Polygraphia Nova
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2022. Rumah tradisional Pulau Pinang adalah rumah tradisional masyarakat Pulau Pinang. Jenis ada beberapa macam yaitu rumah bumbung panjang, rumah serambi dan rumah serambi gajah menyusu. Perbedaanya terletak pada bentuk bumbung. Pada rumah serambi gajah me...

Sediment replacement process Beaches along the Gold Coast of Australia have been subjected to a beach nourishment project.[1] Beach nourishment device Beach nourishment (also referred to as beach renourishment,[2] beach replenishment, or sand replenishment) describes a process by which sediment, usually sand, lost through longshore drift or erosion is replaced from other sources. A wider beach can reduce storm damage to coastal structures by dissipating energy across the surf ...

GamelanPerangkat Gamelan JawaPerangkat Gamelan JawaNama lain Bali: Gambelan Sunda: Gamelan Osing: Gyamelan KlasifikasiAlat musik perkusiKlasifikasi Hornbostel-Sachs(SaronDemungPeking (alat musik)GongKempulGender (musik)SlenthemGambangKendangRebabSiterSulingKemanak)PenciptaJawaDikembangkanIndonesia GamelanWarisan Budaya Tak Benda UNESCOAlat musik gamelanNegaraIndonesiaDomainKerajinan tradisional, tradisi lisan dan ekspresi, seni drama, pengetahuan dan praktik tentang alam dan alam ...

Australian politician Giz WatsonMember of the Western Australian Legislative Council for North Metropolitan RegionIn office22 May 1997 – 21 May 2013 Personal detailsBorn (1957-01-18) 18 January 1957 (age 67)Eastleigh, Hampshire, EnglandPolitical partyGreens WADomestic partnerJune Lowe[1]Alma materMurdoch University Elizabeth Mary Giz Watson (born 18 January 1957) is an English-born former Australian politician, and a former leader of The Greens, Western Australia. Biog...

This article is about an Irish drama. For the Singaporean drama, see Prosperity (Singaporean TV series). Irish TV series or programme ProsperityGenreDramaCreated byMark O'HalloranDirected byLenny AbrahamsonCountry of originIrelandOriginal languageEnglishNo. of seasons1No. of episodes4ProductionProducersEd Guiney Catherine MageeProduction locationDublinRunning time60 minutesOriginal releaseNetworkRTÉ TwoReleaseSeptember 3, 2007 (2007-09-03)RelatedBachelors Walk Pure Mule Prospe...

Peter ParkerPeter Parker / Spider-Man interpretato da Tom Holland in Spider-Man: Homecoming (2017) UniversoMarvel Cinematic Universe Basato suUomo Ragno di Stan Lee Steve Ditko AutoriChristopher Markus Stephen McFeely 1ª app. inCaptain America: Civil War (2016) Interpretato daTom Holland Voce orig.Hudson Thames (What If...?, Your Friendly Neighborhood Spider-Man) Voce italianaAlex Polidori Caratteristiche immaginarieAlter ego Spider-Man Scimmia notturna (in inglese Night Monke...

Trekkies beralih ke halaman ini. Untuk the film, lihat Trekkies (film). Trekker beralih ke halaman ini. Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Trekker (disambiguasi). Artikel ini perlu dikembangkan dari artikel terkait di Wikipedia bahasa Inggris. (Juli 2023) klik [tampil] untuk melihat petunjuk sebelum menerjemahkan. Lihat versi terjemahan mesin dari artikel bahasa Inggris. Terjemahan mesin Google adalah titik awal yang berguna untuk terjemahan, tapi penerjemah harus merevisi kesalahan yang diperlu...

Scottish Labour politician Colin SmythMSPSmyth in 2017Member of the Scottish Parliamentfor South Scotland(1 of 7 Regional MSPs)IncumbentAssumed office 6 May 2016Scottish Labour portfolios2017–2021Shadow Cabinet Secretary for Transport, Infrastructure and Connectivity2021–presentShadow Cabinet Secretary for Constitution, Europe and External Affairs Personal detailsBornNovember 1972 (age 51)Dumfries, ScotlandPolitical partyScottish LabourAlma materUniversity of GlasgowWebsiteO...

Unterseeboot 622 U-Boot type VIIC Autres noms U-622 Type Sous-marin Type VIIC Classe Type VIIC (d) Histoire A servi dans Kriegsmarine Commanditaire Kriegsmarine Chantier naval Blohm & Voss - Hambourg N° de coque : 598 Commandé 15 août 1940 Quille posée 1er juillet 1941 Lancement 19 mars 1942 Mise en service 14 mai 1942 Commission 14 mai 1942, commandant Horst-Thilo Queck Statut Coulé le 24 juillet 1943 Équipage Commandant Horst-Thilo Queck Équipage 4 officiers - 40 ...

Lambang Komune Grandpuits-Bailly-Carrois. Grandpuits-Bailly-CarroisNegaraPrancisArondisemenMelunKantonMormantAntarkomuneCommunauté de communes La Brie NangissiennePemerintahan • Wali kota (2008-2014) Jean-Jacques Brichet • Populasi1953Kode INSEE/pos77211 / 2 Population sans doubles comptes: penghitungan tunggal penduduk di komune lain (e.g. mahasiswa dan personil militer). Grandpuits-Bailly-Carrois merupakan sebuah komune di departemen Seine-et-Marne di region Î...

