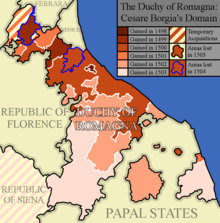
Romagna
|
Read other articles:

Questa voce sull'argomento edizioni di competizioni calcistiche è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Coppa delle Alpi 1981 Competizione Coppa delle Alpi Sport Calcio Edizione 21ª Organizzatore FFF, ASF Luogo Svizzera Francia Partecipanti 8 Risultati Vincitore Basilea(3º titolo) Secondo Sochaux Statistiche Incontri disputati 17 Gol segnati 56 (3,29 per incontro)...

Town in Ontario, CanadaEspanolaTown (single-tier)Town of EspanolaSpanish River and Domtar mill in EspanolaEspanolaCoordinates: 46°15′N 81°46′W / 46.250°N 81.767°W / 46.250; -81.767CountryCanadaProvinceOntarioDistrictSudburySettled1900sIncorporated1958Government • TypeTown • MayorDouglas Gervais • MPCarol Hughes (NDP) • MPPMichael Mantha (NDP)Area[1] • Land82.82 km2 (31.98 sq mi)P...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando il gruppo rock Art Brut, vedi Art Brut (gruppo musicale). Adolf Wölfli, Band-Hain, 1910 Jean Linard Tête d'ange Weltachse mit Haase, di August Natterer, 1919 Il concetto di Art brut (in italiano, letteralmente, Arte grezza, ma tradotto anche come arte spontanea) è stato inventato nel 1945 dal pittore francese Jean Dubuffet per indicare le produzioni artistiche realizzate da non professionisti o pensionanti dell'ospedale psichiatrico che operano al di f...

Dragon Ball KaiGenreShonen, aksi & Laga AnimeDragon Ball KaiStudio Toei Animation Portal anime dan manga Dragon Ball Kai (ドラゴンボール改code: ja is deprecated , Doragon Bōru Kai) adalah serial anime yang merupakan versi terbaru dari Dragon Ball. Dragon Ball Kai pertama kali disiarkan di Jepang pada 5 April 2009 hingga 28 Juni 2015 dengan 159 Episode. Di Indonesia ditayangkan oleh Indosiar, MNCTV & GlobalTV,serial dragonball ini adalah reviasi yang pernah ditanyang...

Letnan JenderalHarbaksh SinghPadma Vibhushan, Padma Bhushan, VrCLahir(1913-10-01)1 Oktober 1913Badrukhan, Punjab, India BritaniaMeninggal14 November 1999(1999-11-14) (umur 86)New Delhi, IndiaPengabdian IndiaDinas/cabang Angkatan Darat IndiaLama dinas1935–1969Pangkat Letnan JenderalKesatuanBerkas:The Regiment Sikh Regiment Battle Insignia.jpg 5 SikhKomandanTentara BaratKorps XXXIIIKorps IVDivisi Infanteri 5Divisi Infanteri 27Brigade Infanteri 163 Berkas:The Regiment Sikh ...

No. 14 SquadronActive15 August 1951 - PresentCountry Republic of IndiaBranch Indian Air ForceRoleInterdictionGarrison/HQAmbala AFSNickname(s)BullsMotto(s)बलं जयय(Balam Jayay)Strength will ConquerAircraft flownAttackSEPECAT Jaguar ISMilitary unit No. 14 Squadron (Bulls), is a ground attack unit, operating out of AFS Ambala. The squadron currently operates SEPECAT Jaguar IS and IBs, operational since March 1981.[1] History Hunters of No. 14 Squadron battled with Sabres...

Daftar berikut ini berisi semua kota (termasuk kota kecil dan desa) di prefektur Yamaguchi, Jepang, yang penduduknya berjumlah lebih dari 5.000 jiwa menurut sensus 2015. Per 1 Oktober 2015, ada 17 tempat yang memenuhi kriteria ini. Daftar ini hanya mencantumkan jumlah penduduk kota, kota kecil, dan desa di dalam batas resminya, tidak termasuk kotamadya atau kota pinggiran lain di kawasan sekitarnya. Daftar Shimonoseki Shunan Iwakuni Tabel berikut ini berisi 17 kota, kota kecil, dan desa di Ya...

这是马来族人名,“尤索夫”是父名,不是姓氏,提及此人时应以其自身的名“法迪拉”为主。 尊敬的拿督斯里哈芝法迪拉·尤索夫Fadillah bin Haji YusofSSAP DGSM PGBK 国会议员 副首相 第14任马来西亚副首相现任就任日期2022年12月3日与阿末扎希同时在任君主最高元首苏丹阿都拉陛下最高元首苏丹依布拉欣·依斯迈陛下首相安华·依布拉欣前任依斯迈沙比里 马来西亚能源转型与�...

Alloy of titanium and iron This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Ferrotitanium – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Samples of ferrotitanium with 70% titanium content, used in the steel industry (placed on A4 sheet) Ferrotitanium...

Veterans FieldAddress1 Veterans Field RoadLocationChatham, MassachusettsCoordinates41°41′04″N 69°57′45″W / 41.684579°N 69.9626°W / 41.684579; -69.9626Capacity8,000Field sizeLeft Field: 325 ftCenter Field: 385 ftRight Field: 314 ftSurfaceGrassOpened1927TenantsChatham Anglers Veterans Field is a baseball venue in Chatham, Massachusetts, home to the Chatham Anglers of the Cape Cod Baseball League (CCBL). The ballpark is located in downtown Chath...

