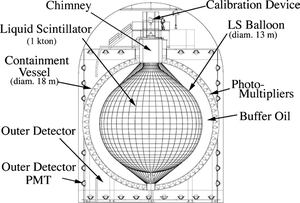
Kamioka Liquid Scintillator Antineutrino Detector
|
Read other articles:
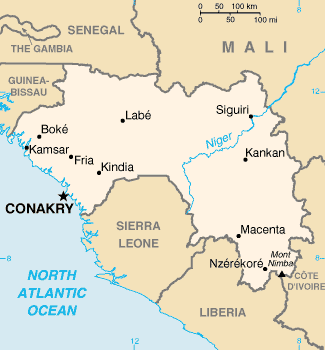
Guinea Berikut adalah daftar kota di Guinea: Beyla Boffa Boké Conakry (ibu kota) Coyah Dabola Dalaba Dinguiraye Dubréka Faranah Forécariah Fria Gaoual Guéckédou Kankan Kérouané Kindia Kissidougou Koubia Koundara Kouroussa Labé Lélouma Lola Macenta Mandiana Mali Mamou Nzérékoré Pita Siguiri Télimélé Timbo Tougué Yomou lbsDaftar kota di duniaAfrika Afrika Selatan Afrika Tengah Aljazair Angola Benin Botswana Burkina Faso Burundi Chad Eritrea Eswatini Etiopia Gabon Gambia Ghana Gu...

Artikel ini perlu dikembangkan agar dapat memenuhi kriteria sebagai entri Wikipedia.Bantulah untuk mengembangkan artikel ini. Jika tidak dikembangkan, artikel ini akan dihapus. الجهمي (en) Yusuf al-Qaradawi(2006) Nama dalam bahasa asli(ar) يُوسُف القرضاوي BiografiKelahiran9 September 1926 Saft Turab (en) Kematian26 September 2022 (96 tahun)Doha 1r Leader of the International Union of Muslim Scholars (en) 2004 – 7 November 2018 ← tanpa nila...

Pour l’article homonyme, voir L'Est républicain (Algérie). Ne doit pas être confondu avec Le Républicain lorrain. L'Est républicain Pays France Langue Français Périodicité Quotidien Format Tabloïd Genre Presse quotidienne régionale Prix au numéro 1,30 € (semaine)2 € (dimanche) Diffusion 105 132[1] ex. (2020/2021) Fondateur Léon Goulette Date de fondation 5 mai 1889 Ville d’édition Nancy Propriétaire Groupe EBRA (BFCM) Directeur de publication Christophe Mahieu...

Queen of Denmark and Norway from 1699 to 1721 Louise of Mecklenburg-GüstrowPortrait by Johann Salomon Wahl, c. 1720Queen consort of Denmark and NorwayTenure25 August 1699 – 15 March 1721Coronation15 April 1700Born(1667-08-28)28 August 1667GüstrowDied15 March 1721(1721-03-15) (aged 53)CopenhagenBurialRoskilde CathedralSpouse Frederick IV of Denmark (m. 1695)IssueChristian VIPrincess Charlotte AmalieHouseMecklenburgFatherGustav Adolph, Duke of Mec...

ロバート・デ・ニーロRobert De Niro 2011年のデ・ニーロ生年月日 (1943-08-17) 1943年8月17日(80歳)出生地 アメリカ合衆国・ニューヨーク州ニューヨーク市身長 177 cm職業 俳優、映画監督、映画プロデューサージャンル 映画、テレビドラマ活動期間 1963年 -配偶者 ダイアン・アボット(1976年 - 1988年)グレイス・ハイタワー(1997年 - )主な作品 『ミーン・ストリート』(1973年)...

Newport News Apprentice School BuildersUniversityNewport News Apprentice SchoolAssociationUSCAA, NCWAConferenceEMACAthletic directorMichael AllenLocationNewport News, VirginiaVarsity teams6Football stadiumApprentice Athletic Field (2,500)Baseball stadiumWar Memorial Stadium (3,750)NicknameBuildersColorsMaroon and Gold Websitewww.gobuilders.com The Apprentice Builders are the athletic teams of the Newport News Apprentice School, located in Newport News, in the U.S. s...

1954 rock and roll song This article is about the song recorded by Bill Haley. For the film, see Rock Around the Clock (film). For the album by Haley, see Rock Around the Clock (album). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Rock Around the Clock – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 20...

土库曼斯坦总统土库曼斯坦国徽土库曼斯坦总统旗現任谢尔达尔·别尔德穆哈梅多夫自2022年3月19日官邸阿什哈巴德总统府(Oguzkhan Presidential Palace)機關所在地阿什哈巴德任命者直接选举任期7年,可连选连任首任萨帕尔穆拉特·尼亚佐夫设立1991年10月27日 土库曼斯坦土库曼斯坦政府与政治 国家政府 土库曼斯坦宪法 国旗 国徽 国歌 立法機關(英语:National Council of Turkmenistan) ...

