Cyclin A
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Carl Philipp Emanuel BachNama dalam bahasa asli(de) Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach BiografiKelahiran8 Maret 1714 Weimar Kematian14 Desember 1788 (74 tahun)Hamburg Kapellmeister Data pribadiAgamaGereja Lutheran PendidikanUniversitas Leipzig Alma Mater Viadrina (en) Thomasschule zu Leipzig (en) Tangan utamaKidal KegiatanPekerjaanKomponis Periode aktif1725 –GenreBarok dan simfoni AliranMusik klasik Murid dariJohann Sebastian Bach MuridJan Ladislav Dussek (en) InstrumenOrgan ...

Robert NozickNozick pada tahun 1977Lahir(1938-11-16)16 November 1938Brooklyn, New York, U.S.Meninggal23 Januari 2002(2002-01-23) (umur 63)Cambridge, Massachusetts, U.S.PendidikanUniversitas Columbia (AB)Universitas Princeton (PhD)Universitas Oxford (Fulbright Scholar)EraFilsuf abad ke-20KawasanFilsafat BaratAliranFilsafat analitikLibertarianismePembimbing doktoralCarl Gustav HempelMinat utamaFilsafat politik, Etika, EpistemologiGagasan pentingUtility monster, experience machin...
هذه المقالة بحاجة لصندوق معلومات. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة صندوق معلومات مخصص إليها. لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع التنظيم (توضيح). التنظيم، هو فصيل مسلح تابع لحركة فتح أسسه مروان البرغوثي سنة 1995.[1][2][3] استقطب التنظيم العديد من الشباب وأصبح له عدة مكاتب ...

Sayap Lescot di Palais du Louvre Pierre Lescot (skt. 1515 – 10 September 1578) merupakan seorang arsitek Prancis yang hidup pada masa Renaisans Prancis. Karyanya yang paling terkenal termasuk Fontaine des Innocents dan Sayap Lescot di Museum Louvre, Paris. Dia memainkan peran penting dalam pengenalan elemen arsitektur klasik ke dalam arsitektur Prancis.[1] Lihat pula Arsitektur Paris Cour Carrée Arsitektur Renaisans Prancis Arsitek luar biasa lainnya dari Renaisans Prancis: Philibe...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

Katedral PalmiKatedral Santo Nikolasbahasa Italia: Concattedrale di S. NicolaKatedral PalmiLokasiPalmiNegaraItaliaDenominasiGereja Katolik RomaArsitekturStatusKatedralStatus fungsionalAktifAdministrasiKeuskupanKeuskupan Oppido Mamertina-Palmi Katedral Palmi atau Gereja Santo Nikolas (bahasa Italia: Concattedrale di Palmi, Chiesa di San Nicola) adalah sebuah gereja katedral Katolik yang terletak di Palmi di Italia, dan merupakan kon-katedral dari Keuskupan Oppido Mamertina-Palmi. Sejar...

Ukrainian Insurgent Army commander (1911–1945) In this name that follows Eastern Slavic naming customs, the patronymic is Semenovych and the family name is Klyachkivsky. Dmytro KlyachkivskyNickname(s)Klym Savur, Okhrim, BilashBorn(1911-11-04)4 November 1911Zbarazh, Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, Austria-Hungary (now Ukraine)Died12 February 1945(1945-02-12) (aged 33)Orzhiv, Ukrainian SSR, Soviet Union (now Ukraine)AllegianceUkrainian Insurgent ArmyCommands heldNorthern Operationa...

МифологияРитуально-мифологическийкомплекс Система ценностей Сакральное Миф Мономиф Теория основного мифа Ритуал Обряд Праздник Жречество Мифологическое сознание Магическое мышление Низшая мифология Модель мира Цикличность Сотворение мира Мировое яйцо Мифическое �...

Soviet politician For the Soviet epidemiologist, see Viktor Zhdanov. For the Russian footballer, see Andrei Zhdanov (footballer). In this name that follows Eastern Slavic naming customs, the patronymic is Aleksandrovich and the family name is Zhdanov. Andrei ZhdanovАндрей ЖдановZhdanov in 1945Second Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet UnionIn office21 March 1939 – 31 August 1948Preceded byLazar KaganovichSucceeded byGeorgy MalenkovHead of the Propaganda a...

David Nelson (died 20 July 1789) was gardener-botanist on the third voyage of James Cook, and botanist on HMS Bounty under William Bligh at the time of the famous mutiny. Nothing is known of his ancestry or early life. In 1776, while working as a gardener at Kew Gardens, he accepted a position as a servant to William Bayly, the official astronomer on HMS Resolution. He was promoted to able seaman; however, his real task as arranged between Joseph Banks and Cook was to collect as ma...

