JANET
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
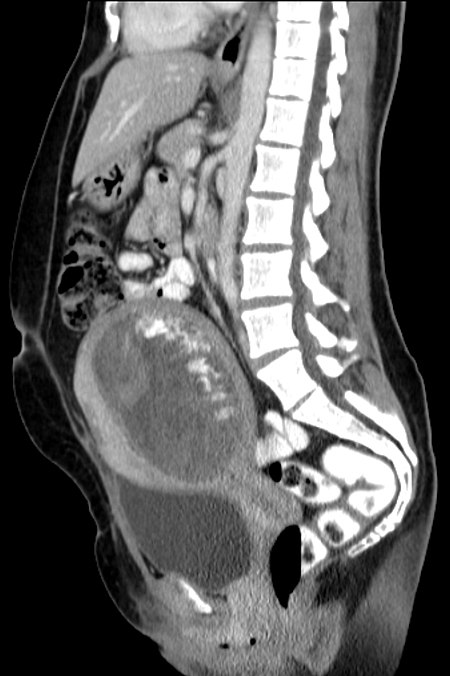
Artikel ini memberikan informasi dasar tentang topik kesehatan. Informasi dalam artikel ini hanya boleh digunakan untuk penjelasan ilmiah; bukan untuk diagnosis diri dan tidak dapat menggantikan diagnosis medis. Wikipedia tidak memberikan konsultasi medis. Jika Anda perlu bantuan atau hendak berobat, berkonsultasilah dengan tenaga kesehatan profesional. Mola hidatidosaMola hidatidosa dilihat menggunakan tomografi terkomputasi.Informasi umumSpesialisasiPatologi Mola hidatidosa (atau hami...
Atletik padaPekan Olahraga Nasional 2016 Lintasan 100 m putra putri 200 m putra putri 400 m putra putri 800 m putra putri 1500 m putra putri 5000 m putra putri 10.000 m putra putri 100 m gawang putri 110 m gawang putra 400 m gawang putra putri 3000 m h'rintang putra putri 10.000 m jalan cepat putra 4×100 m estafet putra putri 4×400 m estafet putra putri Jalan raya Maraton putra putri 20 km jalan cepat putra putri Lapangan Lompat tinggi putra putri Lompat galah putra putri Lompat jauh putra...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant un conflit armé. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Pour les articles homonymes, voir Montiel (homonymie). Bataille de Montiel Informations générales Date 14 mars 1369 Lieu À Montiel, au sud-est de la Castille Issue Victoire franco-castillane Belligérants Castillans trastamaristes Royaume de France Royaume de Castille Émirat de Grenade Commandants Bertra...
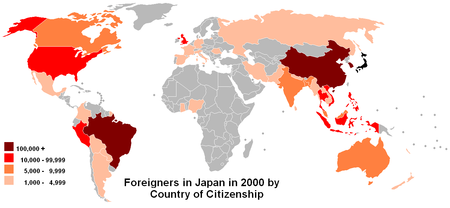
Demography of Japan Among the several native ethnic groups of Japan, the predominant group are the Yamato Japanese, who trace their origins back to the Yayoi period and have held political dominance since the Asuka period. Other historical ethnic groups have included the Ainu, the Ryukyuan people, the Emishi, and the Hayato; some of whom were dispersed or absorbed by other groups. Ethnic groups that inhabited the Japanese islands during prehistory include the Jomon people and lesser-known Pal...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant le Mexique et une unité ou formation militaire. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Consultez la liste des tâches à accomplir en page de discussion. Forces armées mexicainesFuerzas armadas de México Armoiries du Mexique Fondation 1821 Branches Armée mexicaine Marine mexicaine Force aérienne mexicaine Quartier-général Mexico Commandement Commandant Supr...

Sporting event delegationSingapore at the2015 World Championships in AthleticsWA codeSINin BeijingCompetitors1Medals Gold 0 Silver 0 Bronze 0 Total 0 World Championships in Athletics appearances1983198719911993199519971999200120032005200720092011201320152017201920222023← 2013 2017 → Singapore competed at the 2015 World Championships in Athletics in Beijing, China, from 22–30 August 2015. Results (q – qualified, NM – no mark, SB – season best) Women Track and road events At...

51st season in existence of Paris Saint-Germainقالب:SHORTDESC:51st season in existence of Paris Saint-Germain باريس سان جيرمانموسم 2020–21الرئيسناصر الخليفيالمدربتوماس توخل(حتى 29 ديسمبر)ماوريسيو بوتشيتينو(ابتداء من 2 يناير)الملعببارك دي برينسالدوري الفرنسيالثانيكأس فرنساالفائزكأس الأبطال الفرنسيالفائزدوري أبطال أور...

Шалфей обыкновенный Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:РастенияКлада:Цветковые растенияКлада:ЭвдикотыКлада:СуперастеридыКлада:АстеридыКлада:ЛамиидыПорядок:ЯсноткоцветныеСемейство:ЯснотковыеРод:ШалфейВид:Шалфей обыкновенный Международное научное наз...

