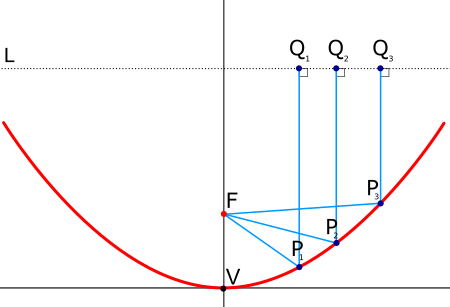
Cerebral polyopia
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Masjid HaroonมัสยิดฮารูณAgamaAfiliasiIslamLokasiLokasiJalan Charoenkrung No.25, Bangrak, BangkokNegaraThailandKoordinat13°43′32″N 100°30′52″E / 13.7255171°N 100.5145188°E / 13.7255171; 100.51451...

Kompas TV JemberPT Jember Mutiara Nunggal RestiJember, Jawa TimurIndonesiaSaluranDigital: 27 UHFSloganIndependen | TepercayaPemrogramanJaringan televisiKompas TVKepemilikanPemilikKG MediaRiwayatSiaran perdana2014Bekas tanda panggilJMTV (2014-2016)Bekas nomor kanal48 UHF (digital)54 UHF (analog)Bekas afiliasiIndependen (2014-2015)Informasi teknisOtoritas perizinanKementerian Komunikasi dan Informatika Republik IndonesiaPranalaNegaraIndonesiaKantor pusatJl. KH. Wahid Hasyim 22-C, Kepatihan, Kal...
Antena komunikasi parabola besar di Erdfunkstelle Raisting, fasilitas terbesar untuk satelit komunikasi di dunia, di Raisting, Bavaria, Jerman. Ini memiliki jaringan jenis Cassegrain. Antena parabola adalah antena yang menggunakan reflektor parabola, permukaan melengkung dengan bentuk penampang parabola, untuk mengarahkan gelombang radio. Bentuk paling umum berbentuk seperti piring dan populer disebut antena parabola atau parabola. Keuntungan utama antena parabola adalah ia memiliki directivi...

This article is about the commune in Paris. For the Nazi concentration camp, see Fort de Romainville. Commune in Île-de-France, FranceRomainvilleCommuneThe church of Saint-Germain-l'Auxerrois, designed by Alexandre-Théodore Brongniart Coat of armsParis and inner ring departmentsLocation of Romainville RomainvilleShow map of FranceRomainvilleShow map of Île-de-France (region)Coordinates: 48°53′02″N 2°26′06″E / 48.884°N 2.435°E / 48.884; 2.435CountryFrance...

1944 film Video of Private Snafu vs. Malaria Mike Private Snafu vs. Malaria Mike is an animated short film, directed by Chuck Jones and first released in March 1944. It features Private Snafu facing a malaria-transmitting mosquito.[1] Plot The film opens to a wanted poster of Malaria Mike, the mosquito, placed on a tree. The surrounding area is a swamp. Mike himself admires his image in the poster, though he is not satisfied with the depiction of his nose. A splash of water alerts Mi...

Daftar keuskupan di Venezuela adalah sebuah daftar yang memuat dan menjabarkan pembagian terhadap wilayah administratif Gereja Katolik Roma yang dipimpin oleh seorang uskup ataupun ordinaris di Venezuela. Konferensi para uskup Venezuela bergabung dalam Konferensi Waligereja Venezuela. Per Juni 2020, terdapat 41 buah yurisdiksi, di mana 9 merupakan keuskupan agung dan 26 merupakan keuskupan sufragan. Terdapat juga 2 buah eksarkat apostolik, 1 buah ordinariat militer, dan 3 vikariat apostolik. ...
Football tournamentFootball at the Goodwill GamesOrganising bodyGoodwill GamesFounded1994 (1994)Abolished1998; 26 years ago (1998)RegionInternational Football has been included at two editions of the Goodwill Games. It was first held as a men's competition in 1994,[1][2][3] and later as a women's competition in 1998.[4][5] The sport was dropped for the 2001 Goodwill Games.[6] Men's tournament Participating nations Nation ...

Buchisin geroglifici Bassorilievo raffigurante il toro Buchis. Nell'ambito della religione egizia Buchis (scritto anche Bakh e Bakha) era la manifestazione della deificazione del Ka, l'antico concetto egizio dell'Anima (potere/forza vitale) della divinità della guerra Montu[1], venerata nella regione di Ermonti. Stele egizia commemorativa concernente la morte di un Buchis, risalente al regno di Tiberio. Veniva scelto, almeno a partire dall'XI dinastia egizia, un toro selvatico bianc...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant le Luxembourg et le Concours Eurovision de la chanson. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Luxembourgau Concours Eurovision 1987 Données clés Pays Luxembourg Chanson Amour, Amour Interprète Plastic Bertrand Langue Français Sélection nationale Radiodiffuseur RTL Type de sélection Sélection interne Concours Eurovision de la chanson 1987 Position en f...

