Mertensia
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2022. Eutocius dari Ascalon (Lahir tahun 480 – wafat tahun 540) merupakan seorang matematik berkebangsaan Yunani yang menulis komentar di dalam beberapa acuan Archimedes dan di dalam Apollonian Conics. Kehidupan dan Karya Tidak banyak yang diketahui tenta...

Archidendron hendersonii Status konservasi Rentan (EPBC Act) Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Plantae Filum: Magnoliophyta Kelas: Magnoliopsida Ordo: Fabales Famili: Fabaceae Subfamili: Mimosoideae Genus: Archidendron Spesies: A. hendersonii Nama binomial Archidendron hendersonii(F.Muell.) & I.C.Nielsen Sinonim Pithecellobium hendersonii F.Muell. Abarema hendersonii (F.Muell.) Kosterm. Archidendron hendersonii adalah pohon hutan hujan di Australia bagian timur. Tumbuhan ini termasu...

Wakil Menteri Pendayagunaan Aparatur Negara dan Reformasi Birokrasi IndonesiaBekas jabatan politikLogo Kementerian Pendayagunaan Aparatur Negara dan Reformasi Birokrasi IndonesiaEko Prasojo, Wakil Menteri Pendayagunaan Aparatur Negara dan Reformasi Birokrasi Indonesia pertama dan terakhirPejabat pertamaEko PrasojoPejabat terakhirEko PrasojoPelantikPresiden IndonesiaJabatan dimulai19 Oktober 2011; 12 tahun lalu (2011-10-19)Jabatan berakhir20 Oktober 2014; 9 tahun lalu (2014-10-20) Wa...

Wilayah Shikoku 四国WilayahWilayah Shikoku di JepangLuas • Total18.297,78 km2 (7,064,81 sq mi)Populasi (Oktober 1, 2015) • Total3.845.534 • Kepadatan210,2/km2 (544/sq mi)Zona waktuUTC+09:00 Shikoku (四国code: ja is deprecated , harafiah: empat provinsi) adalah pulau terkecil dan yang paling sedikit jumlah penduduknya di antara empat pulau utama Jepang. Daerah Shikoku - yang terdiri dari seluruh pulau Shikoku - meliputi sekitar 1...

والاس بروكر (بالإنجليزية: Wallace Smith Broecker) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 29 نوفمبر 1931 [1] شيكاغو الوفاة 18 فبراير 2019 (87 سنة) [1][2] مانهاتن[1] سبب الوفاة فشل القلب الاحتقاني [لغات أخرى][1] مواطنة الولايات المتحدة عضو في الجمعية الملكي�...

English VinglishPoster rilis teatrikalSutradaraGauri ShindeProduserSunil LullaR. BalkiRakesh JhunjhunwalaR. K. DamaniSkenarioGauri ShindeCeritaGauri ShindePemeranSrideviMehdi NebbouPriya AnandAdil HussainPenata musikAmit TrivediSinematograferLaxman UtekarPenyuntingHemanti SarkarPerusahaanproduksiHope ProductionsDistributorEros InternationalTanggal rilis 14 September 2012 (2012-09-14) (TIFF) 05 Oktober 2012 (2012-10-05) (India) Durasi133 minutes[1]NegaraIndiaBah...

Rajive VermaVerma di Ravindra Bhavan, Bhopal pada 2015Lahir28 Juni 1949 (umur 74)Hoshangabad, Central Provinces and Berar, IndiaPekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif1987–sekarang Rajive Verma (lahir 28 Juni 1949) adalah seorang pemeran India.[1][2] Ia telah berkarya dalam film dan televisi. Referensi ^ Getting 'intimate' art!. Indiatimes. 5 January 2010. Diarsipkan dari versi asli tanggal 5 April 2012. Diakses tanggal 28 March 2011. Parameter |url-status= yang ti...

Austronesian language of Lifou Island, New Caledonia DrehuRegionLifou, New CaledoniaNative speakersunknown; est. 13,000 includes many L2 speakers (2009)[1]Language familyAustronesian Malayo-PolynesianOceanicSouthern OceanicNew Caledonian – LoyaltiesLoyalty IslandsDrehuLanguage codesISO 639-3dhvGlottologdehu1237Drehu is not endangered according to the classification system of the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in DangerThis article contains IPA phonetic symbols. Without p...

Sporting event delegationKiribati at theCommonwealth GamesCGF codeKIRCGAKiribati National Olympic CommitteeWebsiteoceaniasport.com/kiribatiMedalsRanked =48th Gold 1 Silver 0 Bronze 0 Total 1 Commonwealth Games appearances (overview)1998200220062010201420182022 Kiribati have competed in five Commonwealth Games, making their debut in 1998 and attending every subsequent Games to date.[1] At the 2014 Commonwealth Games, David Katoatau won Kiribati's first medal, a gold, in men's weightlif...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2017年12月19日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:若望保祿二世 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 �...

Fairy Tale童話Album studio karya Michael WongDirilis2005-01-21GenreMandarin popLabelRock RecordsKronologi Michael Wong Ray of Light(2002)Ray of Light2002 Fairy Tale(2005) Commitment(2006)Commitment2006 Fairy Tale (Hanzi tradisional: 童話; Hanzi: Tóng Huà) adalah album solo ketiga penyanyi Malaysia, Michael Wong yang dirilis pada tanggal 21 Januari 2005. Lagu yang ada Intro 童話 (Tóng Huà; Fairy Tale) 天堂 (Tiān Táng; Heaven) 少年 (Shào Nián; Teenager) 手機留言 (S...

