Caid (sport)
|
Read other articles:

Massacre of Tutsi civilians at the beginning of the Rwandan Genocide Human skulls at the Nyamata Genocide Memorial CentrePart of a series on theRwandan genocide Background History of Rwanda Origins of Hutu, Tutsi and Twa Kingdom of Rwanda Rwandan Revolution Rwandan Civil War Hutu Power Assassination ofHabyarimana and Ntaryamira Events Initial events Chronology Gikondo massacre Musha Church massacre Nyarubuye massacre Parties responsible People indicted by theInternational Criminal Tribunal Ge...

Glufosinat Nama Nama IUPAC (RS)-2-Amino-4-(hydroxy-methyl-phosphoryl)butanoic acid Nama lain Phosphinothricin Penanda Nomor CAS 51276-47-2 N Model 3D (JSmol) Gambar interaktif 3DMet {{{3DMet}}} Nomor EC PubChem CID 4794 Nomor RTECS {{{value}}} CompTox Dashboard (EPA) DTXSID0043973 SMILES CP(=O)(CCC(C(=O)O)N)O Sifat Rumus kimia C5H12NO4P Massa molar 181.127 Kecuali dinyatakan lain, data di atas berlaku pada suhu dan tekanan standar (25 °C [77 °F], 100 ...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Alishan Forest RailwayIkhtisarLokasiKabupaten Chiayi, TaiwanKoordinat23°30′36″N 120°48′15″E / 23.510092°N 120.804239°E / 23.510092; 120.804239Koordinat: 23°30′36″N 120°48′15″E / 23.510092°N...

Asmaji DarmawiLahir16 September 1944 (umur 79)Haruyan, Hulu Sungai Tengah, Kalimantan SelatanKebangsaanIndonesiaPekerjaanPengajarDikenal atasGuru Besar Universitas Lambung Mangkurat Prof. DR. H. Asmaji Darmawi (lahir 16 September 1944) adalah seorang pakar di bidang manajemen pemerintahan dan pengajar Indonesia. Ia merupakan guru besar FISIP Universitas Lambung Mangkurat. Pendidikan Sarjana Ilmu Sosial Politik UGM (1971) Magister Manajemen STIE Jakarta (1996) Doktor Ilmu Administrasi Un...

دوق سودرمانلاند الأمير ألكسندر (بالسويدية: Prins Alexander, hertig av Södermanland) دوق سودرمانلاند معلومات شخصية الاسم الكامل ألكسندر إريك هوبرتوس برتيل الميلاد 19 أبريل 2016 (العمر 7 سنوات)ستوكهولم، السويد المعمودية 9 سبتمبر 2017 مواطنة السويد لون الشعر شعر أشقر الأب كارل ف�...

Trichlorure de phosphoryle Molécule de trichlorure de phosphoryle Identification Nom UICPA Trichlorure de phosphoryle Synonymes Oxychlorure de phosphore No CAS 10025-87-3 No ECHA 100.030.030 No CE 233-046-7 No RTECS TH4897000 PubChem 24813 ChEBI 30336 SMILES O=P(Cl)(Cl)Cl PubChem, vue 3D InChI Std. InChI : vue 3D InChI=1S/Cl3OP/c1-5(2,3)4 Std. InChIKey : XHXFXVLFKHQFAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Apparence liquide incolore, fumant, d'odeur acre[1]. Propriétés chimiques Formule Cl3OPPOCl3 M...

Part of a series onBritish law Acts of Parliament of the United Kingdom Year 1801 1802 1803 1804 1805 1806 1807 1808 1809 1810 1811 1812 1813 1814 1815 1816 1817 1818 1819 1820 1821 1822 1823 1824 1825 1826 1827 1828 1829 1830 1831 1832 1833 1834 1835 1836 1837 1838 1839 1840 1841 1842 1843 1844 1845 1846 1847 1848 1849 1850 1851 1852 1853 1854 1855 1856 1857 1858 1859 1860 1861 1862 1863 1864 1865 1866 1867 1868 1869 1870 1871 1872 1873 1874 1875 1876 1877 1878 ...
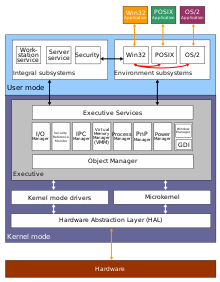
Hardware Abstraction Layer redirects here. For the UNIX-like operating system subsystem, see HAL (software). Sets of routines in software Hardware abstractions are sets of routines in software that provide programs with access to hardware resources through programming interfaces. The programming interface allows all devices in a particular class C of hardware devices to be accessed through identical interfaces even though C may contain different subclasses of devices that each provide a diffe...

Bagian dari seriPendidikan di Indonesia Kementerian Pendidikan, Kebudayaan, Riset, dan Teknologi Republik Indonesia Pendidikan anak usia dini TK RA KB Pendidikan dasar (kelas 1–6) SD MI Paket A Pendidikan dasar (kelas 7–9) SMP MTs Paket B Pendidikan menengah (kelas 10–12) SMA MA SMK MAK SMA SMTK SMAK Utama Widya Pasraman Paket C Pendidikan tinggi Perguruan tinggi Akademi Akademi komunitas Institut Politeknik Sekolah tinggi Universitas Lain-lain Madrasah Pesantren Sekolah alam Sekolah ru...

