United World Wrestling
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Overview of Portuguese colonial forts This article is about former Portuguese forts. For a list of forts in Portugal, see List of forts § Portugal. A map of the Portuguese Empire and its claims, strongholds, trade waters, and economic interests. This article will list all fortifications that were built, partially built, or ordered to be built by the Portuguese throughout the globe. All forts in this list are outside the modern territory of Portugal, and were built for the purpose of col...

BřezskoMunicipality BenderaLambang kebesaranBřezskoKoordinat: 49°36′52″N 16°53′11″E / 49.61444°N 16.88639°E / 49.61444; 16.88639Koordinat: 49°36′52″N 16°53′11″E / 49.61444°N 16.88639°E / 49.61444; 16.88639Country CekoRegionOlomoucDistrictProstějovLuas • Total4,04 km2 (156 sq mi)Ketinggian510 m (1,670 ft)Populasi (2006) • Total238 • Kepadatan0,59/km2...

American baseball park For the minor league ballpark in Boise, Idaho, see Airway Park. Braves FieldThe WigwamThe Bee Hive (1936–1941)Braves Field during the 1916 World SeriesFormer namesNational League Park (1936–1941)Boston University Field (1953–1955)LocationCommonwealth Avenueand Babcock StreetBoston, Massachusetts, U.S.Coordinates42°21′12″N 71°7′9″W / 42.35333°N 71.11917°W / 42.35333; -71.11917OwnerJames E. Gaffney (1915–1932)Estate of James E. ...

Article principal : Géographie de la Côte-d'Or. Le climat de la Côte-d'Or est de type océanique à tendance semi-continentale. L'influence océanique se traduit par des pluies fréquentes en toute saison et un temps changeant. L'influence semi-continentale se traduit par des hivers froids avec des chutes de neige relativement fréquentes et des étés plus chauds que sur les côtes avec, à l'occasion, de très violents orages avec parfois de la grêle voire des débuts de tornades. ...

For the 1971 album of the same name by Judith Durham, see Climb Ev'ry Mountain (album). Show tune from the 1959 musical The Sound of Music Climb Ev'ry MountainSongReleased1959GenreShow tuneComposer(s)Richard RodgersLyricist(s)Oscar Hammerstein II Climb Ev'ry Mountain is a show tune from the 1959 Rodgers and Hammerstein musical The Sound of Music. It is sung at the close of the first act by the Mother Abbess. It is themed as an inspirational piece, to encourage people to take every step toward...

Kailash dan Kailasa dialihkan ke halaman ini. Untuk penggunaan lain, lihat Kailash (disambiguasi) dan Kailasa (grup musik). Mount Kailashགངས་རིན་པོ་ཆེGunung Kailash dari selatanTitik tertinggiKetinggian6.638 m (21.778 ft)Puncak1.319 m (4.327 ft)Koordinat31°4′0″N 81°18′45″E / 31.06667°N 81.31250°E / 31.06667; 81.31250Koordinat: 31°4′0″N 81°18′45″E / 31.06667°N 81.31250°E / 31.0...

2008 single by Kylie Minogue The OneSingle by Kylie Minoguefrom the album X Released28 July 2008 (2008-07-28)Length4:05 (album version)3:42 (remix version)LabelParlophoneMushroomSongwriter(s)Kylie MinogueRichard Biff StannardJames WiltshireRussell SmallJohn AnderssonJohan EmmothEmma HolmgrenProducer(s)Richard Biff StannardFreemasonsKylie Minogue singles chronology All I See (2008) The One (2008) Lhuna (2008) Music videoThe One on YouTube The One is a song by Australian singer a...

Extinct genus of carnivores ChasmaporthetesTemporal range: Pliocene–Early Pleistocene PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N ↓ C. lunensis skull Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Carnivora Suborder: Feliformia Family: Hyaenidae Subfamily: Hyaeninae Genus: †ChasmaporthetesHay, 1921 Species See text Synonyms Euryboas Chasmaporthetes, also known as hunting or running hyena, is an extinct genus of hyenas[1][2]&...
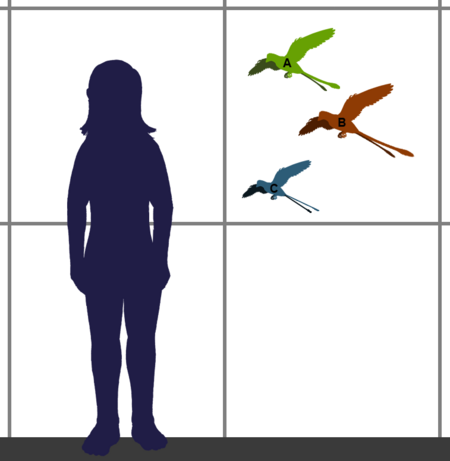
Extinct family of dinosaurs ConfuciusornithidsTemporal range: Early Cretaceous, 131–120 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N Fossil specimen of Confuciusornis sanctus Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Clade: Dinosauria Clade: Saurischia Clade: Theropoda Clade: Avialae Clade: Pygostylia Clade: †ConfuciusornithiformesHou et al., 1995 Family: †ConfuciusornithidaeHou et al., 1995 Type species †Confuciusornis sanctusHou et al., 1995 Genera �...

