Wabar craters
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Papan tombol Colemak (AS) Colemak adalah tata letak papan tombol untuk huruf Latin, dibuat oleh dan dinamai Shai Coleman pada tahun 2006. Tata letak dirancang untuk membuat mengetik lebih efisien dan nyaman dengan menempatkan huruf paling sering di bar...

Nestor Lakoba Ketua Dewan Komisar Rakyat Republik Sosialis Soviet Otonom Abkhazia ke-1Masa jabatanFebruari 1922 – 28 Desember 1936 PendahuluJabatan dibentukPenggantiAvksenty RapavaKetua Komite Eksekutif Pusat Republik Sosialis Soviet Otonom AbkhaziaMasa jabatan17 April 1930 – 28 Desember 1936 PendahuluJabatan dibentukPenggantiAlexei Agrba Informasi pribadiLahir(1893-05-01)1 Mei 1893Lykhny, Okrug Sukhum, Kegubernuran Kutais, Kekaisaran RusiaMeninggal28 Desember 1936(1936-...

Untuk musisi, lihat Frankie Lee (musisi). Untuk penulis lagu, lihat Frankie Lee (musisi Americana). Frankie LeeLee pada 1923Lahir(1911-12-31)31 Desember 1911Gunnison, Colorado, Amerika SerikatMeninggal29 Juli 1970(1970-07-29) (umur 58)Los Angeles, California, Amerika SerikatSebab meninggalLuka tembakPekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif1916–1925 Frankie Lee (31 Desember 1911 – 29 Juli 1970), adalah seorang pemeran cilik Amerika Serikat. Ia tampil dalam 56 film antara 19...

Gudeg Yu DjumGudeg Yu Djum PusatInformasi umumLokasi Sleman, Yogyakarta, IndonesiaAlamatJalan Kaliurang km 4.5 Karangasem CT III/22, Sleman, Yogyakarta (Pusat)PemilikDjuwariah Gudeg Yu Djum merupakan salah satu rumah makan di Yogyakarta yang khusus menjual gudeg. Perintis rumah makan ini adalah ibu Djuwariah yang biasa dipanggil Yu Djum.[1][2] Gudeg yang dijual dapat dikemas dalam kotak, besek, atau kendil yang dapat bertahan hingga dua hari dengan cara pengukusan. Bu Djuwaria...

American animation studio owned by Warner Bros. This article is about the studio founded in 1980. For its predecessor, see Warner Bros. Cartoons. For the feature theatrical film animation division of Warner Bros. since 2013, see Warner Bros. Pictures Animation. Warner Bros. Animation Inc.Logo used since 2010FormerlyWarner Bros. Television Animation (1995–2003)Company typeDivisionIndustryFilmTelevisionAnimationPredecessorsWarner Bros. Cartoons (1933–1969)Hanna-Barbera (1957–2001)FoundedM...

Video game company Xplosiv redirects here. For the album by La Mafia, see Xplosiv (La Mafia album). Not to be confused with Empire Online. Empire InteractiveCompany typeSubsidiaryIndustryVideo gamesFounded1987; 37 years ago (1987)FoundersIan HigginsSimon JeffreyDefunct1 May 2009 (2009-05-01)FateAdministrationHeadquartersLondon, EnglandArea servedEuropeKey peopleIan Higgins (CEO; 1987–2008)Number of employees55 (2009)ParentSilverstar Holdings (2006–200...

السلطنة الكثيرية الدولة الكثيرية -- – 1400 عاصمة سيئون نظام الحكم غير محدّد اللغة العربية التاريخ التأسيس -- الزوال 1400 تعديل مصدري - تعديل خريطة ووثيقة بريطانية توضح قبائل وسلاطين محمية عدن الشرقية ما بين (1886 إلى 1959). سلطنة سيئون أنشئت بمدينة سيئون على قبيلة أل كثير ه�...

