Hong Kong drifter
|
Read other articles:

العلاقات الإندونيسية اللوكسمبورغية إندونيسيا لوكسمبورغ إندونيسيا لوكسمبورغ تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الإندونيسية اللوكسمبورغية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين إندونيسيا ولوكسمبورغ.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عا�...

American convicted murderer (born 1934) This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find so...

العلاقات المالية الموزمبيقية مالي موزمبيق مالي موزمبيق تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات المالية الموزمبيقية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين مالي وموزمبيق.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة ما�...

Valdo Vinay (La Spezia, 10 agosto 1906 – Roma, 25 novembre 1990) è stato un teologo, pastore protestante e predicatore italiano. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Opere principali 3 Bibliografia 4 Altri progetti 5 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Di padre valdese e madre battista, crebbe a Trieste. Avvertì nel 1926 una vocazione pastorale per la quale abbandonò gli studi di ingegneria. Nei primi anni Trenta appartenne a Bonn al ristretto circolo di allievi di Karl Barth, di cui sempre si considerò di...

Spanduk protes di Universitas Manchester Protes Universitas Manchester (2020-2021) yang terjadi pada awal tahun 2020 dan berlanjut hingga tahun 2021 merupakan protes berantai dan mogok sewa yang dilakukan oleh para mahasiswa di Universitas Manchester di Manchester, Britania Raya. Protes ini terjadi sebagai dampak dari kesalahan penanganan pandemi COVID-19 oleh pihak manajemen universitas dan isu yang lebih luas tentang marketisasi pendidikan tinggi di Britania Raya. Mereka mendapatkan dukunga...

Voce principale: Genoa Cricket and Football Club. Genoa 1893Stagione 1980-1981 Sport calcio Squadra Genoa Allenatore Luigi Simoni Presidente Renzo Fossati Serie B3º Coppa ItaliaPrimo turno Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Martina (38) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Russo (13)Totale: Russo (14) StadioLuigi Ferraris Abbonati6 378 Media spettatori24 300[1] 1979-1980 1981-1982 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti il Genoa 1893...

Kastel Batavia, pusat pemerintahan imperium perdagangan Asia, Perusahaan Hindia Timur Belanda, yang membentang dari Tanjung Harapan sampai Jepang. Kastel Batavia (Bahasa Belanda: 't Kasteel Batavia, bahasa Melayu Batavia: Kotta Ientang di Benoa Batawi, bahasa Portugis Tugu: Oen Foertalëja de Batavia[1]) adalah sebuah benteng yang terletak di muara Sungai Ciliwung di Jakarta. Kastel Batavia merupakan pusat pemerintahan Perusahaan Hindia Timur Belanda di Asia.[2] Kastel Batavia...

American media franchise JumanjiThe current logo of the franchiseCreated byChris Van AllsburgOriginal workJumanji (1981)OwnerBooks: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Films: Sony Pictures EntertainmentPrint publicationsBook(s) Jumanji (1981) Zathura (2002) Films and televisionFilm(s) Jumanji (1995) Zathura: A Space Adventure (2005) Jumanji: Welcome to the Jungle (2017) Jumanji: The Next Level (2019) Animated seriesJumanji (1996–1999)GamesTraditional Jumanji: The Game (1995) Zathura: Adventure is Wai...

此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2021年7月4日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:美国众议院 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 美國眾議院 United States House of Representatives第118届美国国会众议院徽章 众议院旗...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...

Koordinat: 0°57′07″S 100°27′44″E / 0.951900°S 100.462238°E / -0.951900; 100.462238 Untuk Semen Padang sebagai klub sepak bola, lihat: Semen Padang FC. SMA Semen PadangInformasiDidirikan10 Januari 1977JenisSwastaAkreditasiAKepala SekolahDrs. Mawardi, M.Pd.[1]Jumlah kelas13 kelas setiap tingkatJurusan atau peminatanMIA dan IISRentang kelasX-XIIKurikulumKurikulum 2013Jumlah siswa772 siswa (2010-11)StatusDikelola Yayasan Igasar Semen Pada...

1976 play about poet Emily Dickinson The Belle of AmherstWritten byWilliam LuceCharactersEmily DickinsonDate premieredApril 28, 1976 (1976-04-28)Place premieredLongacre TheatreNew York CityOriginal languageEnglish China Zorrilla as Emily Dickinson, 1981 The Belle of Amherst is a one-woman play by William Luce. Based on the life of poet Emily Dickinson from 1830 to 1886, and set in her Amherst, Massachusetts, home, the 1976 play makes use of her work, diaries, and letters to rec...