مارك كانتون معلومات شخصية الميلاد 19 يونيو 1949 (75 سنة) كوينز مواطنة الولايات المتحدة عدد الأولاد 3 إخوة وأخوات نيل كانتون الحياة العملية المدرسة الأم جامعة كاليفورنيا المهنة منتج أفلام المواقع IMDB صفحته على IMDB تعديل مصدري - تعديل مارك كانتون ...
57th season in franchise history 2005 Cleveland Browns seasonGeneral managerPhil SavageHead coachRomeo CrennelHome fieldCleveland Browns StadiumLocal radioWTAM · WMMSResultsRecord6–10Division place4th AFC NorthPlayoff finishDid not qualifyPro BowlersNone ← 2004 Browns seasons 2006 → The 2005 season was the Cleveland Browns' 53rd in the National Football League (NFL) and their 57th overall. It was their 1st season under general manager Phil Savage an...

Bandar Udara Frans KaisiepoFrans Kaisiepo AirportIATA: BIKICAO: WABBInformasiJenisPublikPemilikPT Aviasi Pariwisata Indonesia (Persero)PengelolaPT Angkasa Pura I[1]MelayaniPulau BiakLokasiBiak, Kabupaten Biak Numfor, Papua, IndonesiaZona waktuWIT (UTC+09:00)Ketinggian dpl14 mdplKoordinat01°11′24″S 136°06′27″E / 1.19000°S 136.10750°E / -1.19000; 136.10750Koordinat: 01°11′24″S 136°06′27″E / 1.19000°S 136.10750°E&#...

Presidential library in Simi Valley, California Ronald Reagan Presidential LibraryShow map of the Los Angeles metropolitan areaShow map of CaliforniaShow map of the United StatesGeneral informationLocationSimi Valley, California, United StatesCoordinates34°15′34″N 118°49′10″W / 34.2595°N 118.8194°W / 34.2595; -118.8194Named forRonald ReaganConstruction startedNovember 21, 1988CompletedNovember 4, 1991Cost$60 million USDManagementNational Archives and Record...

Mountain in Apache County, Arizona, United States Mount BaldyMount Baldy from a US Forest Service webcamHighest pointElevation11,409 ft (3,477 m) NAVD 88[1]Prominence4,723 ft (1,440 m)[2]ListingNorth America isolated peaks 81stArizona county high point[3]Coordinates33°54′21″N 109°33′45″W / 33.905940617°N 109.562632281°W / 33.905940617; -109.562632281[1]GeographyMount Baldy LocationApache Cou...

أوجهاممعلومات عامةالبداية القرن 4[1] الاسم Ogham (بالإنجليزية) [2]ogam (بالفرنسية) [2] الاسم الأصل ᚛ᚑᚌᚐᚋ᚜ (بالأيرلندية) لغة العمل أو لغة الاسم Primitive Irish (en) Old Irish (en) Pictish (en) تاريخ الانتهاء القرن 10 اتجاه الكتابة bottom-to-top (en) [3]من اليسار نحو اليمين[3] مستوى يونيكود U+1...

صبغي 12زوج صبغي 12 بشري (بعد ارتباط جي).واحد من الأم والآخر من الأب.زوج الصبغي 12 لرجل كما تظهر بواسطة الكاريوغرام.المواصفاتالطول (زوج قواعد)133,275,309 bpعدد المورثات1,950النوعصبغي جسميموقع القطعة المركزية[[قسيم مركزي#{{{centromere position}}}|موسطاني]][1]المعرفاتقاعدة بيانات مرجعيةNC_000012بنك...
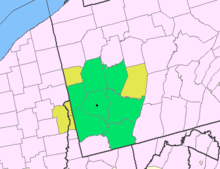
Unincorporated community in Pennsylvania, United StatesKecksburg, PennsylvaniaUnincorporated communityKecksburg, PennsylvaniaLocation within the U.S. state of PennsylvaniaCoordinates: 40°11′05″N 79°27′41″W / 40.18472°N 79.46139°W / 40.18472; -79.46139CountryUnited StatesStatePennsylvaniaCountyWestmorelandFounded byJohann Martin KeckElevation1,209 ft (369 m)Time zoneUTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) • Summer (DST)UTC-4 (EDT) Kecksburg is an uninco...

建議将此條目或章節併入TVB星河頻道重播電視劇列表。(討論) 此條目没有列出任何参考或来源。 (2019年1月1日)維基百科所有的內容都應該可供查證。请协助補充可靠来源以改善这篇条目。无法查证的內容可能會因為異議提出而被移除。 本列表列出香港TVB星河頻道重播的劇集。 首映年份 電視劇集名稱 集數 2012年翡翠台劇集 愛·回家_(第一輯)Come Home Love 804 首映年份 電視劇�...


![Aspen Bluebells (Mertensia arizonica)[25]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b4/Mertensiaarizonica.jpg/120px-Mertensiaarizonica.jpg)
![Short-styled Bluebell (Mertensia brevistyla)[26]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/11/Mertensia_brevistyla_TPrendusi_lg.jpg/120px-Mertensia_brevistyla_TPrendusi_lg.jpg)