1989 video gameIt Came from the DesertAmiga/DOS cover artDeveloper(s)CinemawarePublisher(s)CinemawareProducer(s)Pat CookDesigner(s)David RiordanProgrammer(s)Randy PlattArtist(s)Jeffrey HilbersJeff GodfreyWriter(s)Kenneth MelvilleComposer(s)Greg HaggardJim SimmonsPlatform(s)Amiga, DOS, TurboGrafx-16Release1989 (Amiga)1990 (DOS)1991 (T16)Genre(s)Action-adventureMode(s)Single-player It Came from the Desert is a 1989 action-adventure game by Cinemaware. It was originally released for the Amiga, ...

1958 film The Notorious Mr. MonksDirected byJoseph KaneWritten byPaul FixRichard C. SarafianProduced byRudy RalstonStarringVera RalstonDon KellyPaul FixCinematographyJack A. MartaEdited byFrederic KnudtsonMusic byJerry RobertsProductioncompanyVentura Pictures CorporationDistributed byRepublic PicturesRelease date February 28, 1958 (1958-02-28) Running time70 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglish The Notorious Mr. Monks is a 1958 American drama film directed by Joseph Kane ...

Traditional Japanese art of paper folding For other uses, see Origami (disambiguation). Paper folding redirects here. For other uses, see Paper folding (disambiguation). Origami cranes The folding of an Origami crane A group of Japanese schoolchildren dedicate their contribution of Thousand origami cranes at the Sadako Sasaki memorial in Hiroshima. Origami (折り紙, Japanese pronunciation: [oɾiɡami] or [oɾiꜜɡami], from ori meaning folding, and kami meaning paper (kami ...

Japanese high speed train type N700S seriesJR Central N700S series set J30 on the San'yō Shinkansen in September 2022In service1 July 2020; 3 years ago (2020-07-01) – presentManufacturerHitachi, Nippon SharyoDesignerEiji Mitooka (N700S-8000 series)Family nameShinkansenReplaced700 series, N700 seriesConstructed2017–presentNumber under constructionJR Central: 19 sets (304 vehicles)Number in service696 vehicles (46 sets) (as of 1 April 2022[update])Fo...

Airport in Highland County, Florida Avon Park Executive Airport2006 USGS airphotoIATA: AVOICAO: KAVOFAA LID: AVOSummaryAirport typePublicOwnerCity of Avon ParkServesAvon Park, FloridaElevation AMSL160 ft / 49 mCoordinates27°35′29″N 81°31′44″W / 27.59139°N 81.52889°W / 27.59139; -81.52889Websitewww.avonpark.city/..MapAVOLocation of airport in FloridaShow map of FloridaAVOAVO (the United States)Show map of the United StatesRunways Direction Len...

هذه مقالة غير مراجعة. ينبغي أن يزال هذا القالب بعد أن يراجعها محرر؛ إذا لزم الأمر فيجب أن توسم المقالة بقوالب الصيانة المناسبة. يمكن أيضاً تقديم طلب لمراجعة المقالة في الصفحة المخصصة لذلك. (نوفمبر 2020) رقصة سيف الباسك Mer Dandiya، رقصة سيف تؤديها مجتمعات سوراشترا رقصات السيف هي رق...

Municipal arrondissement in Île-de-France, France10th arrondissement of ParisMunicipal arrondissementThe local town hall, on the Rue du Faubourg Saint-Martin Coat of armsLocation within ParisCoordinates: 48°52′32″N 2°21′28″E / 48.87556°N 2.35778°E / 48.87556; 2.35778CountryFranceRegionÎle-de-FranceDepartmentParisCommuneParisGovernment • Mayor (2020–2026) Alexandra Cordebard (PS)Area2.89 km2 (1.12 sq mi)Population (202...

