Economic reform of Iraq
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini membahas mengenai bangunan, struktur, infrastruktur, atau kawasan terencana yang sedang dibangun atau akan segera selesai. Informasi di halaman ini bisa berubah setiap saat (tidak jarang perubahan yang besar) seiring dengan penyelesaiannya. Al Kazim TowersInformasi umumLokasiDubai, Uni Emirat ArabPerkiraan rampung2008TinggiMenara antena265 m (869 kaki)Data teknisJumlah lantai53Desain dan konstruksiArsitekNational Engineering BureauPengembangAl Shafar General Contracting ...

Patung Lakshmanaswami Mudaliar di Dewan Senat, Universitas Madras Diwan Bahadur Sir Arcot Lakshmanaswami Mudaliar, FRCOG, FACS (14 Oktober 1887 – 1974) adalah seorang edukasionis dan dokter asal India. Ia adalah saudara kembar identik dari Sir Arcot Ramasamy Mudaliar. Ia awalnya dididik di Kurnool dan kemudian pindah ke Chennai pada 1903.[1] Referensi ^ The twin stars of Arcot. The Hindu. 14 October 2012. Diakses tanggal 28 February 2018. S. Muthiah, Achievements in doubl...

American author and politician (born 1945) Tom AllenMember of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom Maine's 1st districtIn officeJanuary 3, 1997 – January 3, 2009Preceded byJim LongleySucceeded byChellie Pingree110th Mayor of PortlandIn office1991–1992Preceded byPeter O'DonnellSucceeded byCharles HarlowMember of the Portland City CouncilIn office1989–1995 Personal detailsBornThomas Hodge Allen (1945-04-16) April 16, 1945 (age 78)Portland, Maine, U.S.Political p...

Char kway teow Hanzi tradisional: 炒粿條 Hanzi sederhana: 炒粿条 Makna harfiah: kwetiau goreng Alih aksara Mandarin - Hanyu Pinyin: cháo guǒ tiáo Min Nan - Romanisasi POJ: chhá-kóe-tiâu Yue (Kantonis) - Jyutping: caau2 gwo2 tiu4 Nama alternatif dikawasan berbahasa Kanton Hanzi tradisional: 炒貴刁 Hanzi sederhana: 炒贵刁 Makna literal: tidak ada Alih aksara Mandarin - Hanyu Pinyin: cháo guì diāo Yue (Kantonis) - Jyutping: caau2 gwai3 diu1 Char kway teowJenisShahe fenTempa...

City in Florida, United StatesMarco Island, FloridaCityCity of Marco IslandNickname: La Isla de San MarcoLocation in Collier County and the state of FloridaCoordinates: 25°58′21″N 81°43′44″W / 25.97250°N 81.72889°W / 25.97250; -81.72889[1]CountryUnited StatesStateFloridaCountyCollierArea[2] • Total24.66 sq mi (63.88 km2) • Land12.16 sq mi (31.49 km2) • Water12.51 sq...

Livio Gratton Livio Gratton (Trieste, 30 luglio 1910 – Frascati, 15 gennaio 1991) è stato un astrofisico italiano. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Alcuni saggi 3 Opere 4 Note 5 Bibliografia 6 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Trasferitosi con tutta la famiglia a Roma nel 1920,[1] si laureò in fisica nel 1931, presso l'Università di Roma La Sapienza, con una tesi in cosmologia relativistica, sotto la guida di Giuseppe Armellini e Guido Castelnuovo, Dopo un periodo di studio e di ricerca all'est...

Maine gubernatorial election 1864 Maine gubernatorial election ← 1863 12 September 1864 1865 → Nominee Samuel Cony Joseph Howard Party Republican Democratic Popular vote 65,583 46,403 Percentage 58.56% 41.44% Governor before election Samuel Cony Republican Elected Governor Samuel Cony Republican Elections in Maine Federal offices U.S. President 1820 1824 1828 1832 1836 1840 1844 1848 1852 1856 1860 1864 1868 1872 1876 1880 1884 1888 1892 1896 1900 1904 1908 1...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Cambridge (homonymie), Duc et marquis de Cambridge, Comte de Strathearn, Baron Carrickfergus et Prince William. William de Galles Le prince William en 2021, alors duc de Cambridge.Titre Prince héritier du Royaume-Uni Depuis le 8 septembre 2022(1 an, 7 mois et 23 jours) Données clés Prédécesseur Charles, prince de Galles Biographie Titulature Prince de GallesDuc de CornouaillesDuc de RothesayDuc de CambridgeComte de ChesterComte de Strathe...
ZFP91 التراكيب المتوفرة بنك بيانات البروتينOrtholog search: PDBe RCSB قائمة رموز معرفات بنك بيانات البروتين 2M9A المعرفات الأسماء المستعارة ZFP91, DMS-8, DSM-8, PZF, ZFP-91, ZNF757, FKSG11, zinc finger protein, zinc finger protein, atypical E3 ubiquitin ligase, DSM8 معرفات خارجية MGI: MGI:104854 HomoloGene: 43144 GeneCards: 80829 علم الوجود الجيني الوظيفة الجزيئي�...

