List of Mil Mi-24 variants
|
Read other articles:

Ace Young Ace Young (lahir di Denver, Colorado, Amerika Serikat, 15 November 1980) adalah penyanyi, penulis lagu, dan aktor dari Amerika.[1] Namanya mulai dikenal ketika ia berhasil menjadi salah satu finalis dalam American Idol Musim Kelima.[1][2] Meskipun sebelumnya, ia sempat menulis sebuah lagu yang sangat populer dan berhasil masuk dalam nominasi Grammy Award 2008, tetapi kalah dari lagu Bruce Springsteen, Radio Nowhere.[1] Kegemarannya selain menyanyi dan...

Gnoma pulverea Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Arthropoda Kelas: Insecta Ordo: Coleoptera Famili: Cerambycidae Genus: Gnoma Spesies: Gnoma pulverea Gnoma pulverea adalah spesies kumbang tanduk panjang yang tergolong famili Cerambycidae. Spesies ini juga merupakan bagian dari genus Gnoma, ordo Coleoptera, kelas Insecta, filum Arthropoda, dan kingdom Animalia. Larva kumbang ini biasanya mengebor ke dalam kayu dan dapat menyebabkan kerusakan pada batang kayu hidup atau kayu yang te...

The 1st AlbumAlbum studio karya Modern TalkingDirilis1 April 1985Direkam1984GenreSynthpopLabelBMG, HansaProduserDieter BohlenKronologi Modern Talking The 1st Album(1985) Let's Talk About Love(1985)Let's Talk About Love1985 Penilaian profesional Skor ulasan Sumber Nilai Allmusic [1] The 1st Album adalah album musik pertama karya Modern Talking. Album ini dirilis tahun 1985 di Jerman. Daftar lagu You're My Heart, You're My Soul — 5:36 You Can Win If You Want — 3:53 There's Too M...

Mexican physician, researcher, professor and public official For other people named Hugo López, see Hugo López (disambiguation). In this Spanish name, the first or paternal surname is López-Gatell and the second or maternal family name is Ramírez. Hugo López-Gatell RamírezDeputy Secretary of Prevention and Health Promotion of MexicoIncumbentAssumed office 1 December 2018PresidentAndrés Manuel López ObradorPreceded byPablo Kuri-Morales Personal detailsBornHugo López-Gatell...

Voce principale: Ghetti nazisti. Ghetto di VilniusGhetto Wilna Una strada del ghetto di Vilnius Stato Lituania CittàVilnius Data istituzione1941 Abitanti40 000 ab. (30 agosto 1941 - 23 settembre 1943) Coordinate: 54°41′N 25°19′E / 54.683333°N 25.316667°E54.683333; 25.316667 Il Ghetto di Vilnius, in lingua tedesca Ghetto Wilna, fu uno dei maggiori tra i ghetti nazisti istituiti nel corso della seconda guerra mondiale dal Terzo Reich nei territori occupati de...

Voce principale: Empire Awards. James Nesbitt, conduttore della 20ª edizione La 20ª edizione degli Empire Awards o 20ª edizione degli Jameson Empire Awards, organizzata dalla rivista cinematografica inglese Empire, si è svolta il 29 marzo 2015 al Grosvenor House Hotel di Londra, ed ha premiato i film che sono usciti nel 2014[1]. Indice 1 Vincitori e candidati 1.1 Miglior film 1.2 Miglior film britannico 1.3 Miglior attore 1.4 Miglior attrice 1.5 Miglior regista 1.6 Miglior debutt...
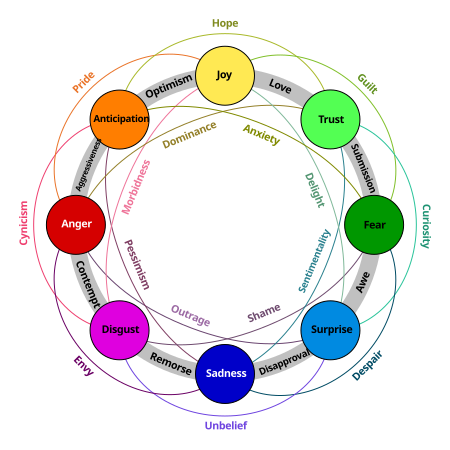
The history of emotions is a field of historical research concerned with human emotion, especially variations among cultures and historical periods in the experience and expression of emotions. Beginning in the 20th century with writers such as Lucien Febvre and Peter Gay, an expanding range of methodological approaches is being applied. Scope In the last decade,[which?] the history of emotions has developed into an increasing productive and intellectually stimulating area of histori...

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁�...

Manor house at Holbæk, Denmark Bjergbygaard at Golbæk, Denmark Bjergbygaard is a manor house and estate located at Holbæk, Denmark. History The estate is first mentioned in the Danish Census Book under the name Stighsburg and was then crown land. In the 14th century, Bjergbygaard came in the hands of Peder Karlsen and later his daughter, Christine, who was married to Mogens Johansen. He pledged the estate in 1371 and after that the ownership seems to have been divided between multiple owne...

ヨハネス12世 第130代 ローマ教皇 教皇就任 955年12月16日教皇離任 964年5月14日先代 アガペトゥス2世次代 レオ8世個人情報出生 937年スポレート公国(中部イタリア)スポレート死去 964年5月14日 教皇領、ローマ原国籍 スポレート公国親 父アルベリーコ2世(スポレート公)、母アルダその他のヨハネステンプレートを表示 ヨハネス12世(Ioannes XII、937年 - 964年5月14日)は、ロ...