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁�...

Ця стаття потребує додаткових посилань на джерела для поліпшення її перевірності. Будь ласка, допоможіть удосконалити цю статтю, додавши посилання на надійні (авторитетні) джерела. Зверніться на сторінку обговорення за поясненнями та допоможіть виправити недоліки. Мат...

Jembatan Vigo di Chioggia Canal Vena Chioggia (bahasa Venesia: Cióxa) ialah sebuah kota di Region Veneto, Provinsi Venezia, Italia. Pada tahun 2006 kota ini berpenduduk 50.888 jiwa. Pertumbuhan penduduk Kota kembar Saint-Tropez, Prancis Lamia, Ellada Wikimedia Commons memiliki media mengenai Chioggia. lbsKomune di Provinsi Venezia, VenetoAnnone Veneto • Campagna Lupia • Campolongo Maggiore • Camponogara • Caorle • Cavallino-Treporti • Cavarzere • Ceggia • Chioggia • Cinto C...

Obstruction placed in tidal waters to trap fish Weir-type fish trap A fishing weir, fish weir, fishgarth[1] or kiddle[2] is an obstruction placed in tidal waters, or wholly or partially across a river, to direct the passage of, or trap fish. A weir may be used to trap marine fish in the intertidal zone as the tide recedes, fish such as salmon as they attempt to swim upstream to breed in a river, or eels as they migrate downstream. Alternatively, fish weirs can be used to chann...

French footballer (born 1995) Anthony Martial Martial playing for Manchester United in 2017Personal informationFull name Anthony Jordan Martial[1]Date of birth (1995-12-05) 5 December 1995 (age 28)[2]Place of birth Massy, FranceHeight 1.81 m (5 ft 11 in)[3]Position(s) ForwardTeam informationCurrent team Manchester UnitedNumber 9Youth career2001–2009 CO Les Ulis2009–2012 LyonSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2012–2013 Lyon B 11 (5)2013 Lyon 3 ...
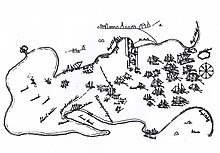
1873 Atlantic hurricane seasonSeason summary mapSeasonal boundariesFirst system formedJune 1, 1873Last system dissipatedOctober 9, 1873Strongest stormNameFive • Maximum winds115 mph (185 km/h)(1-minute sustained) • Lowest pressure959 mbar (hPa; 28.32 inHg) Seasonal statisticsTotal storms5Hurricanes3Major hurricanes(Cat. 3+)2Total fatalities252-630Total damage$4.055 million (1873 USD) Atlantic hurricane seasons1871, 1872, 1873, 1874, 1875 The 1873 Atlantic hurricane se...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2016) تأثير ميكهيف- سميرنوف- وولفنشتاين (يشار إليه أيضاً باسم تأثير المادة) وهي عملية في فيزياء الجسيمات والتي تعمل على تعديل تذبذب النيوترينو في المادة. وقد تم الع...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento centri abitati del Sudafrica non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Fish HoekcittàFish Hoek – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Sudafrica ProvinciaCapo Occidentale DistrettoCittà del Capo Municipalità localeNon presente TerritorioCoordinate34°08′09.6″S 18°25′48″E34°08′09.6″S, 18°25′48″E...

Flemish painter Triple profile portrait attributed to Lucas de Heere Lucas de Heere or Lucas d'Heere (Ghent, 1534 – possibly Paris, 29 August 1584) was a Flemish painter, watercolorist, print artist, biographer, playwright, poet and writer.[1] His costume books and portraits are a valuable resource for knowledge about 16th-century fashion. Life The principal source for the life and work of de Heere is Het Schilder-Boeck written by his pupil Karel van Mander first published in 16...

For other uses, see Choji (disambiguation). Part of a series on theHistory of Japan ListPaleolithicbefore 14,000 BCJōmon14,000 – 1000 BCYayoi 1000 BC – 300 ADKofun 300 AD – 538 ADAsuka 538 – 710Nara 710 – 794HeianFormer Nine Years' WarLater Three-Year WarGenpei War 794–1185KamakuraJōkyū WarMongol invasionsGenkō WarKenmu Restoration 1185–1333MuromachiNanboku-chō periodSengoku period 1336–1573Azuchi–Momoyama Nanban tradeImjin WarBattle of S...
