Várzea forest
|
Read other articles:
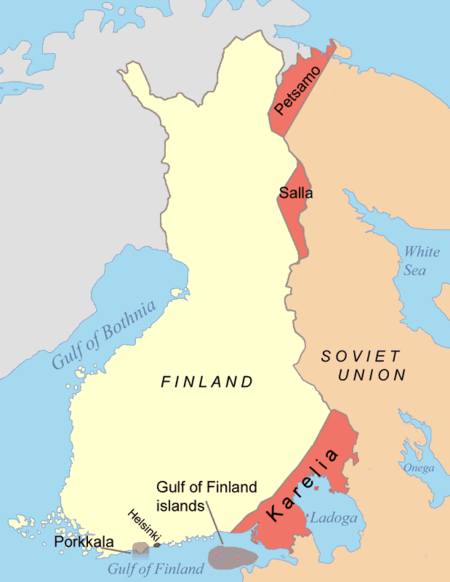
Wilayah yang diserahkan Finlandia kepada Uni Soviet. Porkkala dikembalikan kepada Finlandia pada tahun 1956. Permasalahan Karelia atau isu Karelia (bahasa Finlandia: Karjala-kysymys) adalah isu mengenai status Karelia dan wilayah-wilayah Finlandia lainnya yang diserahkan kepada Uni Soviet selama Perang Musim Dingin. Walaupun disebut isu Karelia, istilah ini juga meliputi pengembalian Petsamo, bagian dari Salla dan Kuusamo yang diserahkan, serta empat pulau di Teluk Finlandia. Namun, dalam...

Bemban Bemban, Donax canniformisdari tepian Kapuas, Kalbar Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Plantae (tanpa takson): Angiospermae (tanpa takson): Monokotil (tanpa takson): Commelinids Ordo: Zingiberales Famili: Marantaceae Genus: Donax Spesies: D. canniformis Nama binomial Donax canniformis(G. Forst.) K. Schum. Sinonim Thalia canniformis G. Forster, 1780 Actophanes canniformis (G. Forst.) K. Schumann Donax arundastrum Loureiro Bemban atau bamban (Donax canniformis) adalah sejenis terna yang ...

Indonesian coffee drink Kopi luwakAlternative namesIndonesian pronunciation: [ˈkopi ˈlu.aʔ]Place of originIndonesia[1]Main ingredientsCoffea arabica Media: Kopi luwak Kopi luwak, also known as civet coffee, is a coffee that consists of partially digested coffee cherries, which have been eaten and defecated by the Asian palm civet (Paradoxurus hermaphroditus). The cherries are fermented as they pass through a civet's intestines, and after being defecated with other...

2022 conflict between Israel and Gaza 2022 Gaza–Israel clashesPart of the Israeli–Palestinian conflictTargeted killing of Tayseer al-Jabari, commander in the Islamic Jihad Movement in PalestineDate5–7 August 2022LocationGaza Strip and West BankResult Ceasefire on 23:30 (UTC+3), 7 August 2022Combatants Israel Israel Defense Forces Israeli Air Force Gaza Strip[1][2][3][4] Islamic Jihad Movement in Palestine (PIJ)[5][6][...

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (novembre 2023). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références ». En pratique : Quelles sources sont attendues ? ...

Then-Major General Pedro del Valle, U.S. Marine Corps (second from left) was the first Puerto Rican to achieve a general rank, is greeted by then-Colonel Chesty Puller, U.S. Marine Corps, on Pavuvu in late October 1944, while Major General Rupertus, U.S. Marine Corps, (far left) looks on. Puerto Ricans and people of Puerto Rican descent have participated as members of the United States Armed Forces in the American Civil War and in every conflict which the United States has been involved sinc...

Transport systems and services in Angola This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Transport in Angola – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Transport in Angola comprises: Roads Two trans-African automobile routes pass through Angola: the...

Selim IIISelim III ritratto da John YoungSultano dell'Impero ottomanoIn carica7 aprile 1789 –29 luglio 1807 PredecessoreAbdül Hamid I SuccessoreMustafa IV TrattamentoPadiscià Altri titoliCaliffo dell'IslamAmir al-Mu'mininCustode delle due Sacre MoscheeQaysar-ı Rum (Cesare dei Romei) NascitaIstanbul, 24 dicembre 1761 MorteIstanbul, 28 luglio 1808 (46 anni) Luogo di sepolturaMoschea di Laleli, Istanbul DinastiaOttomana PadreMustafa III MadreMihrişah Sultan ConsorteNefizar ...

Questa voce sull'argomento Stagioni delle società calcistiche italiane è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Voce principale: Associazione Sportiva Dilettantistica Gladiator 1924. Unione Sportiva GladiatorStagione 1985-1986Sport calcio Squadra Gladiator Allenatore Angelo Mammì Presidente Fernando Vollero Serie C217º posto nel girone C. Retrocessa nel Campionato Interregionale Maggiori...

