Simulator sickness
|
Read other articles:
AVG Anti-Virus 2011 AVG Anti-Virus 2011, versi 10.0.1120 yang dijalankan pada Windows 7GenreAntivirus, Malware removal, Internet SecurityLisensiProprietary (freeware and commercial) Sunting di Wikidata • L • B • Bantuan penggunaan templat ini AVG Anti-Virus 2011 adalah perangkat lunak produksi AVG Technologies, s.r.o yang dilengkapi dengan fitur pendeteksian rootkit pada pustaka data sistem dan pengamanan terhadap pencurian identitas. Program ini resmi dirilis pada awal O...

Dalam nama Korean ini, nama keluarganya adalah Kim. Kim Keon-hee김건희Kim pada tahun 2022 Ibu Negara Korea SelatanPetahanaMulai menjabat 10 Mei 2022PresidenYoon Suk-yeol PendahuluKim Jung-sookPenggantiPetahana Informasi pribadiLahir02 September 1972 (umur 51)Yangpyeong, Korea SelatanSuami/istriYoon Suk-yeol (m. 2012)Tempat tinggalKediaman PresidenAlma mater Universitas Kyonggi [en] (BA) Universitas Wanita Sookmyung [ko] (MA)...
Эту страницу предлагается объединить со страницей Рекурсивная функция.Пояснение причин и обсуждение — на странице Википедия:К объединению/27 апреля 2016.Обсуждение длится не менее недели (подробнее). Не удаляйте шаблон до подведения итога обсуждения. Рекуррентная формул�...

The DescendantsPoster film The DescendantsSutradaraAlexander PayneProduserJim BurkeJim TaylorAlexander PayneDitulis olehJim RashNat FaxonAlexander PayneBerdasarkanThe Descendantsoleh Kaui Hart HemmingsPemeranGeorge ClooneyShailene WoodleyBeau BridgesRobert ForsterJudy GreerMatthew LillardSinematograferPhedon PapamichaelPenyuntingKevin TentPerusahaanproduksiAd Hominem EnterprisesDistributorSearchlight PicturesTanggal rilis 10 September 2011 (2011-09-10) (Festival Film Internasional To...

Об экономическом термине см. Первородный грех (экономика). ХристианствоБиблия Ветхий Завет Новый Завет Евангелие Десять заповедей Нагорная проповедь Апокрифы Бог, Троица Бог Отец Иисус Христос Святой Дух История христианства Апостолы Хронология христианства Ран�...

Makanan antariksa disajikan di atas nampan. Perhatikan penggunaan magnet, pegas, dan velcro untuk menahan alat makan dan bungkus makanan ke nampan. Makanan luar angkasa adalah sebuah jenis produk makanan yang dibuat dan diolah untuk disantap oleh para antariksawan di luar angkasa. Makanan tersebut memiliki persyaratan khusus agar dapat menyediakan nutrisi seimbang untuk orang-orang yang bekerja di luar angkasa, mudah dan aman untuk disiapkan dan disantap dalam lingkungan mikrogravitasi dari p...

Cléon Caractéristiques Longueur 18,5 km [1] Bassin collecteur Seine Cours Confluence l'Armançon Géographie Pays traversés France modifier Le Cléon est un ruisseau français affluent de l'Armançon qui prend sa source dans l’Yonne sur la commune de Tonnerre près de la ferme d'Athée. Il a 18,5 km de long[1] et il traverse cinq communes : Tissey, Vezannes, Dyé, Carisey, Villiers-Vineux. Il a huit affluents : ru de valru rive droite prend sa source sur la com...

Constantine YpsilantisPangeran MoldaviaBerkuasa9 Maret 1799 – 4 Juli 1801PendahuluAlexandru CallimachiPenerusAlexandros SoutzosPangeran Wallachia(masa jabatan ke-1)Berkuasa1 September 1802 – Agustus 1806PendahuluAlexandros SoutzosPenerusJohn CaradjaPangeran Wallachia(masa jabatan ke-2)Berkuasa27 Desember 1806 – 31 Mei 1807PendahuluAlexandros SoutzosPenerusPendudukan RusiaInformasi pribadiKelahiran1760Konstantinopel, Kekaisaran UtsmaniyahKematian24 Juni 1816Kiev, Kekaisaran RusiaAyahAlex...

Voce principale: ACF Fiorentina. AC FiorentinaStagione 1956-1957La Fiorentina con lo scudetto sulle maglie Sport calcio Squadra Fiorentina Allenatore Fulvio Bernardini All. in seconda Virgilio Felice Levratto Presidente Enrico Befani Serie A2º Coppa CampioniFinalista Coppa GrasshoppersVincitore Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Orzan (31)Totale: Cervato, Julinho, Montuori, Orzan, Segato (37) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Montuori (14)Totale: Montuori (15) StadioComunale 1955-1956 1957-1958 S...

