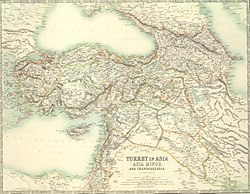
Hattians
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2023. Hania AamirAamir pada 2018Lahir12 Februari 1997 (umur 27)Rawalpindi, Punjab, PakistanAlmamaterFAST-NUCESPekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif2015–sekarang Hania Aamir (lahir 12 Februari 1997)[1] adalah seorang pemeran Pakistan yang tampil da...

Curug CitamburCurug CitamburLokasiDesa Karangjaya, Kecamatan Pasirkuda, Kabupaten Cianjur, Provinsi Jawa Barat, IndonesiaKoordinat7°11′33.6″S 107°14′03.09″E / 7.192667°S 107.2341917°E / -7.192667; 107.2341917Koordinat: 7°11′33.6″S 107°14′03.09″E / 7.192667°S 107.2341917°E / -7.192667; 107.2341917TipePlungeTinggi total130 meter (427 ft)Jumlah titik3 (Tiga)Anak sungaiSungai Citambur Curug Citambur adalah sebuah curug a...

Men's Greco-Roman 58 kg at the 1998 Asian GamesVenueThammasat Gymnasium 1Dates13–14 December 1998Competitors10 from 10 nationsMedalists Kim In-sub South Korea Asliddin Khudoyberdiev Uzbekistan Sheng Zetian China← 19942002 → Wrestling at the1998 Asian GamesFreestyleGreco-Roman54 kg54 kg58 kg58 kg63 kg63 kg69 kg69 kg76 kg76 kg85 kg85 kg97 kg97 kg130 kg130 kgvte Main article: Wrestling at the 1998 As...

Clarence NashClarence Nash tahun 1982 Aktor Suara Donal Bebek ke-1Masa jabatan1934–1985 PenggantiTony Anselmo Informasi pribadiLahirClarence Charles Ducky Nash(1904-12-07)7 Desember 1904Watonga, Oklahoma, Amerika SerikatMeninggal20 Februari 1985(1985-02-20) (umur 80)Glendale, California, Amerika SerikatSuami/istriMargaret SeamansAnak2PekerjaanAktor SuaraSunting kotak info • L • B Clarence Ducky Nash (7 Desember 1904–20 Februari 1985) adalah pengisi suara dari Amerika Se...

Cycling contest at 2015 European Games Cycling at the 2015 European GamesVenueBMX Velopark (BMX)MTB Velopark (mountain biking)Dates16–27 JuneCompetitors346[1]2019 → Cycling at the2015 European GamesRoad cyclingRoad racemenwomenTime trialmenwomenMountain bikingCross countrymenwomenBMXBMXmenwomenvte Three disciplines of cycling were contested at the 2015 European Games: road cycling, mountain biking, and bicycle motocross (BMX). A total of eight medal events were held....

Sporting event delegationIraq at theOlympicsIOC codeIRQNOCNational Olympic Committee of IraqWebsitewww.nociraq.iq (in Arabic and English)MedalsRanked 149th Gold 0 Silver 0 Bronze 1 Total 1 Summer appearances19481952–19561960196419681972–1976198019841988199219962000200420082012201620202024 Iraq first participated at the Olympic Games in 1948. Iraqis missed the 1952 and boycotted the 1956 games over opposition to the Suez Crisis. Following this absence, Iraq returned to win a Bronze me...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с такой фамилией, см. Джонс. Рашида Джонсангл. Rashida Jones Имя при рождении Рашида Лиа Джонс Дата рождения 25 февраля 1976(1976-02-25)[1] (48 лет) Место рождения Лос-Анджелес, Калифорния, США Гражданство США Профессия актриса, сценари�...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant un coureur cycliste français. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?). Pour plus d’informations, voyez le projet cyclisme. Pour les articles homonymes, voir Guégan. Maël GuéganMaël Guégan lors de la première étape du Tour de l'Ain 2023 à Loyettes.InformationsNaissance 19 janvier 1998 (26 ans)Saint-NazaireNationalité françaiseÉquipe actuelle CIC U Nantes AtlantiqueÉquipes amateurs 2008-2016AC Brévi...

烏克蘭總理Прем'єр-міністр України烏克蘭國徽現任杰尼斯·什米加尔自2020年3月4日任命者烏克蘭總統任期總統任命首任維托爾德·福金设立1991年11月后继职位無网站www.kmu.gov.ua/control/en/(英文) 乌克兰 乌克兰政府与政治系列条目 宪法 政府 总统 弗拉基米尔·泽连斯基 總統辦公室 国家安全与国防事务委员会 总统代表(英语:Representatives of the President of Ukraine) 总...

