Research Unix
|
Read other articles:

Disambiguazione – Piazza Affari rimanda qui. Se stai cercando la piazza sede di questo ente, vedi Piazza degli Affari. Borsa ItalianaLogo Palazzo Mezzanotte e Il Dito di Cattelan Stato Italia Forma societariaSocietà per azioni Fondazione1998 a Milano Sede principaleMilano GruppoEuronext Persone chiave Claudia Parzani, presidente Fabrizio Testa, amministratore delegato SettoreFinanza Sito webSito ufficiale Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale La Borsa Italiana è...

RTBFJenistelevisiNegara BelgiaKetersediaanNasionalTanggal peluncuran1930 (radio)1953 (televisi)Situs webwww.rtbf.be RTBF dibentuk tahun 1930. RTBF merupakan stasiun televisi dan radio Belgia. RTBF juga menyediakan berita di internet. Layanan televisi RTBF di Belgia antara lain La Une, La Deux dan La Trois. Kantor pusat stasiun televisi ini berada di Brussels. Serta konsep acaranya tidak terlalu banyak berubah dari stasiun televisi lainnya. Pranala luar Situs resmi Artikel bertopik televi...

Lempeng CocosJenisMinorPerkiraan luas wilayah2,900,000 km2[1]Pergerakan1Utara-TimurKecepatan167mm/tahunWilayahPulau Cocos, Samudra Pasifik1Relatif dengan Lempeng Afrika Detail lempeng tektonik dari: Lempeng tektonik di dunia. Detail lempeng Cocos dan Karibia. From: Plate tectonics map. Lempeng Cocos adalah lempeng tektonik samudra di bawah Samudra Pasifik lepas pantai barat Amerika Tengah dan dinamakan sesuai Pulau Cocos yang terbentang di atasnya. Geologi Lempeng Cocos tercipta dari ...

Chapter of the New Testament Revelation 12← chapter 11chapter 13 →Apocalypse 19. Michael and the angel. Revelation 12:7-9. Scheits. Phillip Medhurst CollectionBookBook of RevelationCategoryApocalypseChristian Bible partNew TestamentOrder in the Christian part27 Revelation 12 is the twelfth chapter of the Book of Revelation or the Apocalypse of John in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. The book is traditionally attributed to John the Apostle,[1][2] but the...

Jordi BolòsBiographieNaissance 17 avril 1955 (68 ans)BarceloneNationalité espagnoleActivités Historien, professeur d'université, écrivainPère Oriol Bolos Capdevilla (en)Autres informationsA travaillé pour Université de LéridaSite web www.blogger.com/profile/13040949313306395284Œuvres principales Repertori d'Antropònims Catalans (d)modifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Jordi Bolòs, né à Barcelone en 1955, est un historien médiéviste catalan, professeur de l'Unive...

Meng Da Meng Da, vaincu par l'armée de Sima Yi, pendant la révolte de Xincheng. général de Wei Naissance inconnueFufeng Décès 228Shangyong Noms Chinois simplifié 孟达 Chinois traditionnel 孟達 Hanyu pinyin Mèng Dá Wade-Giles Mêng Ta modifier Meng Da, nom de courtoisie Zidu, était un général au service du royaume du Wei, en Chine, durant la période des trois royaumes. Il est né à une date inconnue à Fufeng et est mort en 228 à Shangyong. Après avoir servi Liu Zhang et L...

Charles GonthierCharles Gonthier (2007)BiographieNaissance 1er août 1928MontréalDécès 16 juillet 2009 ou 17 juillet 2009Sépulture Cimetière Notre-Dame-des-NeigesNationalité canadienneFormation Faculté de droit de l'Université McGillCollège StanislasActivités Avocat, jugeAutres informationsDistinction Compagnon de l'Ordre du Canadamodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Charles Doherty Gonthier (né le 1er août 1928 à Montréal - mort le 16 juillet 2009 à l'âge de 80 ans...

Form of government This article's lead section may be too long. Please read the length guidelines and help move details into the article's body. (March 2024) Part of the Politics seriesDemocracy HistoryTheoryIndices Types Anticipatory Athenian Cellular Consensus Conservative Cosmopolitan Defensive Deliberative Direct Economic Electronic Empowered Ethnic Grassroots Guided Hybrid regime Inclusive Industrial Jacksonian Jeffersonian Liberal / Illiberal Liquid Majoritarian Media Monitory Multipart...

Public, co-educational school in Wailuku, Hawaii, United StatesHenry Perrine Baldwin High SchoolFront entrance and lawnAddress1650 Ka'ahumanu AvenueWailuku, Hawaii 96793United StatesCoordinates20°53′27″N 156°29′28″W / 20.8908°N 156.4911°W / 20.8908; -156.4911InformationTypePublic, Co-educationalMottoPersonal Responsibility in Developing ExcellenceEstablished1938School districtMaui DistrictPrincipalKeoni WilhelmFaculty83.00 FTE[1]Grades9-12Number of ...

The 17th Politburo Standing Committee, formally the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the 17th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, was elected by the 1st Plenary Session of the 17th Central Committee in 2007, in the aftermath of the 17th National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). It was preceded by the CCP's 16th Politburo Standing Committee and was succeeded by the 18th in 2012. Composition Members of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of t...