Mosque and former monastery in Muş, Turkey Esenlik Mosque39°00′50″N 42°05′49″E / 39.013857°N 42.096970°E / 39.013857; 42.096970LocationEsenlik, Bulanık, Muş, TurkeyType Monastery Mosque (present) MaterialAhlat stone Esenlik Mosque is a historical mosque in Esenlik, Bulanık, Muş, Turkey. History It was built by the Seljuks. It was built by Sheikh Abdülmelik in 1194. Ahlat stone was used. It is a building with a single dome, four windows and two doors. ...
Kolom Winogradsky awalnya Kolom Winogradsky setelah beberapa minggu Kolom Winogradsky adalah suatu miniatur ekosistem buatan untuk membiakkan mikrob yang menyerupai kondisi ekologis sebenarnya dengan menyediakan sumber bakteri jangka panjang untuk pengkayaan kultur.[1] Kolom Winogradsky adalah salah satu cara sederhana untuk mempelajari hubungan silang antara dua komponen suatu lingkungan alami di laboratorium.[1] Penemuan Kolom Winogradsky merupakan ide seorang ilmuwan Rusia ...

This article is about the city. For the adjacent town, see Tomah (town), Wisconsin. City in Wisconsin, United StatesTomahCityDowntown TomahLocation of Tomah in Monroe County, WisconsinTomahLocation within the state of WisconsinCoordinates: 43°59′6″N 90°30′14″W / 43.98500°N 90.50389°W / 43.98500; -90.50389Country United StatesState WisconsinCountyMonroeGovernment • MayorPaul DwyerArea[1] • Total8.26 sq mi (...

Traité EuratomTraité de Rome Traité instituant la Communauté européenne de l'énergie atomique Type de traité Traité constitutif de l'Union européenne Signature 25 mars 1957 Lieu de signature Capitole (Rome, Italie) Signataires Konrad Adenauer, Paul-Henri Spaak, Maurice Faure, Christian Pineau, Lodovico Benvenuti, Joseph Bech, Johannes Linthorst-Homan Parties États membres des Communautés européennes Dépositaire Gouvernement italien Voir le traité sur Wikisource modifier Le Trai...

奥林匹克运动会厄立特里亚代表團厄立特里亚国旗IOC編碼ERINOC厄利垂亞國家奧林匹克委員會历届奥林匹克运动会参赛记录(总结)夏季奥林匹克运动会2000200420082012201620202024冬季奥林匹克运动会20182022其他相关赛事参赛记录 埃塞俄比亚(1956年-1992年) 厄立特里亚(國際奧委會國家編碼為:ERI)(國際奧委會國家編碼為:ERI)于2000年在澳大利亚悉尼第一次参加奥运会。四�...

315th Air DivisionDivision C-130 Hercules deployed to Cam Ranh AB, Vietnam[a]Active1944–1950, 1951–1969Country United StatesBranch United States Air ForceRoleCommand of airlift forcesEngagementsPacific Theater of OperationsKorean WarDecorationsAir Force Outstanding Unit AwardRepublic of Korea Presidential Unit CitationInsignia315th Air Division emblem[b][1]315th Bombardment Wing emblem[c][2]Military unit The 315th Air Division is an inact...

Американо-белорусские отношения США Белоруссия Медиафайлы на Викискладе Дипломатические отношения Соединённых Штатов Америки и Белоруссией были установлены в 1991 году, в результате распада Советского Союза и становления Белоруссии как независимого государства. Со...

Former junior college in Yonkers, New York Elizabeth Seton CollegeTypePrivateActive1961–1989 (merged with Iona College)Religious affiliationRoman Catholic (Sisters of Charity of New York)Academic affiliationsMiddle States Association of Colleges and SchoolsBudget$6.5 million (1989)[1]PresidentMary Ellen Brosnan (1989)Undergraduates980 (1988),[1]400 day students580 weekend studentsLocationYonkers, New York, United StatesCampusYonkers: suburban, 21 acres (8.5 ha)Manhattan...

Das Pushout (auch Kofaserprodukt, kokartesisches Quadrat, Fasersumme, amalgamierte Summe) ist ein Begriff aus dem mathematischen Teilgebiet der Kategorientheorie. Es handelt sich um die zum Pullback duale Konstruktion. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Pushout von Moduln 2 Pushout in Kategorien 3 Beispiele 4 Einzelnachweise Pushout von Moduln Es seien α 1 : X → X 1 {\displaystyle \alpha _{1}:X\rightarrow X_{1}} und α 2 : X → X 2 {\displaystyle \alpha _{2}:X\rightarrow X_{2}} zw...

Questa voce sull'argomento centri abitati della provincia di Pavia è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Torrevecchia Piacomune Torrevecchia Pia – VedutaChiesa della frazione di Cascina Bianca LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Lombardia Provincia Pavia AmministrazioneSindacoGerardo Manfredi (lista civica) dal 12-6-2017 (2º mandato dal 13-6-2022) TerritorioCoordinate45°17′N 9°18′E45°17′N, 9°18′E (To...

Questa voce sull'argomento società calcistiche olandesi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Sparta RotterdamCalcio Kasteelheren (Signori del Castello) Segni distintiviUniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori sociali Bianco, rosso Dati societariCittàRotterdam Nazione Paesi Bassi ConfederazioneUEFA Federazione KNVB CampionatoEredivisie Fondazione1888 Presidente Rob Westerhof Allenatore Jeroen Rijsdijk StadioHet Kasteel(11.026 posti) Sit...

French poet (1895–1952) Éluard and Eluard redirect here. For other uses, see Éluard (disambiguation). Paul ÉluardÉluard c. 1945BornEugène Émile Paul Grindel(1895-12-14)14 December 1895Saint-Denis, FranceDied18 November 1952(1952-11-18) (aged 56)Charenton-le-Pont, FranceOccupationWriterEducationÉcole Supérieure de ColbertPeriod20th centuryGenrePoetryLiterary movementSurrealismNotable worksLibertéSpouse Gala Dalí (m. 1917; div. 192...