NRLA
|
Read other articles:

Butch HartmanHartman pada tahun 2020LahirElmer Earl Hartman IV10 Januari 1965 (umur 59)Highland Park, Michigan, Amerika SerikatPendidikanAnchor Bay High SchoolAlmamaterCalifornia Institute of the ArtsPekerjaanAnimator, penulis, produser, sutradara, pengisi suaraTahun aktif1986–sekarangKarya terkenalThe Fairly OddParentsDanny PhantomT.U.F.F. PuppyBunsen Is a BeastSuami/istriJulieann Hartman (m. 1992)Anak2 Elmer Earl Butch Hartman IV (lahir 10 Januari...

2005 video gameFIFA 06: Road to FIFA World CupCover art featuring RonaldinhoDeveloper(s)EA CanadaPublisher(s)EA SportsSeriesFIFAFIFA World CupPlatform(s)Xbox 360ReleaseNA: 22 November 2005EU: 2 December 2005JP: 10 December 2005KOR: 25 February 2006[1][better source needed]Genre(s)SportsMode(s)Single player, multiplayer, multiplayer online FIFA 06: Road to FIFA World Cup is a video game developed by EA Sports and DICE for the Xbox 360. The game is an officially licen...

Untuk pemain sepak bola Amerika Serikat, lihat Ralph Nelson (pemain sepak bola Amerika Serikat). Artikel ini membutuhkan rujukan tambahan agar kualitasnya dapat dipastikan. Mohon bantu kami mengembangkan artikel ini dengan cara menambahkan rujukan ke sumber tepercaya. Pernyataan tak bersumber bisa saja dipertentangkan dan dihapus.Cari sumber: Ralph Nelson – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR (March 2016) Ralph NelsonPortrait of Ralph Nel...

Ludvig HolbergLahir(1684-12-03)3 Desember 1684Bergen, Denmark-Norwegia (sekarang Norwegia)Meninggal28 Januari 1754(1754-01-28) (umur 69)Kopenhagen, Denmark-Norwegia (sekarang Denmark)Pekerjaan Penulis penulis esai filsuf sejarawan dramawan KebangsaanNorwegia[1]KewarganegaraanDenmark-Norwegia[2]Tanda tangan Ludvig Holberg, Baron of Holberg (3 Desember 1684 – 28 Januari 1754) adalah seorang penulis, penulis esai, filsuf, sejarawan dan penulis drama yang...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Chartres. Chartres-de-Bretagne L'église Notre-Dame. Blason Logo Administration Pays France Région Bretagne Département Ille-et-Vilaine Arrondissement Rennes Intercommunalité Rennes Métropole Maire Mandat Philippe Bonnin (DVG) 2020-2026 Code postal 35131 Code commune 35066 Démographie Gentilé Chartrains Populationmunicipale 8 237 hab. (2021 ) Densité 816 hab./km2 Population agglomération 395 710 hab. Géographie Coordonnées ...

Scottish Division One 1958-1959 Competizione Scottish Division One Sport Calcio Edizione 62ª Organizzatore SFL Date dal 20 agosto 1958al 21 aprile 1959 Luogo Scozia Partecipanti 18 Formula Girone all'italiana A/R Risultati Vincitore Rangers(31º titolo) Retrocessioni FalkirkQueen of the South Statistiche Miglior marcatore Joe Baker (25) Incontri disputati 306 Gol segnati 1 195 (3,91 per incontro) Cronologia della competizione 1957-58 1959-60 Manuale La Scottish ...

Wilfred Thesiger durante la seconda traversata dell'Empty Quarter.[1] Sir Wilfred Patrick Thesiger (Addis Abeba, 3 giugno 1910 – Londra, 24 agosto 2003) è stato un esploratore e scrittore britannico nato in Etiopia. Wilfred Thesiger nel 1934 Anche chiamato col nome arabo di Mubarak bin Landan (in lettere arabe: مُبَارَك بِن لَنْدَن, ossia il benedetto di Londra) fu un ufficiale militare. I suoi libri di viaggi più famosi includono Sabbie Arabe (1959), compiuto a ...