American politician (born 1936) This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (March 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) This biography of a living person ne...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会马来西亚代表團马来西亚国旗IOC編碼MASNOC马来西亚奥林匹克理事会網站olympic.org.my(英文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員30參賽項目10个大项旗手开幕式:李梓嘉和吳柳螢(羽毛球)[1][2]閉幕式:潘德莉拉(跳水)[3]獎牌榜排名第74 金牌 銀牌 銅�...

Feria de la Flor Celebración del 50 aniversario en la feria de 2013.LocalizaciónPaís MéxicoLocalidad Zacatelco, MéxicoDatos generalesTipo Cultural, Turística y ArtesanalCelebrada por Sagrado Corazón de JesúsSede Plaza XochicalcoFecha 10 al 21 de junioOrganizador Patronato de ZacatelcoMotivo Expo venta de florDuración 11 díasPrimer evento 1963 Feria de Zacatelco Feria de la Flor Feria del Cacao [editar datos en Wikidata] La Feria de la Flor (originalmente: Feria ...
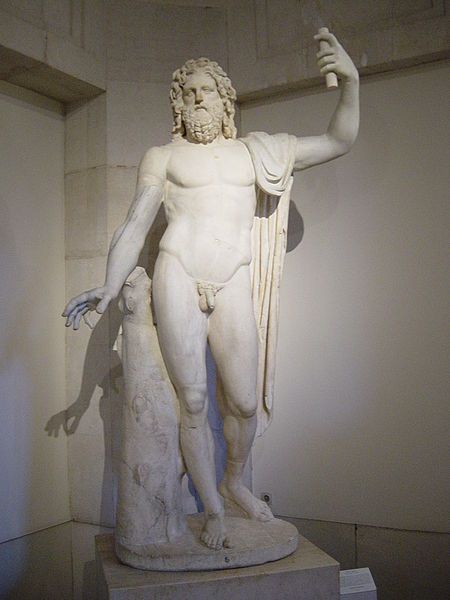

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando il comune della Romania nel distretto di Dolj, vedi Cârna. Questa pagina sull'argomento mitologia sembra trattare argomenti unificabili alla pagina Cardea. Puoi contribuire unendo i contenuti in una pagina unica. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Questa voce sull'argomento mitologia romana è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Carna (...

Sam TeviNazionalità Stati Uniti Altezza198 cm Peso141 kg Football americano RuoloOffensive tackle Squadra Indianapolis Colts CarrieraGiovanili 2013-2016 Utah Utes Squadre di club 2017-2020 Los Angeles Chargers2021- Indianapolis Colts StatistichePartite58 Partite da titolare44 Statistiche aggiornate al 20 maggio 2021 Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Samiuela Tevi (Euless, 15 novembre 1994) è un giocatore di football americano statunitense che milita nel ...

Square dance caller organization CallerlabFounded1974TypeSquare Dance Callers AssociationPurposeTo recruit, promote, and maintain the square dance activity.HeadquartersGreenwood, IndianaWebsitecallerlab.orgSee also: American Callers Association CALLERLAB is the international association of square dance callers, and is the largest square dance association in the United States. CALLERLAB provides guidance and education, certifying caller coaches, maintaining standardized lists of calls and defi...
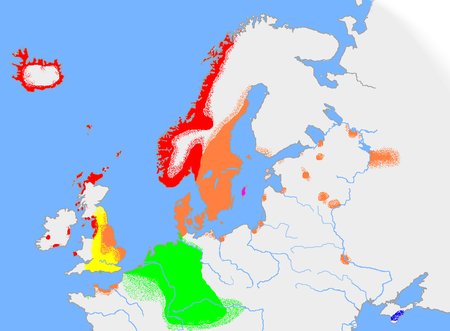
Шведский язык Самоназвание svenska Страны Швеция, Финляндия Регионы Северная Европа Официальный статус Швеция Финляндия Аландские острова Европейский союз Регулирующая организация Шведский языковой совет в Швеции (полуофициальный статус) и Шведское яз�...

VÀO RA A B A AND B 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 Cổng AND là một cổng logic dùng để thực hiện hàm AND hai hay nhiều biến. Cổng AND có các ngõ vào tùy thuộc số biến và một ngõ ra. Ngõ ra của cổng là hàm AND của các biến ngõ vào. Bên phải là bảng chân trị mô tả hoạt động của cổng AND 2 ngõ vào A và B. Ký hiệu Ký hiệu theo chuẩn ANSI Ký hiệu theo chuẩn IEC Ký hiệu theo chuẩn DIN Toán học Phương trình c...

No tengo dinerosingolo discograficoScreenshot tratto dal video del branoArtistaRigheira Pubblicazione1983 Durata3:20 Album di provenienzaRigheira Dischi1 Tracce2 GenereItalo disco EtichettaCGD ProduttoreLa Bionda Formati7 Righeira - cronologiaSingolo precedenteVamos a la playa(1983)Singolo successivoHey Mama(1984) No tengo dinero è un singolo del duo musicale italiano Righeira, pubblicato nel 1983 come terzo estratto dal primo album in studio Righeira. Indice 1 Tracce 2 Formazione 3 Classifi...

Florence Owens ThompsonMigrant Mother, diambil oleh Dorothea Lange tahun 1936.LahirFlorence Leona Christie(1903-09-01)1 September 1903Oklahoma, Amerika SerikatMeninggal16 September 1983(1983-09-16) (umur 80)Scotts Valley, California, Amerika SerikatMakamLakewood Memorial ParkKebangsaanAmerika SerikatPekerjaanBuruh pertanianDikenal atasFoto oleh Dorothea LangeSuami/istriCleo Owens (c.1898–c.1931) m. 1921 George B. Thompson (1902–1974) m.?Anak7 Florence Owens Thompson (1 September 190...