Disambiguazione – Craxi rimanda qui. Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Craxi (disambigua). Bettino CraxiCraxi nel 1984 Presidente del Consiglio dei ministridella Repubblica ItalianaDurata mandato4 agosto 1983 –18 aprile 1987 Capo di StatoSandro PertiniFrancesco Cossiga Vice presidenteArnaldo Forlani PredecessoreAmintore Fanfani SuccessoreAmintore Fanfani Presidente del Consiglio europeoDurata mandato1º gennaio 1985 –30 giugno 1985 Predec...

Helvetii v. Rome, Gallic Wars, 58 BC Battle of BibractePart of the Gallic WarsJulius Caesar and Divico parley after the battle at the Saône. Historic painting of the 19th century by Karl Jauslin.Date58 BCLocationSaône-et-Loire, France46°55′0.001″N 4°1′59.999″E / 46.91666694°N 4.03333306°E / 46.91666694; 4.03333306Result Roman victoryBelligerents Roman Republic Mainly HelvetiiBoiiTulingiRauraciCommanders and leaders Gaius Julius Caesar DivicoStrength Prese...

Ivor Richard Commissario europeo per l'Occupazione e gli Affari Sociali, l'Istruzione e la Formazione ProfessionaleDurata mandato6 gennaio 1981 –6 gennaio 1985 PresidenteGaston Thorn PredecessoreHenk Vredeling (Occupazione e affari sociali)Guido Brunner (Istruzione) SuccessoreManuel Marín Dati generaliPrefisso onorificoThe Right Honourable Partito politicoPartito Laburista Ivor Seward Richard, Barone Richard di Ammanford (Carmarthenshire, 30 maggio 1932 – 18 marzo...

British macroeconomist (born 1943) Patrick MinfordCBEPatrick Minford at MSc dinner for economics students at Cardiff University in February 2008Born (1943-05-17) 17 May 1943 (age 81)Shrewsbury, Shropshire, EnglandSpouse Rosemary Allcorn (m. 1970)Academic careerInstitutionCardiff UniversityUniversity of LiverpoolSchool ortraditionNew classical macroeconomicsAlma materBalliol College, OxfordLondon School of Economics Anthony Patrick Leslie Minford C...
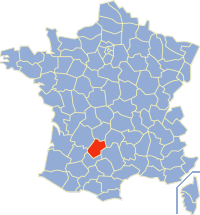
Este artigo não cita fontes confiáveis. Ajude a inserir referências. Conteúdo não verificável pode ser removido.—Encontre fontes: ABW • CAPES • Google (N • L • A) (Janeiro de 2016) LotLot Informações País França Região Occitânia Sede do depto. (Préfecture) Cahors Sub-sedes (Sous-préfectures) FigeacGourdon População 160 197 hab. (1999) Área 5 217 km² Densidade populacional 30,7 hab./km² Arrondi...

Voce principale: Berliner Fußballclub Dynamo. Berliner Fußballclub DynamoStagione 2022-2023Sport calcio Squadra BFC Dynamo Allenatore Heiner Backhaus All. in seconda Nils Weiler Regionalliga6º posto Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Pollasch, Reher (33)Totale: Pollasch, Reher (33) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Beck (16)Totale: Beck (16) StadioSportforum Hohenschönhausen Maggior numero di spettatori2 558 vs. Rot Weiss Erfurt Minor numero di spettatori1 365 vs. Altglienicke Media ...

سانجر علم الإحداثيات 36°42′29″N 119°33′21″W / 36.708055555556°N 119.55583333333°W / 36.708055555556; -119.55583333333 [1] تاريخ التأسيس 1888 تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2][3] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة فريسنو خصائص جغرافية المساحة 14.931844 كيلومتر مربع14.306729...

Client state of the Roman Republic from 37 to 4 BCE Herodian kingdom37 BCE–4 BCEHerodian Kingdom of Judea at its greatest extentStatusClient state of the Roman Republic / Roman EmpireCapitalJerusalemCommon languagesKoine Greek, Aramaic, Latin, HebrewReligion Second Temple JudaismSamaritanismRoman imperial cultGovernmentMonarchyKing • 37 BCE – 4 BCE Herod the Great Historical eraAugustan Age• conquest of Hasmonean kingdom 37 BCE• formation of Tetrarchy 4 BCE ...