquartersPostal HeadquartersLa Rue GrellierRue des Pres Trading Estate[1], Parish of St Saviour, JerseyKey peopleAlan Merry(Chairman)Tim Brown(Chief Executive)[2]Websitejerseypost.com Jersey Post is the licensed universal service provider of mail service for the Bailiwick of Jersey. History Jersey Post...

Loco shed in Kerala, India Diesel & Electric Loco Shed, ErnakulamERS based WDM-3A twins hauling Okha - Ernakulam Express.Location within KeralaLocationLocationKarshaka Road, Kadavanthra, Kochi, Kerala, IndiaCoordinates9°58′24″N 76°17′28″E / 9.9733°N 76.2910°E / 9.9733; 76.2910CharacteristicsOwnerIndian RailwaysOperatorSouthern Railway zoneDepot codeERSXTypeEngine shedRolling stockWDM-3A WDG-3A WDM3D WAG5WDG4Routes servedSouthern Railway and othersHistor...

Chemical compound with similarities to canbisol HU-243Identifiers IUPAC name (6aR,8S,9S,10aR)-9-(hydroxymethyl)-6,6-dimethyl-3-(2-methyloctan-2-yl)-8,9-ditritio-7,8,10,10a-tetrahydro-6aH-benzo[c]chromen-1-ol CAS Number140835-18-3 YPubChem CID3081854IUPHAR/BPS735UNIISKGOA1RZCTChemical and physical dataFormulaC25H40O3Molar mass388.592 g·mol−13D model (JSmol)Interactive image SMILES CC(O1)(C)[C@H]2[C@@H](C[C@H](CO)CC2)C3=C1C=C(C(C)(C)CCCCCC)C=C3O HU-243 (AM-4056) is a synthetic cann...

Dream Shizuka (lahir 6 Maret 1988)[1] adalah seorang penyanyi dan penari pop Jepang. Ia adalah amntan anggota grup vokal perempuan Dream dan E-girls. Ia sekarang aktif sebagai anggota DANCE EARTH PARTY. Saat pertama kali bergabung dengan grup tersebut, pada 7 Juli 2002,[2][3] ia menjadi vokalis pendukung dan penari latar. Kemudian, ia belajar dansa dengan anggota segrupnya Erie, dan kemudian, ia makin dikenal karena kemampuan dansanya. Sejak kelahiran kembali Dram pada...

Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Daerah Kabupaten Ogan Komering UluDewan Perwakilan RakyatKabupaten Ogan Komering Ulu2019-2024JenisJenisUnikameral SejarahSesi baru dimulai16 Agustus 2019PimpinanKetuaIr. H. Marjito Bachri, S.T. (Gerindra) sejak 16 September 2019 Wakil Ketua IYudi Purna Nugraha, S.H. (PAN) sejak 16 September 2019 Wakil Ketua IIYoni Risdianto, S.H. (Golkar) sejak 16 September 2019 KomposisiAnggota35Partai & kursi PDI-P (3) NasDem (3) PKB...

لوح حجري هندي-بارثي، يمثّل عبادة النار، ربما من الطبيعة الزرداشتية. آجني الهندوسي إله النار، كان له مكاناً بارزاً بين آلهة ريجفدا. عبادة أو تأويل النار هي ممارسة عرفت في ديانات مختلفة. كانت النار جزءاً هاماً من ثقافة الهومو منذ العصر الحجري القديم السفلي. أقدم أثر موجود عن �...

Super Street Fighter IIThe New ChallengersDéveloppeur CapcomÉditeur CapcomDate de sortie 11 septembre 1993Genre CombatMode de jeu un ou deux joueursPlate-forme Arcade :CP System IIOrdinateur(s) :Amiga, FM Towns, MS-DOS, Sharp X68000Console(s) :Super Nintendo, Mega Drive, Amiga CD32, PlayStation, Saturn, Wii (Console virtuelle), Nintendo Switch, PlayStation 4, Xbox OneStreet Fighter IIStreet Fighter II': Hyper FightingSuper Street Fighter II: The Tournament Battlemodifier - mo...

Katedral ZadarKatedral Basilika Santa AnastasiaKroasia: Katedrala svete Stošijecode: hr is deprecated Katedral ZadarKatedral Zadar44°6′58.5″N 15°13′28″E / 44.116250°N 15.22444°E / 44.116250; 15.22444Koordinat: 44°6′58.5″N 15°13′28″E / 44.116250°N 15.22444°E / 44.116250; 15.22444LokasiZadarNegaraKroasiaDenominasiGereja Katolik RomaArsitekturStatusKatedralStatus fungsionalAktifGayaRomanesqueGothic (beberapa bagian)Dibangun...

English pop singer (born 1960) This article is about the singer. For her debut album, see Kim Wilde (album). For the fictional character, see Getting On (UK TV series). Kim WildeWilde in 2021Background informationBirth nameKim SmithBorn (1960-11-18) 18 November 1960 (age 63)Chiswick, Middlesex, EnglandGenresPop[1]new wave[1]hi-NRG[2]Occupation(s)Singersongwritertelevision presenterDJYears active1981–presentLabelsRAKMCAEMIColumbia SevenOneWebsitekimwilde.comParen...

