Telephony software for SIP routing
Kamailio, formerly OpenSER (and sharing some common history with SIP Express Router (SER)), is an SIP server licensed under the GPL-2.0-or-later license. It can be configured to act as a SIP registrar, proxy or redirect server, and features presence support, RADIUS / syslog accounting and authorization, XML-RPC and JSON-RPC-based remote control, SQL and NoSQL backends, IMS / VoLTE extensions and others.
Kamailio is a Hawaiian word. Kama'ilio means talk, to converse. "It was chosen for its special flavour."[2]
Features
Kamailio is written in pure C with architecture-specific optimizations;[3] it can be configured for many scenarios including small-office use, enterprise PBX replacements and carrier services—it is SIP signaling server—a proxy—aiming to be used for large real-time communication services. Features include:[4]
- SIP telephony system
- SIP load balancer
- SIP security firewall
- Least cost routing engine
- IMS/VoLTE platform
- Instant messaging and presence services
- SIP IPv4-IPv6 gateway
- MSRP relay
- SIP-WebRTC gateway
Usage
Kamailio is used by large Internet Service Providers to provide public telephony service. The largest public announced deployment with several million of users is in operation at the German ISP 1&1.[5] Another large deployment is in operation at the provider sipgate.
Forks
OpenSIPS
OpenSIPS, a fork of SER which has diverged—deciding to "go their own way" from the SER and OpenSER[6] codebases—is a free software implementation of SIP for voice over IP (VoIP) that can be used to handle voice, text and video communication. OpenSIPS is intended for installations serving thousands of calls and is IETF RFC 3261 compliant.[7] The software was recognized by Google in 2017 with their Open Source Peer Bonus award.[8]
History
Kamailio's roots go back to 2001, when the first line of SIP Express Router (SER) was written; at the time, the working group published results at iptel.org—in September 2002 the code itself was published under the GPL.[6] The first fork of SER came in 2005—OpenSER[6]—which would later merge back into the code that would become Kamailio.[9] The codebases of SER and OpenSER (by then known as Kamailio) converged in December 2012, and it was decided to continue to use Kamailio as the main name of the project, which remains open source.[10]
During the first years of development, serweb—a web-based user provisioning—was available.[citation needed]
Timeline
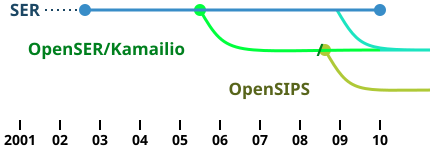
- 2001
-
- 2002
-
- First third-party contribution (ENUM module)[6]
- September
-
- Code is GPL'd and first published[6]
- 2003
-
- Adoption by the general public begins; additional free and open source code is contributed by independent third parties[6]
- 2004
-
- Part of the FOKUS team moves, with the SER copyrights, to the newly created company iptel.org[citation needed]
- Two of the five SER core developers and one main contributor start a new free and open source software project named OpenSER.[citation needed]
- 2005
-
- The company IPtel.org is bought by TEKELEC, and is responsible for the TEKELEC session router and CSCF.[6]
- 2007
-
- May 12
-
- SER 2.0 RC-1 (Ottendorf) is made available
- 2008
-
- August
-
- OpenSER is renamed Kamailio to avoid conflict with similar trademarks[6]
- November 4
-
- Kamailio developers sketch and announce a plan to team up with the SER developers to create the future sip-router project[6]
- 2013
-
- FOKUS and the Kamailio community organize the first iteration of the annual 'Kamailio World' conference in Berlin, Germany.[11]
References
External links