Swedish botanist and taxonomist Sw. redirects here. For other uses, see SW. Olof SwartzOlof SwartzBorn21 September 1760NorrköpingDied19 September 1818 (1818-09-20) (aged 57)StockholmNationalitySwedishAlma materUniversity of UppsalaKnown forpteridophytesScientific careerFieldsbotanyDoctoral advisorCarolus Linnaeus the YoungerAuthor abbrev. (botany)Sw. Olof Peter Swartz (21 September 1760 – 19 September 1818) was a Swedish botanist and taxonomist. He is best know...

Prince of Monaco from 1922 to 1949 This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Louis II, Prince of Monaco – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Louis IIFormal portrait, 1923Prince of MonacoReign26 June 1922 – 9 May 1949PredecessorAlbert ISu...

American musician Tell Me the Truth redirects here. For the Batwoman episode, see Tell Me the Truth (Batwoman). Timothy B. SchmitSchmit performing with the Eagles in 2019Background informationBirth nameTimothy Bruce SchmitBorn (1947-10-30) October 30, 1947 (age 76)Oakland, California, U.S.GenresRockcountry rocksoft rockhard rockOccupation(s)MusiciansongwriterInstrument(s)Vocalsbass guitarguitarYears active1960–presentMember ofEaglesFormerly ofPocoCoral Reefer BandRingo Starr & His ...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Famille de Barral et Barral. Joseph Marie de Barral Fonctions Maire de Grenoble 28 février 1790 – 1er août 1790 (5 mois et 4 jours) décembre 1792 – mai 1794 (1 an et 5 mois) 1800 – 1800 (moins d'un an) Député de l'Isère 27 décembre 1803 – 4 juin 1814 (10 ans, 5 mois et 8 jours) Législature Corps législatif (Consulat et Premier Empire) Biographie Date de naissance 21 mars 1742 Lieu de naissance Grenoble, Dau...

Provincial park in Alberta, Canada Winagami Lake Provincial Park, 1961 Winagami Lake Provincial Park is a provincial park in Alberta, Canada, located on three sides of Winagami Lake and accessible from Highway 2, about 30 km north of High Prairie. The park was established on November 13, 1956. Winagami Wildland Park is an extension of the park. See also List of provincial parks in Alberta List of Canadian provincial parks List of National Parks of Canada External links Alberta Development - W...

ديميت، تكساس ديميت الإحداثيات 34°32′56″N 102°18′28″W / 34.549°N 102.30783333333°W / 34.549; -102.30783333333 [1] [2] تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[3] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة كاسترو عاصمة لـ مقاطعة كاسترو (1891–)[4] خصائص جغرافية المساحة 8.4341 كيلوم�...

Johannes von Miquèl Wakil Presiden Kerajaan PrusiaMasa jabatan1 Juli 1897 – 5 Mei 1901PendahuluKarl Heinrich von BoetticherPenggantiTheobald von Bethmann-HollwegMenteri Keuangan Kerajaan PrusiaMasa jabatan24 Juni 1890 – 5 Mei 1901PendahuluAdolf von ScholzPenggantiGeorg von Rheinbaben Informasi pribadiLahirJohannes Franz Miquel(1828-02-19)19 Februari 1828Neuenhaus, County of Bentheim, Kerajaan HanoverMeninggal8 September 1901(1901-09-08) (umur 73)Frankfurt am Main, ...

Địa vật lý hố khoan còn gọi là địa vật lý lỗ khoan, địa vật lý giếng khoan (tiếng Anh: Borehole Logging hay Well Logging), là một lĩnh vực của Địa vật lý thăm dò, thực hiện các quan sát đo đạc địa vật lý trong hố khoan, từ đó phân tích, giải đoán tài liệu để phân chia đất đá trong không gian quanh hố khoan theo thành phần, tính chất, trạng thái, và xác định các tham số vật lý của ch�...

Tyne and Wear Metro station in Newcastle upon Tyne JesmondTyne and Wear Metro stationGeneral informationLocationJesmond, Newcastle upon TyneEnglandCoordinates54°58′58″N 1°36′21″W / 54.9828211°N 1.6056954°W / 54.9828211; -1.6056954Grid referenceNZ253654Transit authorityTyne and Wear PTEPlatforms2Tracks2ConstructionBicycle facilities5 cycle podsAccessibleStep-free access to platformOther informationStation codeJESFare zoneAHistoryOriginal companyBlyth and Tyn...

約旦第納爾دينار أردني(阿拉伯語)标准代码ISO代码JOD使用地区法定货币 约旦流通货币 约旦河西岸 (巴勒斯坦领土), 以及 以色列谢克尔货币单位 1⁄10迪拉姆 1⁄100吉尔什 或 皮阿斯特(英语:Piastre) 1⁄1000菲尔(英语:Fils (currency))货币符号د.أ发行面额硬币1⁄2, 1, 2 1⁄2, 5, 10 皮阿斯特或吉尔什, 1⁄4, 1⁄2, 1 第纳尔纸币1, 5, 10, 20, 50 dinars...

Itala FilmLogo Stato Italia Forma societariaSocietà a responsabilità limitata Fondazione13 maggio 1907 a Torino Fondata daGiovanni Pastrone, Guglielmo Remmert, Carlo Sciamengo Chiusura1927 Sede principaleTorino SettoreTelecomunicazioni Prodottifilm, serie televisive e documentari Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Agli inizi del Novecento, il chimico Carlo Rossi, l'industriale di origine tedesca Guglielmo Remmert e l'inventore Lamberto Pineschi, fondarono a Torino una ditta ...