Logistics-focused staff corps of the United States Navy U.S. Navy Supply CorpsSupply Corps Oakleaf insigniaActive23 February 1795 – presentCountryUnited States of AmericaAllegiance U.S.BranchU.S. Navy (Active & Reserve Component)TypeStaff CorpsRoleSustain U.S. Navy and U.S. Military Operations worldwideSize~2200 Supply Officers (May 2018)Part ofNaval Supply Systems CommandNickname(s)Suppo, Chop'’Motto(s)Ready for SeaAnniversaries23 FebruaryEngagementsEvery U.S. engagement since t...

Pemerintahan sipil-militerВійськово-цивільні адміністраціїLogo Pusat Anti-Teroris dari Dinas Keamanan UkrainaPemerintahan terkonsentrasi di Zona Operasi Anti-Teroris, diberi warna merah jambu dan kuning.LetakUkrainaDibentuk diOblast Donetsk dan LuhanskDibentuk olehVerkhovna Rada law No.141-VIIIAdopted on 26 February 2015[1]Jumlah wilayah14[2] (hingga 3 Maret 2015)Status tambahanUnit pemerintahan lokal Pemerintahan sipil-militer (Ukr...

هذه المقالة عن المجموعة العرقية الأتراك وليس عن من يحملون جنسية الجمهورية التركية أتراكTürkler (بالتركية) التعداد الكليالتعداد 70~83 مليون نسمةمناطق الوجود المميزةالبلد القائمة ... تركياألمانياسورياالعراقبلغارياالولايات المتحدةفرنساالمملكة المتحدةهولنداالنمساأسترالي�...

爱德华·谢瓦尔德纳泽ედუარდ შევარდნაძე第2任格鲁吉亚總統任期1995年11月26日—2003年11月23日前任茲維亞德·加姆薩胡爾季阿继任米哈伊尔·萨卡什维利苏联外交部部长任期1985年7月2日—1990年12月20日总书记米哈伊尔·戈尔巴乔夫前任安德烈·葛罗米柯继任亚历山大·别斯梅尔特内赫 个人资料出生(1928-01-25)1928年1月25日苏联外高加索苏维埃联邦社会主义共和国古...

American guitarist and singer For the actor, see Kirk Douglas. Captain Kirk DouglasDouglas in 2008Background informationBirth nameKirk DouglasBorn (1973-09-30) September 30, 1973 (age 50)OriginLong Island, New York, U.S.GenresHip hop, Neo soul, Soul, Funk, R&B, Alternative rock, PopOccupationsMusician, SongwriterInstrumentsGuitar, Ukulele, VocalsYears active1993–presentMusical artist Captain Kirk Douglas (born September 30, 1973) is an American guitarist and singer who performs wit...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (سبتمبر_2012) لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع كلية الحاسبات والذكاء الاصطناعي (توضيح). لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع كلية الحاسبات �...

Методологія (грец. μεθοδολογία — вчення про метод) — сукупність прийомів дослідження, що застосовуються в науці; вчення про методи пізнання та перетворення дійсності[1]. Основу методології складає мислення та світогляд, як операційне середовище самодисципліни та...
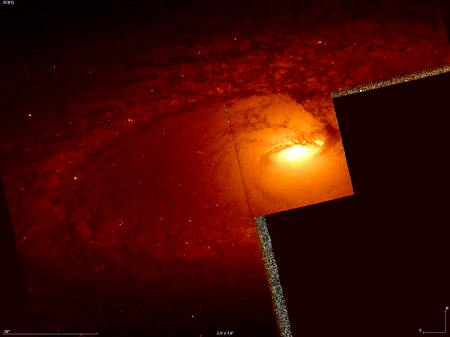
NGC 4274 المكتشف ويليام هيرشل تاريخ الاكتشاف 13 مارس 1785 رمز الفهرس NGC 4274 (الفهرس العام الجديد)PGC 39724 (فهرس المجرات الرئيسية)2MASX J12195066+2936529 (Two Micron All-Sky Survey, Extended source catalogue)MCG+05-29-060 (فهرس المجرات الموروفولوجي)IRAS F12173+2953 (IRAS)IRAS 12173+2953 (IRAS)UGC 7377 (فهرس أوبسالا العام)Z 158-71 (فهرس المجرات وعن...

