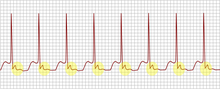
AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Fernando Tissone Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Fernando Damián TissoneTanggal lahir 24 Juli 1986Tempat lahir Quilmes, ArgentinaPosisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini MálagaNomor 12Karier junior Quilmes1997–1999 Independiente1999–2001 LanúsKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2005–2006 Udinese 26 (0)2006–2008 Atalanta 68 (6)2008–2009 Udinese 5 (0)2009–2013 Sampdoria 63 (1)2011–2012 → Mallorca (pinjaman) 27 (0)2013 → Mallorca (pinjaman) 15 (0)2013– Málaga 26...
Daftar keuskupan di Libya adalah sebuah daftar yang memuat dan menjabarkan pembagian terhadap wilayah administratif Gereja Katolik Roma yang dipimpin oleh seorang uskup ataupun ordinaris di Libya. Konferensi para uskup Libya bergabung dalam Konferensi Waligereja Libya. Saat ini terdapat 4 buah yurisdiksi, di mana 3 merupakan vikariat apostolik dan 1 lainnya merupakan prefektur apostolik. Daftar keuskupan Yurisdiksi Tahta Suci Vikariat Apostolik Benghazi: lowong, diisi oleh Administrator Apost...
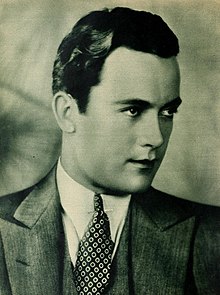
Artikel ini bukan mengenai Charles R. Rogers. Charles "Buddy" RogersRogers pada 1929LahirCharles Edward Rogers(1904-08-13)13 Agustus 1904Olathe, Kansas, Amerika SerikatMeninggal21 April 1999(1999-04-21) (umur 94)Rancho Mirage, California, Amerika SerikatPekerjaanPemeran, musisiTahun aktif1926–1968Suami/istriMary Pickford (m. 1937; kematian Pickford 1979) Beverly Ricondo (m. 1981) Charles Edw...

KemiriKecamatanPeta lokasi Kecamatan KemiriNegara IndonesiaProvinsiBantenKabupatenTangerangPemerintahan • CamatHendarto, S.STP., M.Si.Populasi • Total46,326 jiwaKode Kemendagri36.03.09 Kode BPS3603161 Desa/kelurahan7 desaSitus webhttps://www.tangerangkab.go.id/kemiri Kemiri adalah sebuah kecamatan di Kabupaten Tangerang, Provinsi Banten, Indonesia. Kecamatan Kemiri berdiri pada tanggal 17 Januari 2001, yang merupakan wilayah hasil pemekaran dari Kecamatan Mauk. Se...
Private liberal arts college in California This article contains academic boosterism which primarily serves to praise or promote the subject and may be a sign of a conflict of interest. Please improve this article by removing peacock terms, weasel words, and other promotional material. (March 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this template message)This article contains paid contributions. It may require cleanup to comply with Wikipedia's content policies, particularly neutral point of view....

Terrorism-related operation in Australia This article is part of a series aboutGough Whitlam Early life World War II service Member for Werriwa (1952–1978) Deputy Labor leadership Labor Party spills 1967 1968 1976 May 1977 Prime Minister of Australia Term of government (1972–1975) Vietnam War withdrawal National Sewerage Program Medibank Advance Australia Fair 1973 Murphy raids 1973 referendum Gair Affair 1974 referendum Loans affair Papua independence Family Law reform Racial Discriminat...

Village in Estonia This article is about the Estonian village. For the soup, see Abula (soup). For the Latin name of the town in Iberia, see Ávila, Spain. For the former municipality and former bishopric in Spain, see Abla. Village in Saare County, EstoniaAbulaVillageCountry EstoniaCountySaare CountyParishSaaremaa ParishTime zoneUTC+2 (EET) • Summer (DST)UTC+3 (EEST) Abula is a village in Saaremaa Parish, Saare County in western Estonia.[1][2] Before the admi...

將軍巴育·占奥差ประยุทธ์ จันทร์โอชา上將 MPCh MWM TChW 泰國樞密院議員现任就任日期2023年11月29日君主拉瑪十世議長素拉育·朱拉暖 泰國第29任總理任期2022年9月30日復職—2023年8月22日君主拉瑪十世副總理(英语:Deputy Minister of Thailand) 列表 巴威·翁素万塔那塞·巴滴玛巴功(英语:Thanasak Patimaprakorn) 威沙努·革岸(英语:Wissanu Krea-ngam) 比蒂耶�...

此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2021年7月4日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:美国众议院 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 美國眾議院 United States House of Representatives第118届美国国会众议院徽章 众议院旗...
本表是動態列表,或許永遠不會完結。歡迎您參考可靠來源來查漏補缺。 潛伏於中華民國國軍中的中共間諜列表收錄根據公開資料來源,曾潛伏於中華民國國軍、被中國共產黨聲稱或承認,或者遭中華民國政府調查審判,為中華人民共和國和中國人民解放軍進行間諜行為的人物。以下列表以現今可查知時間為準,正確的間諜活動或洩漏機密時間可能早於或晚於以下所歸�...