Japanese manga series Ristorante ParadisoCover of the first manga volumeリストランテ・パラディーゾ(Risutorante Paradīzo)GenreRomance[1] MangaWritten byNatsume OnoPublished byOhta PublishingEnglish publisherNA: Viz MediaMagazineManga Erotics FOriginal runMay 2005 – March 2006Volumes1 MangaGente: The People of Ristorante ParadisoWritten byNatsume OnoPublished byOhta PublishingEnglish publisherNA: Viz MediaMagazineManga Erotics FOriginal runSeptember 2...

Mazda Parkway 26 (first generation) Mazda Parkway (second generation) The Mazda Parkway is a minibus that was based on the Mazda Titan platform, and was manufactured at the Hiroshima Factory exclusively for the Japanese market. In 1974, the Parkway was installed with the 13B rotary engine and well as a 2000cc gasoline type VA and the diesel 2500cc type XA. It also offered a novel transmission approach added to the manual transmission installed, called a sub transmission to cope with the load ...

Socialist state in East Asia from 1924 to 1992 Mongolian People's Republicᠪᠦᠭᠦᠳᠡᠨᠠᠢᠢᠷᠠᠮᠳᠠᠬᠤᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯᠠᠷᠠᠳᠤᠯᠤᠰ[a]Бүгд Найрамдах Монгол Ард Улс[b]Bügd Nairamdakh Mongol Ard Uls1924–1992 Flag(1945–1992) Emblem(1960–1992) Motto: Орон бүрийн пролетари нар нэгдэгтүн!Oron büriin prolyetari nar negdegtün!Workers of the world, unite!Anthem: Монгол �...

Сельское поселение России (МО 2-го уровня)Новотитаровское сельское поселение Флаг[d] Герб 45°14′09″ с. ш. 38°58′16″ в. д.HGЯO Страна Россия Субъект РФ Краснодарский край Район Динской Включает 4 населённых пункта Адм. центр Новотитаровская Глава сельского пос�...
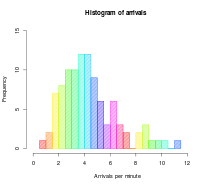
ميّز عن مخطط قضباني. مدرج تكراريمعلومات عامةفرع من رسوميات إحصائية — مخطط شريطي وصفه ISO 3534-1:2006(en) Statistics — Vocabulary and symbols — Part 1: General statistical terms and terms used in probability (en) جانب من إحصاء تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات المدرج التكراري[1][2] أو مخطط التوزع[3] أو مخطط...

British politician (born 1982) Will QuinceOfficial portrait, 2023Minister of State for Health and Secondary Care[a]In office8 September 2022 – 13 November 2023Prime MinisterLiz TrussRishi SunakPreceded byMaria CaulfieldSucceeded byAndrew StephensonMinister of State for School StandardsIn office7 July 2022 – 7 September 2022Prime MinisterBoris JohnsonPreceded byRobin WalkerSucceeded byJonathan GullisParliamentary Under-Secretary of State for Children and FamiliesI...

Nazi police established in 1933 Members of Schutzpolizei (left) and Hilfspolizei (right) patrol Berlin on 5 March 1933, the day of the Reichstag election The Hilfspolizei (abbreviated HiPo or Hipo; meaning auxiliary police) was a short-lived auxiliary police force in Nazi Germany in 1933. The term was later semi-officially used for various auxiliary organizations subordinated to the Ordnungspolizei as well as various military and paramilitary units set up during World War II in German-occupie...

Real Betis FutsalDatos generalesNombre completo Real Betis FutsalAcrónimo RBFApodo(s) Heliopolitanos, VerdiblancosMascota PalmerínDeporte Fútbol SalaFundación 1987 como Fútbol Sala Nazareno 2016 como Real Betis FutsalColores Verde y BlancoPresidente Ángel HaroEntrenador Bruno GarcíaPatrocinador FinetworkInstalacionesEstadio cubierto Pabellón de San PabloUbicación Sevilla, Andalucía, EspañaCapacidad 7.626Uniforme Última temporadaLig...

Wars involving the United States of America The United States has been involved in 108 military conflicts. These include major conflicts like the American Revolutionary War, the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War, the American Civil War, the Spanish-American War, World War I, and World War II, and the Gulf War. It also includes US involvement in widespread periods of conflict like the Indian Wars, the Cold War (including the Korean War and the Vietnam War), and the War on Terror (includi...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento energia è ritenuta da controllare. Motivo: La voce affronta l'argomento energia eolica in un'ottica consumistica, soffermandosi sulla generazione di energia elettrica dall'energia eolica, come se l'energia eolica fosse solo questo. Bisogna spostare i contenuti in voci più specifiche, come Turbina eolica o creare nuove voci, lasciando qui una descrizione generale dell'energia eolica, con tutte le sue possibili applicazioni o risvolti non necessariam...

Northeastern part of London, United Kingdom This article is about part of London, England, United Kingdom. For the city in Eastern Cape, see East London, South Africa. For other uses, see East London (disambiguation). The men of early East London garrisoned the Tower of London East London is the northeastern part of London, England, east of the ancient City of London and north of the River Thames as it begins to widen. East London developed as London's docklands and the primary industrial cen...