(3代)西ノ海 嘉治郎 (3代)西ノ海嘉治郎の絵葉書基礎情報四股名 源氏山 伊セ介→源氏山 大五郎→西ノ海 嘉治郎本名 松山 伊勢助愛称 宿屋泣かせ小便相撲黒仁王生蕃生年月日 1890年11月2日没年月日 (1933-07-28) 1933年7月28日(42歳没)出身 鹿児島県西囎唹郡西国分村浜之市(現・鹿児島県霧島市隼人町真孝)身長 185cm体重 116kgBMI 33.89所属部屋 井筒部屋得意技 突っ張り、�...

Boeing CH-47 Chinook adalah sebuah helikopter Amerika bermesin ganda, tandem rotor dan heavy-lift . Dengan kecepatan tertinggi 170 knot (196 mph, 315 km / h) helikopter itu lebih cepat daripada helikopter serang tahun 1960-an. Helikopter CH-47 adalah salah satu dari beberapa pesawat masa itu yang masih dalam pelayanan lini produksi dan depan, dengan lebih dari 1.179 dibuat sampai saat ini. Peran utamanya meliputi gerakan pasukan, artileri dan memasok perlengkapan medan perang. Memi...
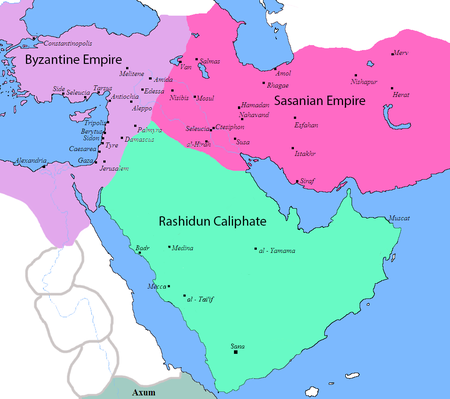
7th-century conquest of the Sassanid Empire Muslim conquest of PersiaPart of the early Muslim conquestsMap of West Asia, depicting the approximate territorial boundaries of the Byzantine Empire, the Rashidun Caliphate, and the Sasanian Empire prior to the Muslim conquestsDate633–651[1]LocationMesopotamia, Caucasus, Persia, and Greater KhorasanResult Muslim victoryTerritorialchanges Expansion of the Rashidun Caliphate into the Iranian PlateauRise of several Iranian dynasties in Tabar...

Voce principale: Qazaqstan Superkubogy. Qazaqstan Superkubogy 2008Қазақстан Суперкубогы 2008 Competizione Qazaqstan Superkubogy Sport Calcio Edizione 2ª Organizzatore KFF Date 2 marzo 2008 Luogo Almaty Partecipanti 2 Formula Gara unica Impianto/i Stadio Centrale Risultati Vincitore Aqtóbe(1º titolo) Secondo Tobyl Statistiche Incontri disputati 1 Gol segnati 2 (2 per incontro) Cronologia della competizione 1995 2010 Manuale La Qazaqstan Superkubogy 2008 è stata la...

Erick PulgarNazionalità Cile Altezza187 cm Peso74 kg Calcio RuoloCentrocampista Squadra Flamengo CarrieraGiovanili ????-2011 Dep. Antofagasta Squadre di club1 2011-2014 Dep. Antofagasta38 (2)2014-2015 Universidad Católica35 (7)2015-2019 Bologna100 (10)2019-2022 Fiorentina74 (8)2022→ Galatasaray11 (0)2022- Flamengo31 (2)[1] Nazionale 2015- Cile53 (4) Palmarès Copa América OroUSA 2016 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti...

Ruined castle in County Cavan, Ireland Cloughoughter CastleCloch Locha UachtairCloughoughter Castle sits on an island in Lough OughterLocation within IrelandGeneral informationLocationLough Oughter, CavanCountryIrelandCoordinates54°01′07″N 7°27′17″W / 54.0187°N 7.4548°W / 54.0187; -7.4548Construction started1200 - 1224Demolished1653ClientWilliam Gorm de Lacy National monument of IrelandOfficial nameClough Oughter CastleReference no.602[1] Cloug...