This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (December 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) The Sager family at the beginning of their journey west The Sager orphans (sometimes referred to as the Sager children) were the children of Henry and Naomi Sager. In April 1844 the Sager family took part in the great westward migration and started their...

Governing body of football in Iraq Iraq Football AssociationAFCShort nameIFAFounded8 October 1948; 75 years ago (1948-10-08)HeadquartersZayouna, Baghdad, Iraq[1]FIFA affiliation1950AFC affiliation1970[2]WAFF affiliation2001 (founding member)PresidentAdnan DirjalVice-PresidentAli Jabbar (1st)Younis Mahmoud (2nd)Websitewww.ifa.iq The Iraq Football Association (IFA) (Arabic: الاتحاد العراقي لكرة القدم) is the governing body of football in ...

Yokohama Municipal SubwayLogoInfoWilayahYokohama, JepangJenisAngkutan cepatJumlah jalur2 (Biru dan hijau)Jumlah stasiun42Situs webwww.city.yokohama.lg.jp/koutuu/subOperasiDimulai1972 April 12 (12-16-1972)OperatorBiro Transportasi Kota YokohamaTeknisPanjang sistem534 km (332 mi)Lebar sepur1.435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) Peta rute Map of Yokohama Municipal Subway Yokohama Municipal Subway (横浜市営地下鉄code: ja is deprecated , Yokohama-shiei chikatetsu)...

В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с такой фамилией, см. Сергиенко; Сергиенко, Николай. Николай Дмитриевич Сергиенко Дата рождения 10 мая 1923(1923-05-10) Место рождения село Журавлёвка, Буландынский район, Акмолинская область Дата смерти 5 мая 1997(1997-05-05) (73 года) Место сме�...

For other uses, see Pokey (disambiguation). POKEY in an Atari 130XE POKEY, an acronym for Pot Keyboard Integrated Circuit,[1] is a digital I/O chip designed by Doug Neubauer at Atari, Inc.[2] for the Atari 8-bit computers. It was first released with the Atari 400 and Atari 800 in 1979 and is included in all later models and the Atari 5200 console. POKEY combines functions for reading paddle controllers (potentiometers) and computer keyboards as well as sound generation and a s...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento siti archeologici della Francia non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Roc-aux-SorciersLocalizzazioneStato Francia LocalitàAngles-sur-l'Anglin Mappa di localizzazione Modifica dati su Wikidata · ManualeCoordinate: 46°42′17.4″N 0°52′38.76″E / 46.704834°N 0.877432°E46.704...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...

Argentine tennis player Santiago Rodríguez TavernaRodríguez Taverna at the 2022 French OpenCountry (sports) ArgentinaBorn (1999-07-16) 16 July 1999 (age 24)Buenos Aires, ArgentinaHeight1.91 m (6 ft 3 in)Turned pro2016PlaysRight-handed (two-handed backhand)CoachGuillermo FrancoPrize moneyUS$ 396,664SinglesCareer record0–1 (0% in ATP Tour and Grand Slam main draw matches, and in Davis Cup)Career titles0Highest rankingNo. 157 (29 August ...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento centri abitati della Lombardia non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Correzzanacomune LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Lombardia Provincia Monza e Brianza AmministrazioneSindacoMarco Beretta TerritorioCoordinate45°40′N 9°18′E / &#...

FIA rally car formula Group Rally1Motor racing formulaCategoryRallyingCountry/RegionInternationalChampionshipsWRCInaugural2022DrivetrainFour Wheel DrivePower to weight3.1 kg/hpAptitudeElite World RallyChampionship Current season 2024 World Rally Championship 2024 WRC2 Championship 2024 WRC3 Championship 2024 Junior WRC Championship Support categories Current: WRC2 WRC3 Junior WRC Former: PWRC SWRC FIA 2-Litre Current car classes Rally1 Rally2 Rally3 Rally4 Rally5 Related lists Drivers ...

African diaspora Template‑classThis template is within the scope of WikiProject African diaspora, a collaborative effort to improve the coverage of African diaspora on Wikipedia. If you would like to participate, please visit the project page, where you can join the discussion and see a list of open tasks.African diasporaWikipedia:WikiProject African diasporaTemplate:WikiProject African diasporaAfrican diaspora articlesTemplateThis template does not require a rating on Wikipedia's content a...

Macro-Jê language branch of Brazil KrenakAimoréBotocudoBorumEthnicityAimoréGeographicdistributionBrazilLinguistic classificationMacro-JêKrenakSubdivisions Krenak Guerén Nakrehé The Aimoré, Botocudoan or Borum languages, now sometimes known as Krenakan after the last one remaining, are a branch of the Macro-Jê languages – spoken mainly in Brazil – including moribund Krenak and extinct languages such as Guerén and Nakrehé. Loukotka (1968)[1] considered them dialects of a s...