Северный морской котик Самец Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:Синапси...

Unfree peasant class of Tsarist Russia A Peasant Leaving His Landlord on Yuriev Day, painting by Sergei V. Ivanov The term serf (Russian: крепостной крестьянин, romanized: krepostnoy krest'yanin, lit. 'bonded peasant'), in the sense of an unfree peasant of tsarist Russia, meant an unfree person who, unlike a slave, historically could be sold only together with the land to which they were attached. However, this stopped being a requirement by the 19th cen...

Welsh politician (born 1954) Mick AntoniwMSМік АнтонівOfficial portrait, 2021Counsel General for WalesIncumbentAssumed office 13 May 2021First MinisterMark DrakefordVaughan GethingPreceded byJeremy MilesIn office27 June 2016 – 14 November 2017First MinisterCarwyn JonesPreceded byTheodore HuckleSucceeded byJeremy MilesMinister for the ConstitutionIn office13 May 2021 – 20 March 2024First MinisterMark DrakefordPreceded byOffice establishedSucceeded byRebecca...

Members of the New South Wales Legislative Council who served from 1877 to 1880 were appointed for life by the Governor on the advice of the Premier. This list includes members between the elections commencing on 24 October 1877 and the elections commencing on 17 November 1880.[1] The President was Sir John Hay.[8] Name Years in office Office George Allen [a] 1856–1861, 1861–1877 Archibald Bell [j] 1879–1883 John Blaxland 1863–1884 William ...

Court interpreting the Constitution of Spain Constitutional CourtTribunal ConstitucionalHeadquarters of the Constitutional CourtEstablished1978JurisdictionSpainLocationMadridComposition methodAppointed by the King after being nominated by the Parliament, the General Council of the Judiciary and the Government.Authorized bySpanish ConstitutionJudge term length9 years, non renewableNumber of positions12Annual budget€ 28.42 million (2022)[1]Websitewww.tribunalconstitucional.esPresiden...

British politician The Right HonourableBob StokerVice chairman of UKIP Northern IrelandIn office2015–201756th Lord Mayor of BelfastIn office1 June 1999 – 1 June 2000DeputyMarie MoorePreceded byDavid AlderdiceSucceeded bySammy WilsonMember of Belfast City CouncilIn office1995 – 22 May 2014Preceded byJim KirkpatrickSucceeded byJeff DudgeonConstituencyBalmoral Personal detailsBornBelfast, Northern IrelandPolitical partyUKIP (2014 - 2017) Ulster Unionist (until 2014) Rober...

Politics of Ukraine Constitution Human rights Presidency President Volodymyr Zelenskyy Office of the President National Security and Defence Council Presidential representatives Presidential symbols Executive Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal Cabinet Shmyhal Government Legislature Verkhovna Rada (parliament) Chairman: Ruslan Stefanchuk Committees People's Deputy of Ukraine Imperative mandate Judiciary Constitutional Court Supreme Court Prosecutor General Local government Local state administratio...

قهرمان البغدادي معلومات شخصية مكان الميلاد بغداد مكان الوفاة قانسو الجنسية الدولة العباسية العرق عربي الديانة مسلم الحياة العملية المهنة جغرافي، وكاتب تعديل مصدري - تعديل مخطوط لابن فضلان من القرن العاشر الميلادي قهرمان البغدادي عالم إسلامي من القرن العاشر ال...
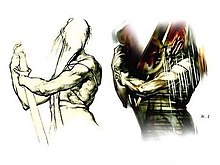
Fictional video game character Fictional character Pyramid HeadSilent Hill characterPyramid Head as he appears in Silent Hill 2First appearanceSilent Hill 2Designed byMasahiro ItoPortrayed byRoberto Campanella Pyramid Head, also known as Red Pyramid, Red Pyramid Thing (赤い三角頭, Akai Sankakutō),[1] or Triangle Head (三角頭, Sankaku Atama) is a character from the Silent Hill series, a survival horror video game series created by Japanese company Konami. Introduced in the 200...

Concept in political philosophy For the early-20th-century periodical, see Social Justice (periodical). For the academic journal established in 1974, see Social Justice (journal). Social justice is justice in relation to the distribution of wealth, opportunities, and privileges within a society where individuals' rights are recognized and protected.[1] In Western and Asian cultures, the concept of social justice has often referred to the process of ensuring that individuals fulfill th...

List of significant events occurring during World War II in 1942 This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Timeline of World War II 1942 – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message)Timelines of World War II Chronological Prelude (in Asiain E...

