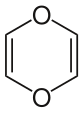
類戴奧辛物質
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. Ini adalah nama Tionghoa; marganya adalah Hu. Hu Zhengyan Hu Zhengyan Hanzi tradisional: 胡正言 Alih aksara Mandarin - Hanyu Pinyin: Hú Zhèngyán - Wade-Giles: Hu Cheng-yen Yuecong Hanzi tradisional: 曰從 Hanzi sederhana: 曰从 Alih aksara Mand...

Kesenian Kethek Ogleng mengenakan kostum Hanuman Kethek Ogleng adalah kesenian tradisional yang berasal dari Sampung, Ponorogo yang kemudian menyebar ke Pacitan dan Wonogiri. Dalam pertunjukan tari yang para pemainnya menirukan gerakan-gerakan monyet hutan Sampung. Tarian tersebut diiringi dengan gamelan atau gending gancaran pancer yang bunyinya kurang-lebih, “ogleng, ogleng, ogleng.” [1] Dari sanalah kemudian seni pertunjukan ini disebut kethek ogleng. Gerakan-gerakan tarian ket...

This article is about the volcano. For other uses, see Sakurajima (disambiguation). Stratovolcano in Kagoshima Prefecture, Kyushu, Japan SakurajimaView of Sakurajima from mainland Kagoshima, 2009Highest pointElevation1,117 m (3,665 ft)Coordinates31°34′50″N 130°39′29″E / 31.58056°N 130.65806°E / 31.58056; 130.65806GeographySakurajimaKagoshima Prefecture, JapanShow map of JapanSakurajimaSakurajima (Kagoshima Prefecture)Show map of Kagoshima Pre...

هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (مارس 2018) مقاطعة نيوبرارا الإحداثيات 43°03′N 104°28′W / 43.05°N 104.47°W / 43.05; -104...

Place in Mid Jutland, DenmarkRøndeLooking down Rønde's main streetRøndeShow map of DenmarkRøndeShow map of Denmark Central Denmark RegionCoordinates: 56°18′02″N 10°28′40″E / 56.30056°N 10.47778°E / 56.30056; 10.47778CountryDenmarkRegionMid Jutland (Midjylland)MunicipalitySyddjursArea • Urban2.3 km2 (0.9 sq mi)Elevation5 - 100 m (−323 ft)Population (2023) • Urban3,295 • Urban densi...

This article is about the archaeological site. For other uses, see Xelha (disambiguation). Xel-HáRuins at Xel-HáLocationQuintana Roo, MexicoRegionYucatán PeninsulaCoordinates20°19′11″N 87°22′01″W / 20.31972°N 87.36694°W / 20.31972; -87.36694TypesettlementHistoryMateriallimestone, stuccoFoundedpre 1st centuryAbandoned19th centuryCulturesMayan Xelha (Spanish pronunciation: [ʃelˈxa], Spanish: Xelhá; Yucatec Maya: Xel-Há) is an archaeological sit...

Artikel ini perlu dikembangkan agar dapat memenuhi kriteria sebagai entri Wikipedia.Bantulah untuk mengembangkan artikel ini. Jika tidak dikembangkan, artikel ini akan dihapus. Plat Liga Nasional Wanita FAMulai digelar2014Wilayah InggrisJumlah tim36 Plat Liga Nasional Wanita FA (Inggris: FA Women's National League Plate) adalah turnamen sepak bola wanita yang diatur oleh Liga Nasional Wanita. Turnamen ini adalah kompetisi piala liga yang berjalan berdampingan dengan Piala Liga Nasion...

Fictional character created by Al Franken Stuart Smalley Stuart Smalley is a fictional character created and performed by comedian and satirist Al Franken. The character originated on the television show Saturday Night Live, in a mock self-help show called Daily Affirmations With Stuart Smalley. It first aired on the show's February 9, 1991 episode hosted by Kevin Bacon. Stuart is Franken's middle name.[1] Franken has stated that his going to Al-Anon meetings inspired [the character] ...

Mid-sized bilingual university in Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada Laurentian University of SudburyOther nameLU, LULMottoEmitte lucem et veritatemMotto in EnglishSend forth thy light and thy truthTypePublicEstablishedMarch 28, 1960Academic affiliationsACUFC, COU, CVU, Universities CanadaEndowmentCA$52.8 millionChancellorVacantPresidentLynn WellsAddress935 Ramsey Lake RoadSudbury, OntarioP3E 2C646°27′57.75″N 80°58′13.77″W / 46.4660417°N 80.9704917°W / ...

Italian duchy (554 – ca. 752) Duchy of PerugiaDucatus PerusianusDuchy of the Byzantine Empire554 – ca. 752Map of the Exarchate and the Lombard territories around the mid-7th century.CapitalPerugiaHistorical eraMiddle Ages• Establishment under the authority of the Praetorian Prefect of Italy 554• Part of the Exarchate of Ravenna 584• De facto control by the Papacy ca. 752 Today part ofItaly The Duchy of Perugia was a duchy (Latin: ducatus) in the Italian part of the By...