This article is about the album. For the song, see One of These Nights (Eagles song). For other uses, see One of These Nights (disambiguation). 1975 studio album by the EaglesOne of These NightsStudio album by the EaglesReleasedJune 10, 1975Recorded1974–1975Studio Criteria, Miami, Florida Record Plant, Los Angeles, California Genre Rock[1] soft rock country rock folk rock[2] Length43:15LabelAsylumProducerBill SzymczykThe Eagles chronology On the Border(1974) One of T...

American lawyer and politician For the British politician, see James Seddon (British politician). For the footballer, see Jimmy Seddon. James Seddon4th Confederate States Secretary of WarIn officeNovember 21, 1862 – February 5, 1865PresidentJefferson DavisPreceded byGeorge RandolphSucceeded byJohn BreckinridgeMember of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom Virginia's 6th districtIn officeMarch 4, 1849 – March 3, 1851Preceded byJohn BottsSucceeded byJohn Caski...

Christina Robertson Información personalNacimiento 17 de diciembre de 1796 Kinghorn (Reino Unido) Fallecimiento 30 de abril de 1854 (57 años)San Petersburgo (Imperio ruso) Sepultura Cementerio Volkovo Nacionalidad BritánicaInformación profesionalOcupación Pintora y editora Años activa 1823-1844Género Retrato [editar datos en Wikidata] Christina Robertson o Christina Saunders (Kinghorn, 17 de diciembre de 1796 - San Petersburgo, 30 de abril de 1854) fue una artista escocesa qu...

ArthurGenreDrama komediPotongan kehidupanPenyelesaian masalahEdutainmentPembuatMarc BrownPengembangKathy WaughSutradaraGreg BaileyPenggubah lagu temaJudy Henderson & Jerry de Villiers Jr.Lagu pembukaBelieve in Yourself oleh Ziggy Marley and the Melody MakersPenata musikRay FabiNegara asalAmerika SerikatKanadaBahasa asliInggrisJmlh. musim25Jmlh. episode253 (493 segments) (daftar episode)ProduksiProduser eksekutifMarc Brown (Musim 10–25)Micheline Charest (musim 1–4)Carol Greenwal...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando l'omonimo attore, vedi Massimo De Santis (attore). Massimo De SantisInformazioni personaliArbitro di Calcio SezioneTivoli Attività nazionale AnniCampionatoRuolo 1995-2006Serie AArbitro Attività internazionale AnniConfederazioneRuolo 2000-2006UEFA e FIFAArbitro Premi AnnoPremio 20032006Premio Giovanni MauroPremio Gentleman Massimo De Santis (Tivoli, 8 aprile 1962) è un ex arbitro di calcio italiano. Indice 1 Carriera 1.1 Controversie 1.1.1 Il processo d...

This is a dynamic list and may never be able to satisfy particular standards for completeness. You can help by adding missing items with reliable sources. This is a list of Ukrainian billionaires based on an annual assessment of wealth and assets compiled and published by Forbes magazine in 2024,[1] as well as the real-time billionaires list as of July 2024[update].[2] image rank name net worth change age source country/territory industry reference 799 Rinat Akhm...

Royal Spanish Athletics FederationSportAthleticsAbbreviation(RFEA)FoundedMarch 27, 1920 (1920-03-27)AffiliationWorld AthleticsAffiliation date1918 (1918)Regional affiliationEAAPresidentRaúl Chapado SerranoSecretaryJosé Luis de CarlosReplacedFederación Atlética EspañolaOfficial websitewww.rfea.es The Royal Spanish Athletics Federation (Spanish: Real Federación Española de Atletismo, RFEA), is the governing body for the sport of athletics in Spain. As of 2023, the fed...

Salvatore LombardoLombardo (al centro) assiste ai convenevoli tra il capitano romanista Tancredi e quello juventino Cabrini, prima della classica di Serie A del 28 febbraio 1988.Informazioni personaliArbitro di Calcio SezioneMarsala ProfessioneNotaio Attività nazionale AnniCampionatoRuolo 1985-1988Serie AArbitro Premi AnnoPremio 197719821989Seminatore d'oroPremio Florindo LongagnaniPremio Saverio Giulini Salvatore Lombardo Sindaco di Marsala(Primo mandato)Durata mandato24 novembre 1993&...

American swimmer Alex ShackellPersonal informationBorn (2006-11-13) November 13, 2006 (age 17)Carmel, Indiana, U.S.SportCountry United StatesSportWomen's swimmingStrokesFreestyleClubCarmel Swim Club[1] Medal record Women's swimming Representing United States Olympic Games 2024 Paris 4x100 m medley 2024 Paris 4×200 m freestyle Alex Shackell (born November 13, 2006) is an American swimmer and 2024 Summer Olympics team member for the United States.[2] Shackell qu...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Roses (disambigua). Rosescomune(ES) Roses/Rosas Roses – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Spagna Comunità autonoma Catalogna Provincia Gerona TerritorioCoordinate42°15′48″N 3°10′30″E42°15′48″N, 3°10′30″E (Roses) Altitudine5 m s.l.m. Superficie45,9 km² Abitanti20 197 (2009) Densità440,02 ab./km² Comuni confinantiCadaqués, Castelló d'Empúries, Palau-saverdera, El Port de la Sel...