Township in Illinois, United StatesUrsa TownshipTownshipLocation in Adams CountyAdams County's location in IllinoisCoordinates: 40°04′55″N 91°24′24″W / 40.08194°N 91.40667°W / 40.08194; -91.40667CountryUnited StatesStateIllinoisCountyAdamsEstablishedNovember 6, 1849Area • Total61.03 sq mi (158.1 km2) • Land57.22 sq mi (148.2 km2) • Water3.81 sq mi (9.9 km2) 6.24%Elevatio...

Model 23, CR, R-6 The CR-1 with Bert Acosta, 1921 Role Racing aircraftType of aircraft Manufacturer Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company First flight 1 August 1921 Primary user United States Navy Number built 4 The Curtiss CR was a racing aircraft designed for the United States Navy in 1921 by Curtiss. It was a conventional single-seater biplane with a monocoque fuselage and staggered single-bay wings of equal span braced with N-struts. Two essentially similar landplane versions were bui...

A major contributor to this article appears to have a close connection with its subject. It may require cleanup to comply with Wikipedia's content policies, particularly neutral point of view. Please discuss further on the talk page. (August 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) District of Columbia Army National GuardDistinctive shoulder insigniaActiveMarch 2, 1802 – presentCountryUnited StatesBranchUnited States ArmyTypeDistrict Army National GuardSize1,350Part ofDistric...

Zeidae Zeus capensis Klasifikasi ilmiah Domain: Eukaryota Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Kelas: Actinopterygii Ordo: Zeiformes Famili: ZeidaeLatreille, 1825 Genus[1] Zenopsis Zeus Zeidae (berasal dari nama dewa dalam mitologi yunani, Zeus) atau juga disebut tetawak atau dori adalah keluarga ikan laut dalam ordo zeiformes yang besar, mencolok, dan bertubuh dalam. Famili ikan ini ditemukan di Samudra Atlantik, Hindia, dan Pasifik, famili ini hanya berisi enam spesies dalam dua genu...

第26回夏季ユニバーシアード 開催都市 中国・深圳参加国・地域数 152参加人数 7,865競技種目数 22競技開会式 2011年8月12日閉会式 2011年8月23日開会宣言 胡錦濤選手宣誓 龔園審判宣誓 王宴最終聖火ランナー 劉翔など5人主競技場 深圳世界大学生運動会体育中心 Portal:オリンピックテンプレートを表示 第26回夏季ユニバーシアード(XXVI Summer Universiade)は、2011年に中国・広東省...

CourtieuxcomuneCourtieux – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Francia RegioneAlta Francia Dipartimento Oise ArrondissementCompiègne CantoneCompiègne-1 TerritorioCoordinate49°23′16″N 3°05′22″E49°23′16″N, 3°05′22″E (Courtieux) Altitudine41 m s.l.m. Superficie2,61 km² Abitanti189[1] (2009) Densità72,41 ab./km² Altre informazioniCod. postale60350 Fuso orarioUTC+1 Codice INSEE60171 CartografiaCourtieux Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale C...

Nagara-class light cruiser This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (April 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Natori off Nagasaki in 1922 History Empire of Japan NameNatori NamesakeNatori River Ordered1919 Fiscal Year BuilderMitsubishi Laid down14 December 1920 Launched16 February 1922 Commissioned15 September 1922[1] Stricken10 O...

Kabupaten Sidenreng RappangKabupatenPLTB Sidrap LambangJulukan: Bumi Nene' Mallomo[1]Motto: Resopa Tammangingngi Malomo Nalatei Pammase DewataPetaKabupaten Sidenreng RappangPetaTampilkan peta SulawesiKabupaten Sidenreng RappangKabupaten Sidenreng Rappang (Indonesia)Tampilkan peta IndonesiaKoordinat: 3°54′S 119°48′E / 3.9°S 119.8°E / -3.9; 119.8Negara IndonesiaProvinsiSulawesi SelatanTanggal berdiri18 Februari 1344 (Hari Lahir) 18 Februari...

Istrana Nước Ý Vùng Veneto Tỉnh tỉnh Treviso (TV) Thị trưởng Độ cao 38 m Diện tích 26,3 km² Dân số - Tổng số (Tháng 12 năm 2004) 8223 - Mật độ 312/km² Múi giờ CET, UTC+1 Tọa độ 45°41′B 12°6′Đ / 45,683°B 12,1°Đ / 45.683; 12.100 Danh xưng istranesi Mã điện thoại 0422 Mã bưu điện 31036 Frazioni Sala, Pezzan, Ospedaletto, Villanova Vị trí của Istrana tại Ý Website: www.istrana.it/ Istran...

High school in Bergen County, New Jersey, US North Arlington High SchoolAddress222 Ridge RoadNorth Arlington, Bergen County, New Jersey 07031United StatesCoordinates40°47′20″N 74°07′58″W / 40.788921°N 74.132834°W / 40.788921; -74.132834InformationTypePublic high schoolMottoPride, Loyalty, Desire[1]Established1935School districtNorth Arlington School DistrictNCES School ID341143000636[3]PrincipalPatrick D. Bott[2]Faculty49.6 FTEs[...