University in Sweden Luleå University of TechnologyLuleå tekniska universitetCampus Luleå on PorsönFormer nameLuleå tekniska högskolaMottoForskning och utbildning i världsklassTypePublic universityEstablished1971, 1997Endowmentkr 106,000,000PresidentBirgitta Bergvall-KårebornAcademic staff1 279 (2021)Administrative staff536 (2021)Students19,155 (2021)Undergraduates8,797 (2020)Postgraduates775 (2020)Doctoral students401 (2021)Other students289 (2020)LocationLuleå, Sweden65°37′...

The Silent SeaPoster promosiHangul고요의 바다 Genre Misteri Fiksi ilmiah Cerita seru BerdasarkanThe Sea of Tranquilityoleh Choi Hang-yongDitulis olehPark Eun-kyoSutradaraChoi Hang-yongPemeran Bae Doona Gong Yoo Lee Joon Negara asalKorea SelatanBahasa asliKoreaJmlh. musim1Jmlh. episode8ProduksiProduser eksekutifJung Woo-sungRumah produksiArtist CompanyDistributorNetflixRilis asliRilis2021 (2021) The Silent Sea (Hangul: 고요의 바다; RR: Goyo-ui bada) adalah...

This is a dynamic list and may never be able to satisfy particular standards for completeness. You can help by adding missing items with reliable sources. This is a list of feature films and pre-1910 short films produced or filmed in New Zealand, ordered by the year of release. Key * = Funded in part by the New Zealand Film Commission. † = Year given is date of principal photography rather than release. Pre 1910 Title Director(s) Genre Notes 1898 Opening of the Auckland Industrial and Mini...

Hospital in Texas, United StatesChildren's Memorial Hermann HospitalMemorial Hermann Health SystemGeographyLocation6411 Fannin Street, Houston, Texas, United StatesCoordinates29°42′50″N 95°23′43″W / 29.713855°N 95.395254°W / 29.713855; -95.395254OrganizationFundingNon-profit hospitalTypeWomen's and Children's hospitalAffiliated universityJohn P. and Kathrine G. McGovern Medical School at University of Texas Health Science CenterServicesEmergency departmentL...

1933 film by John G. Adolfi For other uses, see Working Man (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: The Working Man – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) The Working ManWindow cardDirected byJohn G. AdolfiWritten b...

1987 Indian filmGammat JammatTheatrical release posterDirected bySachin PilgaonkarWritten byVasant SabnisBased onThe Fuzzy Pink Nightgown by Norman TaurogProduced bySatish KulkarniStarringAshok SarafSachin PilgaonkarVarsha UsgaonkarCharusheela SableShrikant MogheAshalata WabgaonkarViju KhoteSatish ShahSudhir JoshiCinematographySuryakant LavandeMusic byArun PaudwalProductioncompanyShree Tulsi Productions[1]Distributed byEverest EntertainmentRelease date 1 May 1987 (1987...

Pioneer 10Sonde spatiale Pioneer H (sonde identique et jamais lancée) au National Air and Space Museum à Washington.Données générales Organisation NASA / Ames Constructeur TRW Programme Pioneer Domaine Exploration de Jupiter et du milieu interplanétaire Nombre d'exemplaires 2 Statut Mission terminée Autres noms Pioneer-F Lancement 2 mars 1972 Lanceur Atlas-Centaur (AC-27)(Atlas 3C # 5007C - Centaur D-1A) Identifiant COSPAR 1972-012A Protection planétaire Catégorie II[1] Principaux j...

تشاتيسغار الاسم الرسمي (بالهندية: छत्तीसगढ)(بالإنجليزية: Chhattisgarh) الإحداثيات 21°16′N 81°36′E / 21.27°N 81.6°E / 21.27; 81.6 [1] تاريخ التأسيس 2000 تقسيم إداري البلد الهند[2][3] التقسيم الأعلى الهند العاصمة رايبور خصائص جغرافية ...

Town in Brandenburg, Germany This article is about the town in Brandenburg. For the city in Hesse, see Frankfurt. For other uses, see Frankfurt (disambiguation). Town in Brandenburg, GermanyFrankfurt (Oder)Frankfurt an der OderFrankfort an de Oder TownClockwise from top: St Mary's Church, Church of Peace, skyline with St Mary's, Oder Tower and city hall, view of the Oder from City Bridge, St Gertrude's Church, view of the city from Słubice FlagCoat of armsLocation of Frankfurt (Oder)Frankfur...

آدم سميث جزء من سلسلة مقالات حولاقتصاد تاريخأفرع تاريخ الاقتصاد مدارس الاقتصاد اقتصاد سائد اقتصاد بدعي المنهجية الاقتصادية اقتصاد سياسي الاقتصاد الجزئي الاقتصاد الكلي اقتصاد دولي اقتصاد تطبيقي اقتصاد رياضي اقتصاد قياسي المفاهيمالنظريةالتقنيات الأنظمة الاقتصادية الن�...

يصف مصطلح صناعة اللحوم زراعة الدواجن الصناعية الحديثة من أجل الإنتاج. تغليف اللحوم وحفظها وتسويقها (على النقيض من منتجات الالبان والصوف وغيرها) وبالنسبة للإقتصاد، هو مزيج من النشاط الاساسى (الزراعة) والثانوى (الصناعة) ويصعب وصفه بدقة بطريقة واحدة فقط. الجزء الأكبر من صناع�...