Henri, Count of Chambord
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Le calendrier berbère est un calendrier utilisé par les Berbères en Afrique du Nord. Il est employé pour régler les travaux agricoles saisonniers. Le calendrier berbère présente des similitudes avec le calendrier julien par le décalage hérité de la réforme du calendrier grégorien[1]. Ce calendrier, notamment la numérotation des années (le calendrier est décalé de 950 années par rapport à l’ère commune : 2023 de l’ère commune correspond à 2973 du calendrier berbè...

EridanusRasi bintangDaftar bintang di rasi bintang EridanusSingkatanEriGenitivusEridaniPengucapan[ɨˈrɪdənəs] Erídanus, genitif /ɨˈrɪdənaɪ/SimbolismeSungaiAsensio rekta 03j 18m 01dDeklinasi −28° 45′ 22″KuadranSQ1Luas1138 derajat persegi (6)Bintang utama24Bintang Bayer/Flamsteed87Bintang dengan planet6Bintang lebih terang dari 3.00m4Bintang di dalam 10.00 parsek (32.62 tahun cahaya)13Bintang paling terangAchernar (α Eri) (0.46m)Objek Me...

Artikel ini terlalu bergantung pada referensi dari sumber primer. Mohon perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan sumber sekunder atau tersier. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) PT Golden Energy Mines TbkSebelumnyaPT Bumi Kencana Eka Sakti (1997-2010)JenisPerusahaan publikKode emitenIDX: GEMSIndustriPertambanganDidirikan13 Maret 1997; 26 tahun lalu (1997-03-13)KantorpusatJakarta, IndonesiaWilayah operasiIndonesiaTokohkunciBonifasius[1](Direktur Uta...
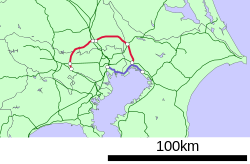
Jalur MusashinoKRL seri E231 di Jalur Musashino, November 2019IkhtisarNama asli武蔵野線JenisAngkutan beratLokasiTokyo, Prefektur Kanagawa, Saitama, ChibaTerminusFuchūhommachiNishi-FunabashiStasiun26Penumpang harian1.064.613 (harian 2015)[1]OperasiDibuka1973PemilikJR EastOperatorJR East, JR FreightDepoKeiyoRangkaianKRL 209-500 series, E231 seriesData teknisPanjang lintas71,8 km (operasi penumpang) 100,6 km (Total)Lebar sepur1.067 mm (3 ft 6 in)Elektrifikasi1,50...

Philip Seymour HoffmanHoffman pada bulan Oktober 2011Lahir(1967-07-23)23 Juli 1967Fairport, New YorkMeninggal2 Februari 2014(2014-02-02) (umur 46)New York City, New YorkPendidikanBFAAlmamaterUniversitas New YorkPekerjaanAktor, sutradaraTahun aktif1991–2014PasanganMimi O'Donnell(1999–2014)Anak3, termasuk Cooper Philip Seymour Hoffman Philip Seymour Hoffman (23 Juli 1967 – 2 Februari 2014) adalah seorang pemeran film asal Amerika Serikat. Ia memulai debut pada tah...

American ice hockey player (1970–9/11/2001) Ice hockey player Mark Bavis Born (1970-03-13)March 13, 1970Roslindale, Massachusetts, U.S.Died September 11, 2001(2001-09-11) (aged 31)New York City, U.S.Height 6 ft 1 in (185 cm)Weight 190 lb (86 kg; 13 st 8 lb)Position Left wingShot LeftPlayed for Providence BruinsFredericton CanadiensSouth Carolina StingraysNHL Draft 181st overall, 1989New York RangersPlaying career 1993–1996 Mark Lawrence Bavis (M...

Bagian dari seri tentangLiberalisme Mazhab Liberalisme konservatif Liberalisme sosial Neoliberalisme Pemikiran Liberalisme konservatif Liberalisme budaya Kapitalisme demokratik Pendidikan demokratik Liberalisme ekonomi Egalitarianisme Perdagangan bebas Prinsip bahaya Individualisme Laissez-faire Demokrasi liberal Kenetralan liberal Ekonomi pasar Kebebasan negatif / positif Masyarakat terbuka Masyarakat permisif Kebebasan politik Kedaulatan rakyat Hak (individu) Sekularisme Pemisahan agama dan...

Questa voce sull'argomento cestisti congolesi (Repubblica del Congo) è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Giovan Oniangue Giovan Oniangue con la maglia del Paris-Levallois Nazionalità Rep. del Congo Francia Altezza 197 cm Peso 101 kg Pallacanestro Ruolo Ala piccola Squadra Pau-Lacq-Orthez Carriera Giovanili Paris-Levallois Squadre di club 2009-2017 Paris-Levalloi...

Pour l’article homonyme, voir Blague à tabac. Couverture du journal Les Petits bonshommes (1er avril 1913). Une blague, aussi nommée histoire drôle ou gag, est une mise en scène sous forme d'histoire ou de devinette, généralement assez courte, qui déclenche le rire. La blague se décline par sa forme simple en jeux de mots et calembours, devinettes, contrepèteries, etc. Étymologie Définitions du Dictionnaire du bas-langage de Charles-Louis D'Hautel (1808). La blague, largement pr...

