Sporveisbussene
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Perangko AS yang memperingati perekam kaset video. Perekam kaset video adalah suatu jenis perekam pita video yang menggunakan kaset pita video yang berisikan pita magnetis untuk merekam audio dan video dari siaran televisi sehingga dapat dimainkan kembali kelak. Banyak alat perekam ini yang mempunyai tunernya sendiri (agar dapat langsung menerima siaran TV) dan timer yang dapat diprogram sehingga dapat merekam siaran tertentu pada suatu waktu tertentu tanpa harus ditunggui. Pranala luar Total...
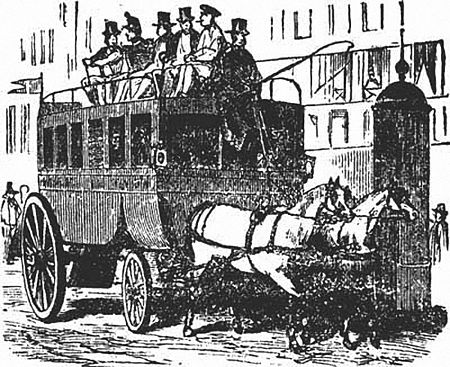
Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Bus (disambiguasi). Bus tingkat New Routemaster, beroperasi untuk Arriva London pada rute London Bus 73 Bus atau omnibus,[1] (disebut juga multibus, otobus atau motorbus; sering juga dilafalkan sebagai /bas/ atau /bəs/; ejaan tidak baku bis) adalah kendaraan darat yang dirancang untuk mengangkut banyak penumpang. Bus dapat memiliki kapasitas hingga 30 penumpang.[2] Jenis bus yang paling umum adalah bus tunggal satu lantai; bila muatan yang diangkut ...

91PaProtaktiniumSampel protaktinium-233 (area lingkaran gelap) dalam cahaya dari radioaktivitasnya sendiri Garis spektrum protaktiniumSifat umumNama, lambangprotaktinium, PaPengucapan/protaktinium/[1] Penampilanmetalik keperakan yang berkilau cerahProtaktinium dalam tabel periodik 91Pa Hidrogen Helium Lithium Berilium Boron Karbon Nitrogen Oksigen Fluor Neon Natrium Magnesium Aluminium Silikon Fosfor Sulfur Clor Argon Potasium Kalsium Skandium Titanium Vanadium Chromium Mangan Be...

Building, park and museum in Ghana Kwame Nkrumah MausoleumLocation within GhanaEstablished1 July 1992 (1992-07-01)DissolvedThe Museum was shutdown for one year for renovations and was opened to the public on the 4th of July 2023. The newly renovated Museum was commissioned by the president of Ghana, Pre. Akufo Addo.[1]LocationAccra, Ghana Kwame Nkrumah MausoleumKwame Nkrumah's grave inside the Kwame Nkrumah Memorial in Accra The Kwame Nkrumah Mausoleum and Memorial Park...
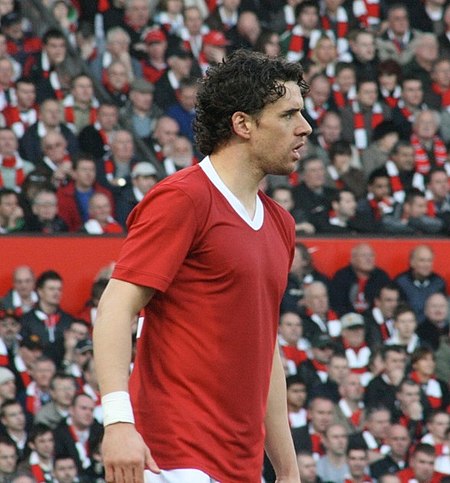

Owen Hargreaves Hargreaves bermain untuk Manchester United tahun 2008Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Owen Lee HargreavesTanggal lahir 20 Januari 1981 (umur 43)Tempat lahir Calgary, Alberta, KanadaTinggi 180 cm (5 ft 11 in)[1][2]Posisi bermain GelandangKarier junior1994–1997 Calgary Foothills1997–1999 Bayern MünchenKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1999–2001 Bayern München II 26 (6)2000–2007 Bayern München 145 (5)2007–2011 Manchester United 27 ...

The Best IntentionsPoster bioskopSutradaraBille AugustProduserIngrid DahlbergDitulis olehIngmar BergmanPemeran Samuel Fröler Pernilla August Max von Sydow Ghita Nørby SinematograferJörgen PerssonDistributorThe Samuel Goldwyn Company (AS)Artificial Eye (Britania)Tanggal rilis Mei 1992 (1992-05) (Cannes) 2 Oktober 1992 (1992-10-02) (Swedia) Durasi323 menit (televisi)174 menit (teater)NegaraSwediaBahasaSwediaAnggarankr 67 juta[1] Untuk album We Are the In Crowd tahun...

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...

Wŏnsan 원산Wŏnsan CityTranskripsi Korea • Hangul원산시 • Hanja元山市 • McCune-ReischauerWŏnsan-si • RomanisasiWonsan-siWonsanNegara Korea UtaraProvinsiKangwŏnRegionKwandongPendirianc. 1800Divisi40 dong, 15 riLuas • Total269 km2 (104 sq mi)Populasi (2000 (perk.)) • Total331,000 • DialekSeoul Wŏnsan adalah kota pelabuhan dan basis militer di Korea Utara bagian tenggara....