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Rantau Prapat. Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Parapat (disambiguasi). ParapatKelurahanKantor Lurah ParapatNegara IndonesiaProvinsiSumatera UtaraKabupatenSimalungunKecamatanGirsang Sipangan BolonKodepos21174Kode Kemendagri12.08.16.1004 Kode BPS1209050003 Luas15.002[1]Jumlah penduduk9,138 jiwa (2021)[1]Kepadatan577.00 jiwa/km2[1] Parapat adalah salah satu kelurahan yang berada di wilayah Kecamatan Girsang Sipangan Bolon, Kabupaten Simalungun, ...
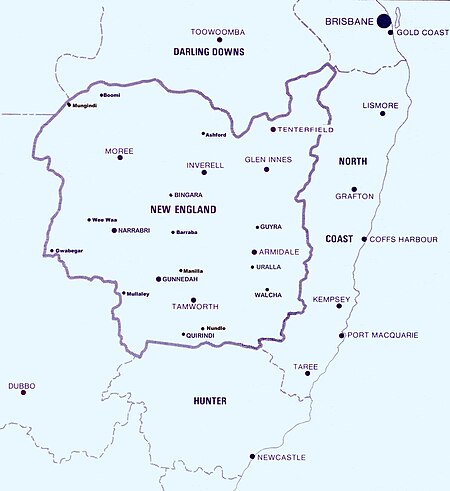
This article is about the electoral district of Australia. For other New Englands, see New England (disambiguation). Australian federal electoral division Australian electorate New EnglandAustralian House of Representatives DivisionDivision of New England in New South Wales, as of the 2022 federal electionCreated1901MPBarnaby JoycePartyNationalsNamesakeNew EnglandElectors113,465 (2022)Area66,394 km2 (25,634.9 sq mi)DemographicRural Electorates around New England: Maranoa(Q...

乔冠华 中华人民共和国外交部部长 中国人民对外友好协会顾问 任期1974年11月—1976年12月总理周恩来 → 华国锋前任姬鹏飞继任黄华 个人资料性别男出生(1913-03-28)1913年3月28日 中華民國江蘇省盐城县逝世1983年9月22日(1983歲—09—22)(70歲) 中华人民共和国北京市籍贯江蘇鹽城国籍 中华人民共和国政党 中国共产党配偶明仁(1940年病逝) 龚澎(1970年病逝) 章含�...

Chinese general (1910–1983) In this Chinese name, the family name is Huang. Huang YongshengHuang Yongsheng in 1955Native name黄永胜BornNovember 17, 1910Xianning, Hubei, Qing ChinaDiedApril 26, 1983 (aged 72)Qingdao, Shandong, People's Republic of ChinaAllegiance People's Republic of ChinaService/branchPeople's Liberation ArmyYears of service1927–1971RankGeneral (1955)UnitFirst Corps, Chinese Red ArmyCommands held31st Division of the 11th Red Army, 16th Division of the 22nd Re...

International award in arts and sciences AwardWolf PrizeAwarded forOutstanding achievement in Agriculture, Chemistry, Mathematics, Medicine, Physics, and ArtsCountryIsraelPresented byWolf FoundationReward(s)US $100,000First awarded1978; 46 years ago (1978)Websitewww.wolffund.org.il The Wolf Prize is an international award granted in Israel, that has been presented most years since 1978 to living scientists and artists for achievements in the interest of mankind and friendly ...
Paghimo ni bot Lsjbot. 42°10′00″N 14°42′00″E / 42.16667°N 14.7°E / 42.16667; 14.7 Fosso Lebba Suba Nasod Italya Rehiyon Abruzzo Gitas-on 22 m (72 ft) Tiganos 42°10′00″N 14°42′00″E / 42.16667°N 14.7°E / 42.16667; 14.7 Timezone CET (UTC+1) - summer (DST) CEST (UTC+2) GeoNames 3174965 Suba ang Fosso Lebba sa Italya.[1] Nahimutang ni sa rehiyon sa Abruzzo, sa sidlakang bahin sa nasod, 180 km s...

Viswanathan Anand and Magnus Carlsen competing in Linares in 2007. Chess in Spain refers to Spain's contribution to the history of chess, from its integration around the 10th century to the present day. The Spanish received Shatranj, one of the predecessors of chess, from the Arabs during the Muslim conquest of the Iberian Peninsula between the 7th and 15th centuries. As chess spread to the rest of Europe, Spain contributed to the chess literature of the period, culminating with the Libro de...

Ilustrasi formasi ala catenaccio Catenaccio adalah sistem taktis dalam permainan sepak bola yang menitikberatkan kekuatan pada pertahanan.[1] Dalam bahasa Italia, catenaccio berarti Kunci sehingga dapat diartikan bahwa catenaccio adalah strategi permainan dengan pertahanan yang terorganisir dan efektif agar lawan kesulitan menyerang atau mencetak gol.[1] Strategi ini dikenal luas ketika pada tahun 1960-an Helenio Herrera menerapkannya pada Internazionale.[1] Ciri khusu...