Development of agricultural output of Cuba in 2015 US$ since 1961 A sugarcane plantation in rural Cuba Agriculture in Cuba has played an important part in the economy for several hundred years. Today, it contributes less than 10% to the gross domestic product (GDP), but it employs about 20% of the working population. About 30% of the country's land is used for crop cultivation.[1] History Cuba's agricultural history can be divided into five periods, reflecting Cuban history in general...
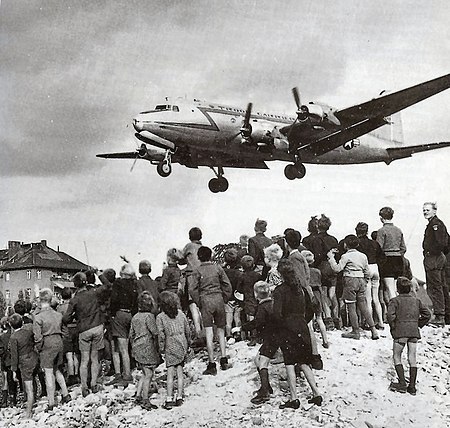

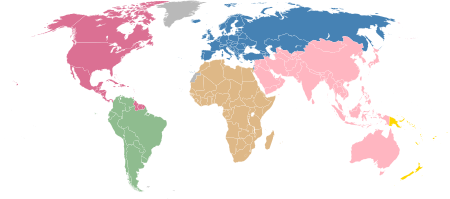
Phase of the Cold War 1953 World Map of alignments. Part of a series onHistory of the Cold War Origins World War II Hiroshima and Nagasaki Eastern Bloc Western Bloc Iron Curtain Periods Cold War (1947–1948) Cold War (1948–1953) Cold War (1953–1962) Cold War (1962–1979) Cold War (1979–1985) Cold War (1985–1991) Frozen conflicts Related topics Arab Cold War Cold War in Asia Historiography List of related conflicts Post-Soviet conflicts Reagan Doctrine Second Cold War Timeline of eve...
National association football team This article uses bare URLs, which are uninformative and vulnerable to link rot. Please consider converting them to full citations to ensure the article remains verifiable and maintains a consistent citation style. Several templates and tools are available to assist in formatting, such as reFill (documentation) and Citation bot (documentation). (August 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Thailand Under-20Nickname(s)ช้างศึก(The War...

此條目没有列出任何参考或来源。 (2013年12月7日)維基百科所有的內容都應該可供查證。请协助補充可靠来源以改善这篇条目。无法查证的內容可能會因為異議提出而被移除。 雪月花(讀法為せつげつか或せつげっか)是日本的慣用語之一,代表自然界的美麗景物,和語叫「月雪花(つきゆきはな)」。其典故出自中國唐朝詩人白居易的七言律詩《寄殷協律》: 五歲優游同�...

I-180 I-180-3 prototype Role FighterType of aircraft Manufacturer Polikarpov Designer Nikolai Nikolaevich Polikarpov First flight 15 December 1938 Status Cancelled Primary user Soviet Air Forces Produced 1938–1940 Number built 10 production + 3 prototypes Developed from Polikarpov I-16 Developed into Polikarpov I-185 The Polikarpov I-180 (Russian: И-180) was a 1938 Soviet fighter prototype. It was the last attempt to extract performance from the basic Polikarpov I-16 design.[1 ...


