Dot-winged antwren
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (يناير 2015) الأمثلة متعددة الأهداف (بالإنجليزية: Multi-objective optimization) الأمثلة متعددة الأهداف (المعروف أيضا باسم البرمجة متعددة الاهداف أو الأمثلة متعددة المعايير) هو مجال ...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. Badai Tropis Marco adalah badai terjadi di Benua Amerika. Tercatat sebanyak 3 kali Badai tersebut berhasil membuat kekacauan di negeri Paman Sam Tersebut. Badai Marco pertama terjadi di pantai barat Florida pada tahun 1990 dan menyebabkan hujan lebat ...

Jawa Tengah IVDaerah Pemilihan / Daerah pemilihanuntuk Dewan Perwakilan RakyatRepublik IndonesiaWilayah Daftar Kabupaten : Karanganyar Sragen Wonogiri ProvinsiJawa TengahPopulasi3.013.632 (2023)[1]Elektorat2.313.625 (2024)[2]Daerah pemilihan saat iniDibentuk2004Kursi7Anggota Luluk Nur Hamidah (PKB) Bambang Wuryanto (PDI-P) Agustina Wilujeng Pramestuti (PDI-P) Paryono (PDI-P) Dolfie Othniel Frederic Palit (PDI-P) Endang Maria Astuti (Gol...

Airline formed as a joint venture between Pan American World Airways and Grace Shipping Company Pan American-Grace AirwaysPan American-Grace Airways Douglas DC-2 IATA ICAO Callsign PY PY Panagra FoundedSeptember 1928Commenced operationsSeptember 12, 1928Ceased operationsFebruary 1, 1967 (February 1, 1967) (merged with Braniff International Airways)Hubs Tocumen International Airport Limatambo Airport Jorge Chavez International Airport Secondary hubs John F. Kennedy International Airport M...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant une localité anglaise. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Thornton-in-CravenGéographiePays Royaume-UniRégion Yorkshire-et-HumberRégion Angleterre du Nord-EstComté cérémonial Yorkshire du NordRégion du conseil Yorkshire du NordDistrict non métropolitain CravenCoordonnées 53° 55′ 55″ N, 2° 08′ 35″ OFonction...

Dewa-Dewi Olimpus. Mitologi YunaniDewa-Dewi Yunani Titan dan Dewa-Dewi Olimpus Dewa Laut Dewa Dunia Bawah Dewa Lainnya Dewa-Dewi Olimpus Zeus Hera Afrodit Apollo Athena Ares Artemis Demeter Dionisos Hades Hefaistos Hermes Hestia Poseidon Daftar tokoh mitologi Yunani lbs Wikibooks Mitologi Yunani memiliki halaman di: Dewa Olimpus 12 Dewa Olimpus juga dikenal dengan sebutan Dodekatheon (Greek: δωδεκα /dodeka = 12, θεον /theon = dewa) dalam mitologi Yunani adalah dewa-dewi utama Yunani...

Commuter rail station in Chicago, Illinois This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Museum Campus/11th Street station – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2021) Museum Campus/11th St.General informationLocationMichigan Avenue at 11th StreetChicago Loop, Chicago, IllinoisCoord...

Voce principale: Mantova Football Club. Mantova SportivaStagione 1941-1942Sport calcio Squadra Mantova Allenatore Giovanni Battistoni Presidente cav. uff. Giacomo Azzalli Serie C3º posto nel girone B. StadioStadio Settimio Leoni 1940-1941 1942-1943 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa pagina raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti la Mantova Sportiva nelle competizioni ufficiali della stagione 1941-1942. Indice 1 Stagione 2 Rosa 3 Risultati 3.1 Serie C 3.1.1 Girone di andata 3.1...

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁�...

非常尊敬的讓·克雷蒂安Jean ChrétienPC OM CC KC 加拿大第20任總理任期1993年11月4日—2003年12月12日君主伊利沙伯二世总督Ray HnatyshynRoméo LeBlancAdrienne Clarkson副职Sheila Copps赫布·格雷John Manley前任金·坎貝爾继任保羅·馬田加拿大自由黨黨魁任期1990年6月23日—2003年11月14日前任約翰·特納继任保羅·馬田 高級政治職位 加拿大官方反對黨領袖任期1990年12月21日—1993年11月...

