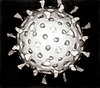
Hemagglutination assay
|
Read other articles:

Je partiraiSingel oleh Anggundari album EchosDirilisMei 2011FormatDigital download; CD SingleDirekam2010GenrePopDurasi4:22LabelApril Earth, WarnerPenciptaAnggun, Marie Bastide, Christophe Cottin, Gioacchino MauriciProduserAnggun Je partirai adalah singel pertama oleh penyanyi Indonesia Anggun C. Sasmi dari album internasional kelimanya untuk versi berbahasa Prancis yang bertajuk Echoes. Lagu ini juga direkam dalam bahasa Indonesia dengan judul Yang Terlarang dalam album versi berbahasa Inggri...

artikel ini perlu dirapikan agar memenuhi standar Wikipedia. Tidak ada alasan yang diberikan. Silakan kembangkan artikel ini semampu Anda. Merapikan artikel dapat dilakukan dengan wikifikasi atau membagi artikel ke paragraf-paragraf. Jika sudah dirapikan, silakan hapus templat ini. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Patung makara di Candi Lesung Batu (foto diambil pada tahun 1877-1879) Candi Lesung Batu adalah situs arkeologi yang terletak di Kecamatan Rawas U...

Unincorporated community in Virginia, United States Unincorporated community in Virginia, United StatesForks of Waters, VirginiaUnincorporated communityAerial view of Forks of Waters. The South Branch Potomac River flows diagonally across the image.Forks of WatersShow map of VirginiaForks of WatersShow map of the United StatesCoordinates: 38°28′56″N 79°30′31″W / 38.48222°N 79.50861°W / 38.48222; -79.50861CountryUnited StatesStateVirginiaCountyHighlandElevat...

Signature of Mathematicus Christophorus Rothmannus Bernburgensis Christoph Rothmann (between 1550 and 1560 in Bernburg, Saxony-Anhalt – probably after 1600 in Bernburg) was a German mathematician and one of the few well-known astronomers of his time. His research contributed substantially to the fact that Kassel became a European center of the astronomy in the 16th century. Life It is not known today when Rothmann was born, although it is known that his place of birth was Bernberg on the Sa...

Village in Maharashtra This article is an orphan, as no other articles link to it. Please introduce links to this page from related articles; try the Find link tool for suggestions. (February 2018) Village in Maharashtra, IndiaPotegaonvillageCountry IndiaStateMaharashtraDistrictSolapur districtLanguages • OfficialMarathiTime zoneUTC+5:30 (IST) Potegaon is a village in the Karmala taluka of Solapur district in Maharashtra state, India. Demographics Covering 779 hectares (1,920...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Mariano. Charlie MarianoBiographieNaissance 12 novembre 1923BostonDécès 16 juin 2009 (à 85 ans)CologneNom de naissance Carmine Ugo MarianoNationalité américaineFormation Berklee College of MusicActivités Hautboïste, musicien de jazz, saxophoniste, artiste d'enregistrementPériode d'activité à partir de 1945Conjoint Toshiko AkiyoshiEnfant Monday Michiru (en)Autres informationsInstruments Saxophone, hautboisLabels Bethlehem Records, Edition of Co...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...
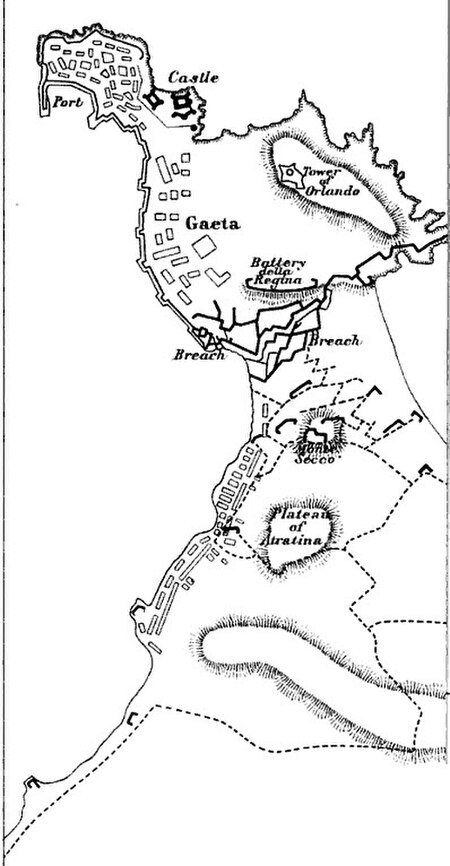
1815 siege during the Neapolitan War Siege of GaetaPart of the Neapolitan WarMap of the 1806 Siege of Gaeta showing the terrainDate28 May – 8 August 1815LocationGaeta, present-day Italy41°13′00″N 13°34′00″E / 41.2167°N 13.5667°E / 41.2167; 13.5667Result Coalition victory[1]Belligerents Austrian Empire United Kingdom Kingdom of Sicily Kingdom of NaplesCommanders and leaders Joseph Freiherr von Lauer Maresciallo di Campo Aless...