Zoo in Wuppertal, Germany Wuppertal ZooZoo-Gaststättengebäude51°14′23″N 7°06′44″E / 51.23972°N 7.11222°E / 51.23972; 7.11222Date opened8 September 1881LocationWuppertal, GermanyLand area24 ha (59 acres)No. of animals5,000No. of species500Websitewww.zoo-wuppertal.de/index.php?id=73&L=2 Wuppertal Zoo (German: Zoologischer Garten Wuppertal or Zoo Wuppertal) is a 24-hectare (59-acre) zoo in Wuppertal, Germany. About 5,000 animals from around the worl...

Questa voce sull'argomento centri abitati della Bassa Sassonia è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. UetzeComune Uetze – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Germania Land Bassa Sassonia DistrettoNon presente CircondarioHannover TerritorioCoordinate52°28′N 10°12′E / 52.466667°N 10.2°E52.466667; 10.2 (Uetze)Coordinate: 52°28′N 10°12′E / 52.4666...

For the gospel album by The Blind Boys of Alabama, see Down in New Orleans. 2009 song by Dr. JohnDown in New OrleansSong by Dr. Johnfrom the album The Princess and the Frog: Original Songs and Score Released2009Recorded2008[1]GenreNew Orleans R&BLength2:25LabelWalt Disney RecordsSongwriter(s)Randy Newman Down in New Orleans is a song from Disney's 2009 animated film The Princess and the Frog, written by Randy Newman. Several versions of the song were recorded for use in different ...

This article may contain excessive or inappropriate references to self-published sources. Please help improve it by removing references to unreliable sources where they are used inappropriately. (January 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Historical Demographics Altar of Domitius Ahenobarbus Articles Demographic history Historical demography World population estimates List of Countries by Population 1700 1800 1900 This is a list of countries by population in 1800. Estimate num...

العلاقات الدنماركية الفلسطينية الدنمارك دولة فلسطين تعديل مصدري - تعديل تشير العلاقات الدنماركية الفلسطينية إلى العلاقات الحالية والتاريخية بين الدنمارك ودولة فلسطين. لدى الدنمارك مكتب تمثيلي في رام الله.[1] ولدولة فلسطين وفد عام في كوبنهاغن.[2]...

United States historic placeCalifornia Granite CompanyU.S. National Register of Historic Places Location5255 Pacific St., Rocklin, CaliforniaCoordinates38°47′21″N 121°14′08″W / 38.78917°N 121.23556°W / 38.78917; -121.23556Area7.2 acres (2.9 ha)Built1865NRHP reference No.12000375[1]Added to NRHPJuly 3, 2012 The California Granite Company, at 5255 Pacific St. in Rocklin, California, dates from 1865. It was listed on the National Registe...

Comparison of Buddhism and Gnosticism Part of a series onGnosticism Gnostic concepts Adam kasia Adam pagria Aeon Anima mundi Archon Barbelo Demiurge Five Seals Gnosis Kenoma Luminary Manda Monad Ogdoad Pleroma Sophia Uthra World of Light World of Darkness Yaldabaoth Gnostic sects and founders List of Gnostic sects Proto-Gnosticism Maghāriya Thomasines Judean / Israelite Adam Mandaeism Elksai Elkasaites Samaritan Baptist Dositheos Simon Magus (Simonians) Menander Quqites Christian Gnos...

Football tournament season 2008 Norwegian Football CupNorgesmesterskapet i fotball for herrerTournament detailsCountry NorwayTeams128 (main competition)Final positionsChampionsVålerenga (4th title)Runner-upStabækTournament statisticsMatches played127Goals scored518 (4.08 per match)Top goal scorer(s)Mohammed Abdellaoue Veigar Pall Gunnarson (7 goals each) [1]← 20072009 → Ullevaal Stadion, Oslo - venue for the Norwegian Cup final The 2008 Norw...

Kaia KanepiKaia Kanepi nel 2022Nazionalità Estonia Altezza181 cm Peso74 kg Tennis Carriera Singolare1 Vittorie/sconfitte 586 - 352 Titoli vinti 4 Miglior ranking 15º (20 agosto 2012) Ranking attuale ranking Risultati nei tornei del Grande Slam Australian Open QF (2022) Roland Garros QF (2008, 2012) Wimbledon QF (2010, 2013) US Open QF (2010, 2017) Altri tornei Giochi olimpici 3T (2008) Doppio1 Vittorie/sconfitte 47 - 69 Titoli vinti 0 Miglior ranking 106º...

Front page of the Dresden score of Wagner's 1845 opera Tannhäuser Richard Wagner's works for the stage, representing more than 50 years of creative life, comprise his 13 completed operas and a similar number of failed or abandoned projects. His first effort, begun when he was 13, was a prose drama, Leubald, but thereafter all his works were conceived as some form of musical drama. It has been suggested that Wagner's wish to add incidental music to Leubald, in the manner of Beethoven's treat...

v · m Yukon Municipalités Carmacks Cité de Dawson Faro Haines Junction Mayo Teslin Watson Lake Whitehorse Communautésnon-incorporées Beaver Creek Burwash Landing Carcross Champagne Landing Destruction Bay Ibex Valley Johnsons Crossing Keno City Marsh Lake Mount Lorne Old Crow Pelly Crossing Ross River Tagish Upper Liard Villes fantômes Canyon City Clinton Creek Elsa Forty Mile Paris Snag Régions Klondike Parcs nationaux Ivvavik Kluane Vuntut Documentation de palette[pur...