2020 album LikewiseStudio album by Frances QuinlanReleasedJanuary 31, 2020 (2020-01-31)StudioHeadroom (Philadelphia)GenreIndie rock[1]LabelSaddle CreekProducerJoe Reinhart, Frances QuinlanSingles from Likewise Rare ThingReleased: October 22, 2019 Now That I'm BackReleased: November 19, 2019 Your ReplyReleased: 2020 Likewise is the debut studio album by Frances Quinlan of Hop Along. It was released on January 31, 2020, by Saddle Creek Records. Production Quinlan in 2...

This article needs to be updated. Please help update this to reflect recent events or newly available information. (December 2020)This article is missing information about transfers. Please expand the article to include this information. Further details may exist on the talk page. (December 2020) 2012–13 CA Osasuna SeasonOsasuna 2012–13 football seasonOsasuna2012–13 seasonPresidentMiguel ArchancoHead coachJosé Luis MendilibarStadiumEl SadarLa Liga16thCopa del ReyRound of 16 Home colou...

مراكز السيطرة على الأمراض والوقاية منها (بالإنجليزية: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)[1][2] مراكز السيطرة على الأمراض والوقاية منها تفاصيل الوكالة الحكومية البلد الولايات المتحدة تأسست 1 يوليو 1946؛ منذ 77 سنة (1946-07-01) المركز أتلانتا، جورجيا، الولايا�...

Компенсационный температурный шов в автодорожном мосту, используется для предотвращения повреждения дорожного полотна от теплового расширения Теплово́е расшире́ние (также используется термин «термическое расширение») — изменение линейных размеров и формы твёрдо...

Genus of birds AptenodytesTemporal range: Pliocene to recent[1] Emperor penguins swimming Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Aves Order: Sphenisciformes Family: Spheniscidae Genus: AptenodytesMiller, JF, 1778 Type species Aptenodytes patagonicus Aptenodytes p. patagonicus Aptenodytes patagonicus halli Aptenodytes forsteri Aptenodytes ridgeni (fossil) breeding grounds The genus Aptenodytes contains tw...

Audience NetworkDiluncurkan25 November 1999 (1999-11-25)PemilikDirecTVFormat gambar720p HDTV(downscaled to letterboxed 480i for the SDTV feed)NegaraAmerika SerikatBahasaInggrisKantor pusatEl Segundo, CaliforniaNama sebelumnyaFreeview (1999–2005)The 101 Network (2005–11)Audience Network (2011–16) Audience Network (lebih dikenal sebagai Audience dari 2016 hingga 2020)[1] adalah saluran televisi berbayar Amerika yang dimiliki oleh AT&T. Ini menampilkan campuran serial asli...

Elevated dual carriageway section of A40 road in West London For other uses of Westway, see Westway (disambiguation). The Westway looking east. On the horizon is Trellick Tower. The Westway is a 2.5-mile (4 km) elevated dual carriageway section of the A40 trunk road in West London running from Paddington in the east to North Kensington in the west. It connects the London Inner Ring Road to the West London suburbs. The road was constructed between 1962 and 1970 to connect the proposed Lon...

1990 studio album by Toshiko AkiyoshiRemembering Bud: Cleopatra's DreamStudio album by Toshiko AkiyoshiReleased1990Recorded31 July and 1 August 1990StudioVan Gelder Studio, Englewood Cliffs, NJGenreJazzLength56:34LabelNippon Crown / EvidenceToshiko Akiyoshi chronology Four Seasons(1990) Remembering Bud: Cleopatra's Dream(1990) Chic Lady(1991) Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRatingAllmusic linkThe Penguin Guide to Jazz Recordings [1] Remembering Bud: Cleopatra's Dream is...

Interessengemeinschaft Bauernhaus e.V. (IGB) Rechtsform gemeinnütziger eingetragener Verein Gründung 1973 in Kirchseelte Gründer Julius H. W. Kraft Sitz Syke Schwerpunkt Erhaltung historischer Baukultur auf dem Land Vorsitz Hajo Maiborg Geschäftsführung Julia Ricker Mitglieder 6.000 (2020) Website igbauernhaus.de Kennzeichnung der Interessengemeinschaft Bauernhaus Die Interessengemeinschaft Bauernhaus e.V. (IgB) mit Sitz in Syke ist die einzige deutschlandweit tätige Vereinigung f...

Silvia SalisSilvia Salis nel 2009Nazionalità Italia Altezza179 cm Peso74 kg Atletica leggera SpecialitàLancio del martello Record Martello 71,93 m (2011) CarrieraSocietà 1993-2000 Atletica Albaro '822001-2006 CUS Genova2005-2010 Forestale2010- CUS Genova2011-2016 Fiamme Azzurre Nazionale 2006-2015 Italia20 Palmarès Competizione Ori Argenti Bronzi Giochi del Mediterraneo 1 0 1 Vedi maggiori dettagliStatistiche aggiornate al 26 giugno 2013 Modifica dati su Wikidata �...