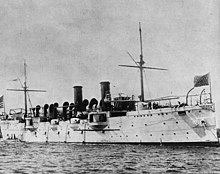
USS Philadelphia (C-4)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Gregory HelmsHelms di WWE WrestleMania XXV Axxess pada bulan April 2009Nama lahirGregory Shane Helms[1][2]Lahir12 Juli 1974 (umur 49)[2][3]Smithfield, Carolina Utara, Amerika Serikat[2][3]Anak1Karier gulat profesionalNama ringGregory Hanes[3]Gregory Helms[1]Gregory Shane HelmsThe Hurricane[4]Hurricane Helms[3]Shane HelmsTinggi6 ft 0 in (1,83 m)[4]Berat200 pon (91 kg)[4]...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Universitas Baiturrahmah – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR MotoUniversitas terkemuka dan unggul ditingkat regional serta didukung oleh insan yang memiliki akhlakul karimahJenisPerguruan...

العلاقات البوروندية الموزمبيقية بوروندي موزمبيق بوروندي موزمبيق تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات البوروندية الموزمبيقية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين بوروندي وموزمبيق.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين:...

العلاقات الرواندية الليبية رواندا ليبيا رواندا ليبيا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الرواندية الليبية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين رواندا وليبيا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة رواندا ...

Human gene QDPRAvailable structuresPDBOrtholog search: PDBe RCSB List of PDB id codes1HDRIdentifiersAliasesQDPR, DHPR, PKU2, SDR33C1, quinoid dihydropteridine reductase, HDHPRExternal IDsOMIM: 612676 MGI: 97836 HomoloGene: 271 GeneCards: QDPR Gene location (Human)Chr.Chromosome 4 (human)[1]Band4p15.32Start17,460,261 bp[1]End17,512,206 bp[1]Gene location (Mouse)Chr.Chromosome 5 (mouse)[2]Band5 B3|5 24.9 cMStart45,591,363 bp[2]End45,607,578 bp[2&...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Mirone (disambigua). Discobolo Lancellotti. Copia in marmo del II secolo d.C. (provenienza: scavi dell'Esquilino, 1871), da originale bronzeo di Mirone datato al 450 a.C. circa. Roma, Museo nazionale romano, Palazzo Massimo, Collezione Lancellotti. Mirone di Elèutere (Eleutere, ... – V secolo a.C.) è stato uno scultore greco antico attivo tra il 480 e il 440 a.C. Fu uno dei più elogiati rappresentanti dello stile severo. Indic...

Japanese art of target test cutting Tameshigiri using a goza target on a stand (2006) Ren Kuroda demonstrates Shofu at the Mugairyu Meishi-ha dojo in Tokyo, Japan Tameshigiri (試し斬り, 試し切り, 試斬, 試切) is the Japanese art of target test cutting. The kanji literally mean test cut (kun'yomi: ためし ぎり tameshi giri). This practice was popularized in the Edo period (17th century) for testing the quality of Japanese swords.[1] It continues to the present day, but h...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要編修,以確保文法、用詞、语气、格式、標點等使用恰当。 (2013年8月6日)請按照校對指引,幫助编辑這個條目。(幫助、討論) 此條目剧情、虛構用語或人物介紹过长过细,需清理无关故事主轴的细节、用語和角色介紹。 (2020年10月6日)劇情、用語和人物介紹都只是用於了解故事主軸,輔助�...

معتمدية سيدي بوزيد الغربية الإحداثيات 35°00′21″N 9°24′39″E / 35.00578°N 9.41072°E / 35.00578; 9.41072 تقسيم إداري البلد تونس[1] التقسيم الأعلى ولاية سيدي بوزيد رمز جيونيمز 2465836 تعديل مصدري - تعديل معتمدية سيدي بوزيد الغربية إحدى معتمديات الجمهورية التونسي�...

قطار ينقل فوسفات من منطقة خريبكة متجه نحو الدار البيضاء. ديار عمال بمصانع الفوسفات بمدينة آسفي. الفوسفات في المغرب هو ثالث مصدر عالمي للفوسفات، ويتوفر المغرب على %75 من الاحتياطي العالمي.[1] ويتوزع بنسب متفاوتة بين عدة مناطق أساسية وهي: وادي زم بن جرير بوكراع خريبكة اليوس...