Giovan Battista Contini Data i miejsce urodzenia 1642 Montalcino Data i miejsce śmierci 1723 Rzym Zawód, zajęcie architekt Multimedia w Wikimedia Commons Giovan Battista Contini (ur. w 1642 w Montalcino, zm. 1723 w Rzymie) – włoski architekt, aktywny w epoce baroku. Contini był uczniem Carla Fontany i Berniniego. Rozpoczął samodzielną praktykę w 1658, stając się czołowym architektem Stolicy Świętej po śmierci Berniniego. Współpracował z Carlo Fontaną w latach 1...

20 [Twenty]Album studio karya F.T. IslandDirilis16 Mei 2012 (2012-05-16)Direkam2011–12South KoreaGenreRockDurasi44:02BahasaJapaneseLabelWarner Music JapanKronologi F.T. Island Grown-Up(2012)Grown-Up2012 20 [Twenty](2012) Five Treasure Box(2012)Five Treasure Box2012 Singel dalam album 20 Let It Go!Dirilis: 27 Juli 2011 (2011-07-27) DistanceDirilis: 30 November 2011 (2011-11-30) NeverlandDirilis: 18 April 2012 (2012-04-18) Templat:Contains Japanese text 20 [Twenty] (di...

Iglesia de San Pedro y San Ildefonso Bien de interés culturalPatrimonio histórico de España LocalizaciónPaís España EspañaComunidad Castilla y León Castilla y LeónProvincia ZamoraZamoraLocalidad ZamoraDatos generalesCategoría MonumentoCódigo RI-51-0003938Declaración 1974Construcción Siglo XI - Siglo XVIIIEstilo Románico en origen, muy modificado en épocas posteriores.[editar datos en Wikidata] La iglesia Arciprestal de San Pedro y San Ildefonso, es...

Православний літургійний календар Ґрунтується на Юліанський календар і Новоюліанський календар Календарі Базові поняття Час Минуле Сьогодення Майбутнє Вічність Доба Тиждень Місяць Рік зоряний календарний тропічний Десятиліття Століття Тисячоліття Ера Інтерка�...
فيليكس كاستيلو معلومات شخصية الميلاد 21 فبراير 1928(1928-02-21)تشينتشا ألتا الوفاة 12 أكتوبر 1978 (50 سنة) ليما مركز اللعب نصف الجناح الجنسية بيرو المسيرة الاحترافية1 سنوات فريق م. (هـ.) 1945–1949 أليانزا ليما 1950–1951 أمريكا دي كالي 1952–1960 أليانزا ليما المنتخب الوطني 1947–1956 �...

Stasiun Toyotomi (豊富駅 Toyotomi-eki) adalah sebuah stasiun kereta api yang berada di Jalur Utama Sōya di Toyotomi, Distrik Teshio, Hokkaido, Jepang, yang dioperasikan oleh JR Hokkaido. Stasiun ini diberi nomor W74. Stasiun Toyotomi豊富駅Bangunan Stasiun ToyotomiLokasi7 Chome Toyotomi Nishi 3 Jo, Toyotomi, Distrik Teshio, Prefektur Hokkaido 098-4113, JepangJepangKoordinat45°6′16.3″N 141°46′20.6″E / 45.104528°N 141.772389°E / 45.104528; 141.772389 Le...
Puerto Rico i olympiska spelen IOK-landskodPUR KommittéPuerto Ricos Olympiska KommittéOlympiska sommarspelen 1992 i BarcelonaDeltagare75 deltagare i 12 grenarFanbärareLuis Martínez Medaljsummering Guld0 Silver0 Brons1 Totalt1 Puerto Rico i olympiska sommarspelen1948 • 1952 • 1956 • 1960 • 1964 • 1968 • 1972 • 1976 • 1980 • 1984 • 1988 • 1992 • 1996 • 2000 • 2004 • 2...

1974 song by Kaveret Natati La KhayayEurovision Song Contest 1974 entryCountryIsraelArtist(s)KaveretAsPoogyLanguageHebrewComposer(s)Danny SandersonLyricist(s)Danny Sanderson, Alon OleartchikConductorYoni RechterFinals performanceFinal result7thFinal points11Entry chronology◄ Ey Sham (1973)At Va'Ani (1975) ► Natati La Khayay (Hebrew script: נתתי לה חיי, lit. 'I gave her my life'; the translation used by the band is She looked me in the eye) is a song performed in Heb...

この記事の項目名には以下のような表記揺れがあります。 ユン・ソンニョル ユン・ソギョル ユン・ソンヨル ユン・ソクヨル 尹 錫悦윤석열 大統領公式肖像(2022年) 大韓民国 第20代 大統領 任期 2022年5月10日 – 在任中 首相 金富謙(2022年5月10日 - 5月11日) 秋慶鎬(権限代行、2022年5月12日 - 2022年5月20日) 韓悳洙(2022年5月21日 - 現職) [1][2] 大韓...

Place in Jabrayil, AzerbaijanÇulluÇulluCoordinates: 39°24′23″N 46°42′50″E / 39.40639°N 46.71389°E / 39.40639; 46.71389Country AzerbaijanDistrictJabrayilTime zoneUTC+4 (AZT) Çullu (Chullu) is a village situated on Goyan steppe, 27 km west of the city of Jabrayil,[1] within the Dagh Tumas administrative-territorial unit of Jabrayil District, Azerbaijan.[2] Toponym According to the Encyclopaedic Dictionary of Toponyms of Azerbaijan, the...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir March. Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite aucune source et peut contenir des informations erronées (signalé en septembre 2024). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Note...
