Social media conglamerate The Meet Group, Inc.Type of businessPublicType of siteSocial networking serviceAvailable inEnglish, Portuguese, Spanish, French, Italian, German, Chinese, Russian, Japanese, Korean, Dutch, Turkish, Malay, Indonesian.Traded asNasdaq: MEET (2014–2020)FoundedApril 2005; 19 years ago (2005-04) (as MyYearbook)HeadquartersNew Hope, Pennsylvania, U.S.OwnerProSiebenSat.1 MediaFounder(s)Geoff CookDavid CookCatherine CookParentParshipMee...

Clarins Open 1992 Sport Tennis Data 14 settembre – 20 settembre Edizione 6ª Superficie Terra rossa Campioni Singolare Sandra Cecchini Doppio Sandra Cecchini / Patricia Tarabini 1991 2022 Il Clarins Open 1992 è stato un torneo di tennis giocato sulla terra rossa. È stata la 6ª edizione del torneo, che fa parte della categoria Tier IV nell'ambito del WTA Tour 1992. Si è giocato a Parigi in Francia, dal 14 al 20 settembre 1992. Indice 1 Campionesse 1.1 Singolare 1.2 Doppio 2 Collegamenti...

2017 American television series This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article may need to be rewritten to comply with Wikipedia's quality standards. You can help. The talk page may contain suggestions. (September 2023) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be...

إدموند ألنبي (بالإنجليزية: Edmund Allenby, 1. Viscount Allenby) مناصب معلومات شخصية الميلاد 23 أبريل 1861نوتنغهامشير، إنجلترا الوفاة 14 مايو 1936لندن سبب الوفاة نزف مخي مكان الدفن دير وستمنستر[1] الجنسية بريطاني الحياة العملية المدرسة الأم هيليبيري وامبريال سيرفيس كوليج[1]ا...

Constituency of Bangladesh's Jatiya Sangsad Gazipur-5Constituencyfor the Jatiya SangsadDistrictGazipur DistrictDivisionDhaka DivisionElectorate302,555 (2018)[1]Current constituencyCreated2008PartyIndependentMember(s)Akhtaruzzaman Gazipur-5 is a constituency represented in the Jatiya Sangsad (National Parliament) of Bangladesh since 2008 by Meher Afroz Chumki of the Awami League. Boundaries The constituency encompasses Kaliganj Upazila, Gazipur City Corporation wards 40 through 42, and...

American actor Mark Linn-BakerLinn-Baker at the 39th Primetime Emmy Awards buffet in 1987BornMark Linn Baker (1954-06-17) June 17, 1954 (age 69)St. Louis, Missouri, U.S.EducationYale University (BA, MFA)Occupation(s)Actor, directorYears active1979–presentSpouses Adrianne Lobel (m. 1995; div. 2009) Christa Justus (m. 2012)[1] Children1 Mark Linn-Baker (born Mark Linn Baker; June 17, 1954) is ...

City in Iowa, United StatesMaquoketa, IowaCityMaquoketa Middle SchoolNickname: Timber CityMotto: One of a KindLocation of Maquoketa, IowaCoordinates: 42°4′1″N 90°39′58″W / 42.06694°N 90.66611°W / 42.06694; -90.66611Country United StatesState IowaCountiesJackson[1]IncorporatedJanuary 27, 1857[2]Government • MayorTom MesserliArea[3] • Total4.54 sq mi (11.76 km2) • ...

Sporting event delegationCyprus at the2002 Winter OlympicsIOC codeCYPNOCCyprus Olympic CommitteeWebsitewww.olympic.org.cy (in Greek and English)in Salt Lake CityCompetitors1 in 1 sportFlag bearer Theodoros ChristodoulouMedals Gold 0 Silver 0 Bronze 0 Total 0 Winter Olympics appearances (overview)198019841988199219941998200220062010201420182022 Cyprus sent a delegation to compete at the 2002 Winter Olympics in Salt Lake City, United States from 8–24 February 2002. This was Cyprus'...

Copyright license for free use of a work This article is about the Creative Commons licenses. For the organization that produced them, see Creative Commons. Creative Commons logo A video explaining how Creative Commons licenses can be used in conjunction with commercial licensing arrangements A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted work.[a] A CC license is used when an author wants to giv...

2014 battle in the war in Donbas For other uses, see Battle of Mariupol. This article needs to be updated. The reason given is: add in brief info about 2022 siege of Mariupol and connections between the two that were made. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (November 2023) Battle of MariupolPart of the war in DonbasDamage in MariupolDate6 May – 14 June 2014(1 month, 1 week and 1 day)LocationMariupol, Donetsk Oblast, Ukrain...