County in Kansas, United States County in KansasBourbon CountyCountyBourbon County Courthouse in Fort Scott (2016)Location within the U.S. state of KansasKansas's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 37°51′N 94°51′W / 37.850°N 94.850°W / 37.850; -94.850Country United StatesState KansasFoundedAugust 25, 1855Named forBourbon County, KentuckySeatFort ScottLargest cityFort ScottArea • Total639 sq mi (1,660 km2) • Lan...

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (janvier 2022). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références ». En pratique : Quelles sources sont attendues ? C...

This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (March 2021) Place in Hama, SyriaMasyaf مصيافA view of Masyaf, 2008MasyafLocation in SyriaCoordinates: 35°03′55″N 36°20′32″E / 35.06528°N 36.34222°E / 35.06528; 36.34222Country SyriaGovernorateHamaDistrictMasyafSubdistrictMasyafElevation447 m (1,467&#...

NGC 3308 جزء من عنقود هيدرا المجري الكوكبة الشجاع[1] رمز الفهرس NGC 3308 (الفهرس العام الجديد)PGC 31438 (فهرس المجرات الرئيسية)ESO 501-34 (European Southern Observatory Catalog)2MASX J10362237-2726172 (Two Micron All-Sky Survey, Extended source catalogue)MCG-04-25-032 (فهرس المجرات الموروفولوجي)ESO-LV 501-0340 (The surface photometry catalogue of the ESO-Uppsala ga...

Paul van Tongeren, 2021 Paul van Tongeren (* 26. August 1950 in Deventer) ist ein niederländischer Philosoph, der als Spezialist für Ethik und Friedrich Nietzsche hervorgetreten ist. Er lehrt seit 1993 als ordentlicher Professor an der Radboud-Universität Nijmegen. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Werdegang 2 Werke 3 Auszeichnungen 4 Weblinks Werdegang Paul van Tongeren studierte Theologie und Philosophie an der Universität Utrecht und der Katholieke Universiteit Leuven. Dort schloss er mit einer Dis...

Japanese Zen Buddhist master Soyen Shaku釈 宗演TitleZen MasterPersonalBornJanuary 10, 1860Fukui JapanDiedOctober 29, 1919 (1919-10-30) (aged 59)Kamakura, JapanReligionZen BuddhismNationalityJapaneseSchoolRinzaiSenior postingPredecessorImakita KōsenSuccessorTetsuo Sōkatsu Soyen Shaku (釈 宗演, January 10, 1860 – October 29, 1919; written in modern Japanese Shaku Sōen or Kōgaku Shaku Sōen) was the first Zen Buddhist master to teach in the United States. He was a rō...

奥林匹克运动会中国香港代表團香港特别行政区区旗IOC編碼HKGNOC中國香港體育協會暨奧林匹克委員會網站www.hkolympic.org(英文)(繁體中文)獎牌榜 金牌 銀牌 銅牌 總計 2 3 4 9 历届奥林匹克运动会参赛记录(总结)夏季奥林匹克运动会1952195619601964196819721976198019841988199219962000200420082012201620202024冬季奥林匹克运动会200220062010201420182022 中國香港(國際奧委會國家或地區編碼為:HK...

أركان الحربمعلومات عامةصنف فرعي من تنظيم عسكريوحدة عسكريةقيادة تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات الرتب العسكرية المقارنة القوات البرية القوات البحرية القوات الجوية الضباط الأمراء مشيرفريق أولفريقلواءعميد مشيرفريق أولفريقلواءعميد مشيرفريق أولفريقلواءعميد الضباط...

US MilaneseCalcio Gli Scacchi Segni distintiviUniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori sociali Nero, bianco Dati societariCittàMilano Nazione Italia ConfederazioneFIFA Federazione FIGC Fondazione1902 Scioglimento1928Rifondazione1945Scioglimento1946Stadiovia Comasina, Cascina Mojetta, via Stelvio.( posti) PalmarèsTrofei nazionali1 Palla Dapples Si invita a seguire il modello di voce L'Unione Sportiva Milanese era una polisportiva ciclistica, calcistica, rugbistica e cestistica italiana, c...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant un film italien. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les conventions filmographiques. Nilla Pizzi dans une scène du film Une fille formidable (titre original : Ci troviamo in galleria) est un film italien réalisé par Mauro Bolognini sorti en 1953. Synopsis Ignazio Panizza, dont le nom de scène est « Gardenio », est un comédien de lever de rideau qui va d’un échec à l’autre jusqu�...

Scientist specializing in the field of physics For the album, see Physicist (album). Not to be confused with Physician. Albert Einstein, a key theoretical physicist in the 20th century who developed the theory of relativity and parts of early quantum theory Part of a series onPhysics Index Outline Glossary History (timeline) Branches Acoustics Astrophysics Atomic physics Biophysics Classical physics Electromagnetism Geophysics Mechanics Modern physics Nuclear physics Optics Thermodynamics Res...