Philadelphia mayoral election 1923 Philadelphia mayoral election← 19191927 → Nominee W. Freeland Kendrick A. Raymond Raff Party Republican Democratic Popular vote 286,398 37,239 Percentage 88.49% 11.51% Mayor before election J. Hampton Moore Republican Elected Mayor W. Freeland Kendrick Republican Elections in Pennsylvania Federal government U.S. President 1789 1792 1796 1800 1804 1808 1812 1816 1820 1824 1828 1832 1836 1840 1844 1848 1852 1856 1860 1864 1868...

English footballer For other people named Matthew Taylor, see Matthew Taylor (disambiguation). For the defender turned manager, see Matt Taylor (footballer, born 1982). For the Oxford-born midfielder nine years his senior, see Matthew Taylor (footballer). Matty Taylor Taylor warming up for Bristol Rovers in 2015Personal informationFull name Matthew James Taylor[1]Date of birth (1990-03-30) 30 March 1990 (age 34)[2]Place of birth Kidlington, England[3]Height 5 ...

Частина серії проФілософіяLeft to right: Plato, Kant, Nietzsche, Buddha, Confucius, AverroesПлатонКантНіцшеБуддаКонфуційАверроес Філософи Епістемологи Естетики Етики Логіки Метафізики Соціально-політичні філософи Традиції Аналітична Арістотелівська Африканська Близькосхідна іранська Буддій�...

Pasote Dysphania ambrosioides TaksonomiDivisiTracheophytaSubdivisiSpermatophytesKladAngiospermaeKladmesangiospermsKladeudicotsKladcore eudicotsOrdoCaryophyllalesFamiliAmaranthaceaeSubfamiliChenopodioideaeTribusDysphanieaeGenusDysphaniaBagianDysphania sect. AdenoisSpesiesDysphania ambrosioides Mosyakin dan Clemants, 2002 Tata namaBasionimChenopodium ambrosioides Sinonim takson Ambrina ambrosioides (L.) Spach Ambrina parvula Phil. Ambrina spathulata Moq. Atriplex ambrosioides (L.) Crantz Blitum...
British philosopher, jurist, and social reformer (1748–1832) Jeremy BenthamPortrait of Bentham by Henry William PickersgillBorn(1748-02-15)15 February 1748 [O.S. 4 February 1747/8]London, EnglandDied6 June 1832(1832-06-06) (aged 84)London, EnglandEducationThe Queen's College, Oxford (MA)Era18th-century philosophy19th-century philosophyRegionWestern philosophySchoolUtilitarianismLegal positivismLiberalismRadicalismEpicureanismMain interestsPolitical philosophy, philosophy of law...

Parliamentary constituency in the United Kingdom, 1885–1950 Bow and BromleyFormer Borough constituencyfor the House of CommonsBow and Bromley in London 1885-1918Bow and Bromley in London 1918-501885–1950SeatsOneCreated fromTower HamletsReplaced byPoplar Bow and Bromley was a constituency in the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Located in the Metropolitan Borough of Poplar in London, it was created by the Redistribution of Seats Act for the 1885 general election and returned one Member of...

County in Minnesota, United States County in MinnesotaFillmore CountyCountyFillmore County CourthouseLocation within the U.S. state of MinnesotaMinnesota's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 43°41′N 92°05′W / 43.68°N 92.09°W / 43.68; -92.09Country United StatesState MinnesotaFoundedMarch 5, 1853Named forMillard FillmoreSeatPrestonLargest citySpring ValleyArea • Total862 sq mi (2,230 km2) • Land861 sq ...

1881 shootout in Tombstone, Arizona, United States For the film, see Gunfight at the O.K. Corral (film). O.K. Corral redirects here. For the location, see O.K. Corral (building). The OK Corral redirects here. For the Doctor Who episode, see The Gunfighters. Gunfight at the O.K. CorralTombstone in 1881DateOctober 26, 1881LocationTombstone, Arizona Territory, U.S.31°42′50″N 110°04′03″W / 31.71389°N 110.06750°W / 31.71389; -110.06750Participants Wyatt Earp Mor...

Ingeborg di NorvegiaSigillo di Ingeborg di Norvegia.Duchessa di ÖlandPrincipessa di NorvegiaStemma Nome completoIngebjørg Eiriksdatter NascitaBergen, 1297 MorteÖland, 1357 DinastiaBellachioma PadreEirik II di Norvegia MadreIsabel Bruce ConsorteValdemaro di Finlandia FigliErik ReligioneCattolicesimo Ingebjørg Eiriksdatter, meglio nota come Ingeborg di Norvegia, duchessa di Öland (Bergen, 1297 – Öland, 1357), è stata una nobile norvegese, figlia di re Eirik II. Indice 1 Biografia...

Group of science education and research institutes in India Not to be confused with Indian Institute of Science or National Institute of Science Education and Research. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Indian Institutes of Science Education and Research – news · newspapers · books · scholar · ...

Alma CoganAlma Cogan nel 1963 Nazionalità Regno Unito GenerePop Periodo di attività musicale1952 – 1966 EtichettaHMV, EMI Columbia Sito ufficiale Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Alma Cogan, nata Alma Angela Cohen (Whitechapel, 19 maggio 1932 – Londra, 26 ottobre 1966), è stata una cantante britannica. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Discografia parziale 2.1 Album 3 Note 4 Altri progetti 5 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Ha esordito all'età di 20 anni con il 7 To ...

French video game development company This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Delphine Software International – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Delphine Software InternationalCompany typePrivateIndustryVideo gamesFounded1988Defu...