Metro station in Delhi, India Noida Sector 61 Delhi Metro stationGeneral informationLocationSector 61, Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201307Coordinates28°35′51.4716″N 77°22′20.2757″E / 28.597631000°N 77.372298806°E / 28.597631000; 77.372298806Owned byDelhi MetroOperated byDelhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC)Line(s)Blue LinePlatformsSide platformPlatform-1 → Noida Electronic CityPlatform-2 → Dwarka Sector 21Tracks2ConstructionStructure typeElevated, Double-trackPla...

U.S. Supreme Court justice from 1956 to 1990 For persons of a similar name, see William Brennan (disambiguation). William J. Brennan Jr.Official portrait, 1972Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United StatesIn officeOctober 16, 1956 – July 20, 1990[1]Nominated byDwight D. EisenhowerPreceded bySherman MintonSucceeded byDavid SouterAssociate Justice of the New Jersey Supreme CourtIn officeApril 1, 1951 – October 13, 1956Nominated byAlfred E. DriscollPrec...

Philatelic history of an island This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (September 2011) Antigua was discovered by Christopher Columbus, in 1493, and was named after the church of Santa Maria la Antigua in Seville. It was first settled in 1632. By the Treaty of Breda in 1667 it became a British Possession. First stamps The postal arrangements of Antigua were controlled by the British Postmaster General in Londo...

Diskografi PartibrejkersPartibrejkers performing in 2003Album studio7Album rekaman langsung2Album kompilasi2Singel1Penampilan lainnya6 Diskografi Partibrejkers (grup musik rock dari Serbia) meliputi tujuh album studio, dua album live, dua album kompilasi, satu singel, satu album video, dan penampilan lainnya. Album studio Judul Rilis Partibrejkers I 1985 Partibrejkers II 1988 Partibrejkers III 1989 Kiselo i slatko 1994 Ledeno doba 1997 Gramzivost i pohlepa 2002 Sloboda ili ništa 2007 Sirotin...
هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (يوليو 2018) منتخب الأرجنتين لكرة اليد البلد ؟؟ الزي الأساسي الزي الإحتياطي تعديل مصدري - تع...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع صبيح (توضيح). تحتاج هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر إضافية لتحسين وثوقيتها. فضلاً ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة بإضافة استشهادات من مصادر موثوق بها. من الممكن التشكيك بالمعلومات غير المنسوبة إلى مصدر وإزالتها. (أبريل 2018) صبيح صبيحالعلم صبيحالشعار تقسي�...

1969 book by Gilles Deleuze The Logic of Sense Cover of the French editionAuthorGilles DeleuzeOriginal titleLogique du sensTranslatorsMark Lester, Charles StivaleLanguageFrenchSeriesEuropean PerspectivesSubjectMeaningPublished 1969 (Les Éditions de Minuit, in French) 1990 (Columbia University Press, in English) Publication placeFranceMedia typePrint (hardcover and paperback)Pages392 (French edition)393 (Columbia University Press edition)ISBN978-0231059831 The Logic of Sense (French...

Sydafrika i olympiska spelen IOK-landskodRSA KommittéSydafrikas olympiska kommittéOlympiska sommarspelen 1960 i RomDeltagare55 deltagare i 12 grenar Medaljsummering Guld0 Silver1 Brons2 Totalt3 Sydafrika i olympiska sommarspelen1904 • 1908 • 1912 • 1920 • 1924 • 1928 • 1932 • 1936 • 1948 • 1952 • 1956 • 1960 • 1964 • 1968 • 1972 • 1976 • 1980 • 1984 ...
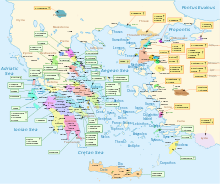
This article is about the history and evolution of the Greek language. For the history of the Greek people, see Greeks. For the history of the Greek culture, see culture of Greece. Greek is an Indo-European language, the sole surviving descendant of the Hellenic sub-family. Although it split off from other Indo-European languages around the 3rd millennium BCE (or possibly before), it is first attested in the Bronze Age as Mycenaean Greek. During the Archaic and Classical eras, Greek speakers...