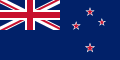
National Māori flag
|
Read other articles:

Women's 30 kilometre freestyleat the XVIII Olympic Winter GamesVenueSnow HarpDates20 FebruaryCompetitors68 from 25 nationsWinning time1:22:01.5Medalists Yuliya Chepalova Russia Stefania Belmondo Italy Larisa Lazutina Russia← 19942002 → Cross-country skiing at the1998 Winter Olympics5 kmwomen10 kmmenPursuitmenwomen15 kmwomen30 kmmenwomen50 kmmenRelaymenwomenvte The women's 30 kilometre freestyle cross-country skiing competition at the 1998 Winter ...

Yordania merupakan bagian tak terpisahkan dari dunia Arab sehingga tradisi budaya Arab mendominasi daerah itu. Salah satunya mengenai makna keluarga.[1] Meskipun jumlah mereka telah turun karena banyak yang telah menetap dan mengadopsi budaya urban, penduduk Badui pedesaan mempertahankan cara hidup yang lebih tradisional, melestarikan kebiasaan yang diwariskan dari generasi ke generasi.[1] Kehidupan desa berputar di sekitar keluarga besar, pertanian, dan perhotelan; modernitas...

Indian politician Tiruvellore Thattai KrishnamachariKrishnamachari in 2002 stamp of IndiaMember of Parliament, Lok Sabha for Madras SouthIn office1957–1962Prime MinisterPandit NehruPreceded byNoneMember of Parliament, Lok Sabha for MadrasIn office1951–1957Prime MinisterPandit Jawaharlal NehruPreceded byNoneSucceeded byBifurcated into Madras North and Madras South constituencies Personal detailsBorn1899Madras, British IndiaDied1974 (age 74-75)Political partyIndian National CongressChildren...

This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: List of important publications in physics – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) This list has no precise inclusion criteria as described in the Manual of Style for standalone lists. Please improve this article by adding inclusion criteria, o...

National forest in Pennsylvania, United States Allegheny National ForestMead Run in the Allegheny National ForestLocationWarren, McKean, Forest, and Elk counties, Pennsylvania, USANearest cityWarren, PACoordinates41°39′11″N 79°2′5″W / 41.65306°N 79.03472°W / 41.65306; -79.03472Area513,175 acres (2,076.75 km2)[1]EstablishedSeptember 24, 1923[2]Governing bodyU.S. Forest ServiceWebsiteAllegheny National Forest The Allegheny Natio...

ヨハネス12世 第130代 ローマ教皇 教皇就任 955年12月16日教皇離任 964年5月14日先代 アガペトゥス2世次代 レオ8世個人情報出生 937年スポレート公国(中部イタリア)スポレート死去 964年5月14日 教皇領、ローマ原国籍 スポレート公国親 父アルベリーコ2世(スポレート公)、母アルダその他のヨハネステンプレートを表示 ヨハネス12世(Ioannes XII、937年 - 964年5月14日)は、ロ...

Untuk perusahaan jamu, lihat Jamu Air Mancur.Sebuah animasi yang itofmemperlihatkan air mancur. Air mancur adalah sebuah aliran air yang menyebar secara diagonal dari sebuah sumber air. Air mancur bisa berupa air mancur dinding atau air mancur berdiri. Air mancur dapat dibuat dengan wadah yang terbuat dari berbagai bahan konstruksi seperti batu, beton atau logam. Pengaliran air di dalam air mancur dapat ditata menjadi beberapa tingkatan. Sumber air pada air mancur umumnya berasal dari wadah b...

Richard Alan Rick MastracchioLahir11 Februari 1960 (umur 64)Waterbury, ConnecticutStatusPurnawirawanKebangsaanAmerika SerikatPekerjaanInsinyurKarier luar angkasaAntariksawan NASAWaktu di luar angkasa227 hari, 13 jam , 38 menitSeleksi1996 NASA GroupTotal EVA9Total waktu EVA53 jam, 4 menitMisiSTS-106, STS-118, STS-131, Soyuz TMA-11M (Expedition 38/39)Lambang misi Richard Alan Rick Mastracchio (lahir 11 Februari 1960) adalah seorang insinyur Amerika Serikat dan mantan antariksawan NASA. Ia...

Highway designed for high-speed, regulated traffic flow Control of access, Freeway, and Motorway redirect here. For the security concept, see Access management. For the 2012 Chinese film, see Motorway (film). For other uses, see Freeway (disambiguation) and Motorway (disambiguation). The cloverleaf interchange between US 131, M-6 and 68th Street in Cutlerville, Michigan, United States, shows many of the features of controlled-access highways: entry and exit ramps, median strips for oppos...

Enrico Bombieri Premio Caccioppoli 1966 Medaglia Fields nel 1974 Enrico Bombieri (Milano, 26 novembre 1940) è un matematico italiano, primo italiano a ricevere la medaglia Fields, nel 1974. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Attività scientifica 3 L'ipotesi di Riemann 4 Onorificenze 5 Note 6 Bibliografia 7 Altri progetti 8 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Dotato di un talento precocissimo, pubblicò il suo primo articolo scientifico a soli 17 anni, nel 1957. Laureato all'Università degli Studi di Milano c...