豪栄道 豪太郎 場所入りする豪栄道基礎情報四股名 澤井 豪太郎→豪栄道 豪太郎本名 澤井 豪太郎愛称 ゴウタロウ、豪ちゃん、GAD[1][2]生年月日 (1986-04-06) 1986年4月6日(38歳)出身 大阪府寝屋川市身長 183cm体重 160kgBMI 47.26所属部屋 境川部屋得意技 右四つ・出し投げ・切り返し・外掛け・首投げ・右下手投げ成績現在の番付 引退最高位 東大関生涯戦歴 696勝493敗...

Частина серії проФілософіяLeft to right: Plato, Kant, Nietzsche, Buddha, Confucius, AverroesПлатонКантНіцшеБуддаКонфуційАверроес Філософи Епістемологи Естетики Етики Логіки Метафізики Соціально-політичні філософи Традиції Аналітична Арістотелівська Африканська Близькосхідна іранська Буддій�...

بندكت الثالث عشر (باللاتينية: Benedictus PP. XIII) معلومات شخصية اسم الولادة (بالإيطالية: Pietro Francesco Orsini) الميلاد 2 فبراير 1650(1650-02-02)غرافينا في بوليا الوفاة 21 فبراير 1730 (80 سنة)روما الديانة الكنيسة الرومانية الكاثوليكية مناصب كاردينال تولى المنصب22 فبراير 1672 مطران كاثول...

مستعمرة إيسيكويبو مستعمرة إيسيكويبوالعلم مستعمرة إيسيكويبوالشعار الأرض والسكان إحداثيات 7°02′00″N 58°27′00″W / 7.03333333°N 58.45°W / 7.03333333; -58.45 الحكم التأسيس والسيادة التاريخ تاريخ التأسيس 1616 وسيط property غير متوفر. تعديل مصدري - تعديل جزء من سلسلة حول ت�...

Series of wars in England, 1642–1651 For other civil wars in England, see List of English civil wars. For other uses, see English Civil War (disambiguation). English Civil WarPart of the Wars of the Three KingdomsThe Battle of Naseby, 14 June 1645; Parliamentarian victory marked the decisive turning point in the English Civil War.DateAugust 1642 – September 1651LocationGreat BritainResult Parliamentarian victory Execution of Charles I Establishment of the Commonwealth of EnglandBelligeren...
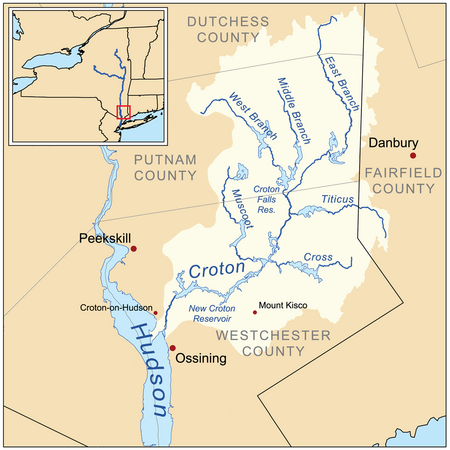
River in the U.S. state of New York Map of the Croton River watershed showing the East Branch The East Branch Croton River is a tributary of the Croton River in Dutchess, Putnam, and Westchester counties in the state of New York. It lies within the Croton River watershed and is part of the New York City water supply system's Croton Watershed.[1] Path The river rises in the town of Pawling in Dutchess County, flowing west and then south through the village of Pawling. It crosses into P...

American politician Carl M. WeidemanDetroit Free Press, November 10, 1932Member of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom Michigan's 14th districtIn officeMarch 4, 1933 – January 3, 1935Preceded byDistrict createdSucceeded byLouis C. Rabaut Personal detailsBorn(1898-03-05)March 5, 1898Detroit, Michigan, U.S.DiedMarch 5, 1972(1972-03-05) (aged 74)Grosse Pointe Park, Michigan, U.S.Resting placeWoodlawn Cemetery, Detroit, MichiganPolitical partyDemocraticAlma materDetr...

La MorraKomuneComune di La MorraNegaraItaliaWilayahPiedmontProvinsiProvinsi Cuneo (CN)FrazioniAnnunziata, Santa Maria, Rivalta, BerriLuas • Total24,3 km2 (94 sq mi)Ketinggian513 m (1,683 ft)Populasi (Dec. 2004) • Total2.668 • Kepadatan11/km2 (28/sq mi)DemonimLamorresiZona waktuUTC+1 (CET) • Musim panas (DST)UTC+2 (CEST)Kode pos12064Kode area telepon0173Situs webSitus web resmi La Morra adalah komune yang terlet...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (نوفمبر 2015) الهيئة العالمية للتعريف بالنبي صلى الله عليه وسلم ونصرته المقر الرئيسي الرياض منطقة الخدمة السعودية تعديل مصدري - تعديل الهيئة العالمية للتعريف بال...

One of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus Christ SaintJames the LesserSt James the Minor by Peter Paul Rubens (1613)Apostle and MartyrBornc. 1st century ADGalilee, Judaea, Roman EmpireDiedc. 62 ADJerusalem, Judaea, Roman Empire or Aegyptus, Roman EmpireVenerated inAll Christian denominations that venerate saintsFeast1 May (Anglican Communion),May 3 (Roman Catholic Church), 9 October (Eastern Orthodox Church)AttributesCarpenter's saw; fuller's clubPatronageApothecaries; druggists; dying people;...