Johnstown RiverhawksEstablished 1999Folded 2008Played in Johnstown, Pennsylvaniaat the Cambria County War Memorial Arena League/conference affiliations Indoor Football League (1999–2000) Indoor Professional Football League (2001) National Indoor Football League (2002–2004) Atlantic Indoor Football League (2005–2006) American Indoor Football (2007–2008) Current uniformTeam colorsBlue, black, silver, white PersonnelOwner(s)James Wallace and Mike...

2010 Japanese science fiction novel by Tomihiko Morimi Penguin HighwayThe cover of the novel, as published by Kadokawa Shoten in 2010ペンギン・ハイウェイ(Pengin Haiwei)GenreComing-of-age[1]Science fiction[1] NovelWritten byTomihiko MorimiPublished byKadokawa ShotenEnglish publisherNA: Yen PressPublishedMay 28, 2010 MangaWritten byKeito YanoPublished byMedia FactoryEnglish publisherNA: Yen PressMagazineMonthly Comic AliveDemographicSeinenOriginal r...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Ini bibliografi karya penulis novel dan esai, Virginia Woolf. Novel The Voyage Out (1915) Night and Day (1919) Jacob's Room (1922) Mrs Dalloway (1925) To the Lighthouse (1927) Orlando: A Biography (1928) The Waves (1931) The Years (1937) Between the Ac...

One of the largest coastal dune systems in California Guadalupe-Nipomo Dunes National Wildlife RefugeIUCN category IV (habitat/species management area)Guadalupe-Nipomo Dunes.Map of the United StatesLocationSan Luis Obispo County, Santa Barbara County, California, United StatesNearest cityGuadalupe, CaliforniaCoordinates35°00′13″N 120°36′51″W / 35.0035°N 120.6143°W / 35.0035; -120.6143[1]Area2,553 acres (10.33 km2)Established2000Governing&#...

Artikel ini adalah bagian dari seriPembagian administratifIndonesia Tingkat I Provinsi Daerah istimewa Daerah khusus Tingkat II Kabupaten Kota Kabupaten administrasi Kota administrasi Tingkat III Kecamatan Distrik Kapanewon Kemantren Tingkat IV Kelurahan Desa Dusun (Bungo) Finua Gampong Kute Kalurahan Kampung Kalimantan Timur Lampung Papua Riau Lembang Nagari Nagori Negeri Maluku Maluku Tengah Negeri administratif Ohoi Pekon Tiyuh Lain-lain Antara III dan IV Mukim Di bawah IV Banjar Bori Pedu...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

土库曼斯坦总统土库曼斯坦国徽土库曼斯坦总统旗現任谢尔达尔·别尔德穆哈梅多夫自2022年3月19日官邸阿什哈巴德总统府(Oguzkhan Presidential Palace)機關所在地阿什哈巴德任命者直接选举任期7年,可连选连任首任萨帕尔穆拉特·尼亚佐夫设立1991年10月27日 土库曼斯坦土库曼斯坦政府与政治 国家政府 土库曼斯坦宪法 国旗 国徽 国歌 立法機關(英语:National Council of Turkmenistan) ...

Luchuan-Pingmian campaignsMap of the overview of Luchuan-Pingmian campaigns that contains the Ming attack routes in the year of 1441,1444 and 1449 battles that under Wang Ji's command.Date1436–49LocationModern-day Burma and Yunnan, ChinaResult Ming victoryBelligerents Ming dynasty Möng MaoCommanders and leaders Wang JiFang Zheng Si RenfaSi JifaStrength 295,000 ?Casualties and losses ? 55,000+ vteMing conquest of Yunnan 1st Mong Mao War Dao Ganmeng rebellion 2nd Mong Mao War The Luchuan–P...

American racing driver (born 1985) NASCAR driver Kyle BuschBusch at Las Vegas Motor Speedway in 2024BornKyle Thomas Busch (1985-05-02) May 2, 1985 (age 39)Las Vegas, Nevada, U.S.Height6 ft 1 in (185 cm)Weight185 lb (84 kg)Achievements2015, 2019 NASCAR Cup Series Champion2018, 2019 NASCAR Cup Series Regular Season Champion2009 Xfinity Series Champion2008 Southern 500 Winner2015, 2016 Brickyard 400 Winner2018 Coca-Cola 600 Winner2017 Monster Energy NASCAR All-Star ...

Türkvizyonsongfestival 2014 Gastland Tatarije Locatie TatNeft Arena, Kazan, Tatarije Omroep MTV Halve finale 19 november 2014 Finale 21 november 2014 Presentatoren Artjom SjalimovNarmin AgajevaRanil Noeriev Winnaar Land Kazachstan Lied Izin körem Artiest Janar Duğalova Andere gegevens Stemgegevens Een jurylid per deelnemend land/gebied geeft elk lied een score van 1-10 punten. Aantal landen 26 (15 in finale) Debuterend Albanië Bulgarije Duitsland Iran Moskou Turkmenistan Terugtrekkend Al...

تقويم رومانيمعلومات عامةالبلد روما القديمة حل محله تقويم يولياني تاريخ البدء 753 ق.م تاريخ الانتهاء 31 ديسمبر 46 ق.م تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات استنساخ من Fasti Antiates Maiores مجزأة Fasti Antiates Maiores (ق. 60 ق.م)، مع استمرار الشهرين السابع والثامن في التسمية كنتيليس (QVI) و سكستيليس&#...