Socrates Sofyan YomanLahir15 Desember 1969 (umur 54)Situbondo, Jawa TimurKebangsaanIndonesiaPekerjaanPendeta, aktivis Socrates Sofyan Yoman (lahir 15 Desember 1969) adalah seorang pendeta dan aktivis atau pejuang Gerakan Papua di bidang politik (GSP/P). Ia aktif memperjuangkan kemerdekaan Papua. Pada 8 November 2004, dalam acara peringatan ulang tahun Universitas Cendrawasih, Jayapura, ia menyampaikan makalah berjudul Pepera 1969 di Papua Barat Tidak Demokratis. Ia bersama Tom Beanal, T...

GuadeloupeDépartement d'Outre-Mer de la Guadeloupe— Vùng và tỉnh hải ngoại của Pháp — Hiệu kỳHuy hiệuBiểu trưng chính thức của GuadeloupeBiểu trưngGuadeloupeQuốc gia PhápThủ phủBasse-TerreTỉnh1Chính quyền • President of the Regional CouncilAry ChalusDiện tích • Tổng cộng1.628,43 km2 (628,74 mi2)Dân số (2020) • Tổng cộng390,253 • ...

American cartoonist This article may rely excessively on sources too closely associated with the subject, potentially preventing the article from being verifiable and neutral. Please help improve it by replacing them with more appropriate citations to reliable, independent, third-party sources. (July 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) John PorcellinoPorcellino, photographed at the 2004 Alternative Press Expo (APE) in San Francisco.Born (1968-09-18) September 18, 1968 (age ...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento governi non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Presidente dello Stato di Palestina L’attuale Presidente, Mahmoud Abbas. Nome originale(AR) رئيس دولة فلسطين Stato Palestina TipoCapo di Stato In caricaMahmūd Abbās (Fatah) da8 maggio 2005 Istituito2 aprile 1989 Nominato daEletto dai cittad...

أيمن حسين معلومات شخصية الاسم الكامل أيمن حسين غضبان المفرجي الميلاد 22 مارس 1996 (28 سنة) الحويجة الطول 189 سنتيمتر مركز اللعب مهاجم الجنسية العراق معلومات النادي النادي الحالي القوة الجوية الرقم 9 مسيرة الشباب سنوات فريق 2009–2010 العلم 2011–2012 الطوز 2012–2013 غاز الش...

كأس أمم أوقيانوسيا معلومات عامة الرياضة كرة القدم انطلقت 1973 (منذ 51 سنة) المنظم اتحاد أوقيانوسيا لكرة القدم المنطقة أوقيانوسيا عدد النسخ 21 التواتر كل 4 سنوات (سابقًا سنتين) عدد المشاركين 8 منتخبات في البطولة قائمة الفائزين آخر بطل نيوزيلندا (اللقب السادس) الأكثر تتويجًا &#...
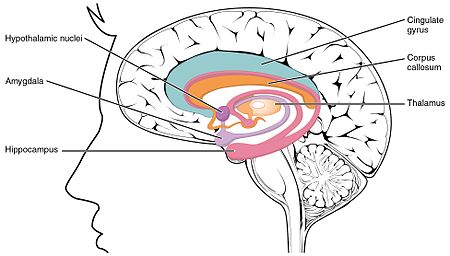
邊緣系統紅色部分為大腦的邊緣系統(包括边缘叶)。边缘叶为边缘系统的主要部分标识字符拉丁文Systema limbicumMeSHD008032NeuroNames(英语:NeuroNames)2055FMAFMA:242000《神经解剖学术语(英语:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy)》[在维基数据上编辑] 邊緣系統(英文:Limbic system)指包含海馬體及杏仁體在內,支援多種功能例如情緒、行為及長期記憶的大腦結構。這種被描述為邊緣�...

Study of cultures, communities, and activities of peoples of the world Original mapping by John Snow showing the clusters of cholera cases in the London epidemic of 1854, which is a classical case of using human geography Part of a series onGeography Portal Outline History of geography Graeco-Roman Chinese Islamic Age of Discovery History of cartography Historical geography Environmental determinism Regional geography Quantitative revolution Critical geography Human geographyFields Cognitive ...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Meije. La Meije La Meije vue du nord, avec le Grand Pic au premier plan Géographie Altitude 3 983 m, Grand pic de la Meije[1] Massif Massif des Écrins (Alpes) Coordonnées 45° 00′ 17″ nord, 6° 18′ 31″ est[1] Administration Pays France Régions Auvergne-Rhône-AlpesProvence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Départements IsèreHautes-Alpes Ascension Première 16 août 1877 par E. Boileau de Castelnau avec P. Gaspard père ...

American filmmaker and producer (1952-2001) Carolyn BeugBorn(1952-12-11)December 11, 1952DiedSeptember 11, 2001(2001-09-11) (aged 48)North Tower, World Trade Center, New York City, U.S.Cause of deathPlane crash during the September 11 attacksOccupation(s)Filmmaker and video producerSpouseJohn BeugChildren3ParentMary Alice Wahlstrom (Mother) Carolyn Ann Mayer-Beug (December 11, 1952 – September 11, 2001) was a filmmaker and video producer from Santa Monica, California. She died in ...