South Korean singer (born 1994) For the eponymous EP, see Kai (EP). In this Korean name, the family name is Kim. KaiKai in March 2023BornKim Jong-in (1994-01-14) January 14, 1994 (age 30)Suncheon, South Jeolla, South KoreaEducationSchool of Performing Arts SeoulOccupationsSingeractordancermodelYears active2011 (2011)–presentMusical careerGenresK-popR&BHip hop soulInstrument(s)VocalsLabelsSMMember ofExoExo-KSM TownYounique UnitSuperMWebsiteOfficial website Musical artistKo...

Compromiso por Galicia Secretario/a general Juan Carlos PiñeiroFundación 2012Ideología Galleguismo Progresismo Reformismo Europeísmo [1]Posición CentroizquierdaPartidoscreadores Ver lista Máis Galiza Acción Galega Partido Nacionalista Galego-Partido Galeguista (PNG-PG) Partido Galeguista Demócrata (PGD) Coalición Galega (CG) Unidade Veciñal 26 de abril de Carral Partido Galeguista de A Estrada Espazo Ecosocialista Galego Sede Rúa Concheiros, 37 1º derecha, 15703, Santiago de...

Croatian water polo player (born 1973) Samir BaraćBarać at 2012 Summer OlympicsPersonal informationBorn (1973-11-02) November 2, 1973 (age 50)Rijeka, YugoslaviaSportSportWater polo Medal record Representing Croatia Olympic Games 2012 London Team World Championship 2007 Melbourne Team competition 2009 Rome Team competition 2011 Shanghai Team competition European Championship 2010 Zagreb Team competition 1999 Florence Team competition 2003 Kranj Team competition World Cup 2010 Orad...

American actress and writer Nicole DubucDubuc receiving the AWC WGA Award (2018)BornNicole Danielle Dubuc (1978-11-06) November 6, 1978 (age 45)Orange County, California, U.S.Occupation(s)Actress, writerYears active1983–presentSpouse Brian Hohlfeld (m. 2014) Nicole Danielle Dubuc (born November 6, 1978) is an American actress and writer, known for her work on the Transformers franchise, including Transformers: Prime, Rescue Bots, Rescue Bots Academy,...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant l’environnement, la conservation de la nature, les réserves naturelles et autres zones protégées et la région Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Réserve naturelle nationale des Pics du CombeynotLe col du Lautaret devant les pics de Combeynot.GéographiePays FranceRégion Provence-Alpes-Côte d'AzurDépartement Hautes-AlpesCo...

RighteousAmong the Nations The Holocaust Rescuers of Jews Righteousness Seven Laws of Noah Yad Vashem By country Austrian Croatian Czech German Hungarian Lithuanian Norwegian Polish (list) Romanian Serbian Ukrainian vte During the occupation of Norway by Nazi Germany, its Jewish community was subject to persecution and deported to extermination camps. Although at least 764 Jews in Norway were killed, over 1,000 were rescued with the help of non-Jewish Norwegians who risked their lives to smu...

Railway station in Pakistan Landi Kotal Railway Stationد لنډي کوتل د اورګاډي اډهLandi Kotal station in 1939 or 1940, photo by Annemarie SchwarzenbachGeneral informationLocationTorkham Road PakistanCoordinates34°05′36″N 71°08′49″E / 34.093461°N 71.146862°E / 34.093461; 71.146862Owned byMinistry of RailwaysLine(s)Khyber Pass RailwayTracks4Other informationStatusClosedStation codeLDKNHistoryOpened3 November 1925 (1925-11...

The final of the 2005–06 edition of the UEFA Champions League Football match2006 UEFA Champions League finalEvent2005–06 UEFA Champions League Barcelona Arsenal 2 1 Date17 May 2006VenueStade de France, Saint-DenisMan of the MatchSamuel Eto'o (Barcelona)[1]RefereeTerje Hauge (Norway)Attendance79,610[1]WeatherPartly cloudy15 °C (59 °F)33% humidity[2]← 2005 2007 → The 2006 UEFA Champions League final was an association football match between Ba...

Serbian politician, diplomat, physician and prolific writer For the Serbian volleyball player, see Vladan Đorđević (volleyball). Vladan ĐorđevićВладан ЂорђевићPrime Minister of SerbiaIn office11 October 1897 – 12 July 1900MonarchAlexander IPreceded byĐorđe SimićSucceeded byAleksa Jovanović Personal detailsBorn(1844-11-21)21 November 1844Belgrade, Principality of SerbiaDied31 August 1930(1930-08-31) (aged 85)Baden bei Wien, AustriaPolitical partySerbian ...

Mythical being or legendary creature in European folklore For other uses, see Fairy (disambiguation). Fay redirects here. For other uses, see Fay (disambiguation). Fairy1888 illustration by Luis Ricardo Falero of common modern depiction of a fairy with butterfly wingsGroupingLegendary creaturePixieSpriteTuatha Dé DanannFirst attestedIn folkloreRegionEurope A fairy (also fay, fae, fey, fair folk, or faerie) is a type of mythical being or legendary creature, generally described as anthropomorp...