Administrador de la National Aeronautics and Space Administration Insignia del administrador de la NASA Bill Nelson Desde el 03 de mayo de 2021Titular de Administración Nacional de Aeronáutica y del EspacioDesignado por Presidente de los Estados UnidosCreación 19 de agosto de 1958Primer titular T. Keith GlennanSitio web NASA Administrator[editar datos en Wikidata] El administrador de la NASA es el puesto más alto en la NASA, la agencia espacial estadounidense. Sirve como as...

American consumer electronics company Not to be confused with Microsoft Visio. Vizio Holding Corp.FormerlyV Inc. (2002–2004)Company typePublic (sale to Walmart pending)Traded asNYSE: VZIO (Class A)Russell 2000 componentIndustryElectronicsFoundedOctober 2002; 21 years ago (2002-10), in Costa Mesa, California, U.S.FoundersWilliam WangHeadquartersIrvine, California, U.S.Area servedNorth AmericaKey peopleWilliam Wang (CEO)[1]Adam Townsend (CFO)[2]Mike...

Motivate LLCFormerlyAlta BicycleShare[1]Company typeSubsidiaryHeadquartersNew York, NY, United StatesArea servedUnited StatesKey peopleMatthew Parker (CEO)ServicesBicycle-sharing system and urban service providerRevenue100 millionNumber of employees1500+[2] (2021)ParentLyftWebsitemotivateco.com Motivate LLC (formerly Alta Bicycle Share and also Motivate International Inc.) is a company based in New York City that services bicycle sharing systems and other urban services ...

This article may rely excessively on sources too closely associated with the subject, potentially preventing the article from being verifiable and neutral. Please help improve it by replacing them with more appropriate citations to reliable, independent, third-party sources. (January 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) .белIntroduced2014TLD typeInternationalised (Cyrillic) country code top-level domainStatusactive[1]Intended useEntities connected with BelarusRegistere...

El regimiento n.º 88 de Infantería (Connaught Rangers), conocidos con el sobrenombre the Devil's Own, fue uno de los 8 regimientos irlandeses al servicio del Ejército Británico estacionados en Irlanda. Como parte de las reformas Cardwell-Childers fue fusionado con el 94.º el 1 de julio de 1881 dando lugar a los Connaught Rangers. Historia Creado el 25 de septiembre de 1793 con reclutas de Connacht por John Thomas de Burgh, 13.º Earl de Clanricard, sirvió en Flandes en la desastrosa Exp...

Button or lever to activate fire alarms For other uses, see Fire alarm (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Manual fire alarm activation – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Simplex single action T-bar pull stati...

October, 1833 Wikisource has original text related to this article: Baltimore Saturday Visiter The Baltimore Saturday Visiter was a weekly periodical in Baltimore, Maryland, in the 19th century. It published some of the early works of Baltimore writer Edgar Allan Poe. History It was established in 1832 by Charles Cloud and Lambert Wilmer, a friend of Poe. Popular at first, the Visiter later became abolitionist, and in 1847 was absorbed by the abolitionist National Era of Washington D.C. Poe s...
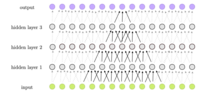
Artificial neural network For other uses, see CNN (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Convolutional neural network – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Part of a series onMachine learningand data mining Paradigms S...

1940–91 Soviet occupation of the Baltic states Occupation of the Baltic statesPart of World War II and the Cold WarA protest sign from the 1970s calling on the United Nations to abolish Soviet colonialism in the Baltic statesDate15 June 1940 – 6 September 1991 (1940-06-15 – 1991-09-06)Military presence: 28 September 1939 – 31 August 1994 (1939-09-28 – 1994-08-31)LocationEstonia, Latvia, and LithuaniaParticipants&#...

Not to be confused with Real Noroeste Capixaba Futebol Clube. Soccer clubNoroesteFull nameEsporte Clube NoroesteNickname(s)NoruscaMaquininha VermelhaFoundedSeptember 1, 1910 (114 years ago) (1910-09-01)GroundEstádio Alfredo de CastilhoCapacity18,866[1]PresidentEmílio Brumati[2]Head coachMoisés Egert[3]LeagueCampeonato Paulista Série A22023 [pt]Paulista Série A2, 3rd of 16WebsiteClub website Home colors Away colors Esporte Clube Noroeste,...




