Harry Gordon Johnson
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Jaswandi Panglima Komando Daerah Militer JayakartaMasa jabatan23 Februari 2017 – 2 Maret 2018 PendahuluMayjen TNI Teddy Lhaksmana W.K.PenggantiMayjen TNI Joni SupriyantoPanglima Komando Daerah Militer IV/DiponegoroMasa jabatan25 Juli 2015 – 31 Maret 2017 PendahuluMayjen TNI Bayu PurwiyonoPenggantiMayjen TNI Tatang Sulaiman Informasi pribadiLahir12 Maret 1960 (umur 64)Blora, Jawa TengahAlma materAkademi Militer (1985)Karier militerPihak IndonesiaDinas/cabang TNI...

Balada Si RoyPoster rilis teatrikalSutradaraFajar NugrosProduserSusanti DewiDitulis olehSalman AristoBerdasarkanBalada Si Royoleh Gol A GongPemeran Abidzar Al Ghifari Febby Rastanty Bio One Penata musik Aghi Narottama Bemby Gusti Tony Merle SinematograferPadri NadeakPenyuntingAline JusriaPerusahaanproduksiIDN PicturesTanggal rilis 13 Oktober 2022 (2022-10-13) (JFW) 18 Oktober 2022 (2022-10-18) (BFFI) 29 November 2022 (2022-11-29) (JAFF) 19 Januari 2023 (2...

Sudut kota Racine Racine merupakan sebuah kota di Amerika Serikat. Kota ini letaknya di bagian utara. Tepatnya di negara bagian Wisconsin. Pada tahun 2010, kota ini memiliki jumlah penduduk sebesar 78.860 jiwa dan memiliki luas wilayah 48,4 km². Kota ini memiliki angka kepadatan penduduk sebesar 2.033,8 jiwa/km². Pranala luar Situs resmi Diarsipkan 2010-09-19 di Wayback Machine. Racine.WI.Net Diarsipkan 2007-11-15 di Wayback Machine. Racine County Convention and Visitors Bureau Racine ...
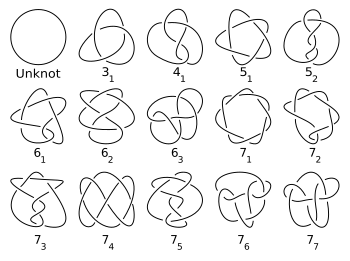
Теория узлов — изучение вложений одномерных многообразий в трёхмерное евклидово пространство или в сферу S 3 {\displaystyle S^{3}} . В более широком смысле предметом теории узлов являются вложения сфер в многообразия и вложения многообразий в целом. Содержание 1 Основные понятия �...

1997 song by Bob Dylan Make You Feel My LoveSheet music for the first verseSong by Bob Dylanfrom the album Time Out of Mind ReleasedSeptember 30, 1997RecordedJanuary 1997StudioCriteria Studios (Miami, FL)GenreFolk rock[1]Length3:32LabelColumbiaSongwriter(s)Bob DylanProducer(s)Daniel LanoisTime Out of Mind track listing11 tracks Love Sick Dirt Road Blues Standing in the Doorway Million Miles Tryin' to Get to Heaven 'Til I Fell in Love with You Not Dark Yet Cold Irons Bound Make You Fee...

2002 single by P. Diddy I Need a Girl (Part One)Single by P. Diddy featuring Usher and Loonfrom the album We Invented the Remix ReleasedFebruary 25, 2002 (2002-02-25)Length4:26LabelBad BoyAristaSongwriter(s)Sean CombsChauncey HawkinsMario WinansMichael Carlos JonesAdonis ShropshireJack KnightProducer(s)Mario WinansDiddyP. Diddy singles chronology Pass the Courvoisier, Part II (2002) I Need a Girl (Part One) (2002) I Need a Girl (Part Two) (2002) Usher singles chronology...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Тур. Запрос «Bos taurus primigenius» перенаправляется сюда; см. также другие значения. † Тур Скелет тура Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:В...

Untuk stasiun televisi lokal di Kepulauan Riau yang dikenal dengan singkatan TVTPI, lihat Tanjungpinang TV. MNCTVNama sebelumnyaTPI (1991—2010)JenisJaringan televisiNegaraIndonesiaBahasaBahasa IndonesiaPendiriSiti Hardijanti RukmanaTanggal siaran perdana26 Desember 1990 (siaran percobaan)Tanggal peluncuran23 Januari 1991 (sebagai TPI)20 Oktober 2010 (sebagai MNCTV)Kantor pusatMNC Studios, Jl. Raya Perjuangan No. 1, Kebon Jeruk, Jakarta Barat, IndonesiaWilayah siaranNasionalPemilikMedi...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2017年12月19日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:若望保祿二世 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 �...

This article is about the independent Christian denomination founded by Joseph René Vilatte in the United States. For the Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, in the United States, see Catholic Church in the United States. For other uses, see American Catholic Church. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Americ...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Meyer et David Meyer. David MeyerDavid Meyer à Bruxelles en 2008.BiographieNaissance 1967ParisNationalité françaiseActivité RabbinPère Georges Meyer (d)Mère Léone-Noëlle MeyerFratrie Léone-Noëlle MeyerAlexandre Meyermodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata David Meyer, né à Paris en 1967, est un rabbin franco-israélien de la mouvance juive libérale. Écrivain, il est professeur de littérature rabbinique et de pensée juive contemporaine...

Granting governmental powers to parts of the UK Parts of this article (those related to Section 35 of The Scotland Act 1998 and Gender Recognition Reform (Scotland) Bill) need to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (June 2023) This article is part of a series onPolitics of the United Kingdom Constitution Magna Carta Bill of Rights Treaty of Union (Acts of Union) Parliamentary sovereignty Rule of law Separation of powers Other co...

Costume in the years 1400-1500 Full-bodied houppelandes with voluminous sleeves worn with elaborate headdresses are characteristic of the earlier 15th century. Detail from Très Riches Heures du Duc de Berry. Fashion in 15th-century Europe was characterized by a series of extremes and extravagances, from the voluminous robes called houppelandes with their sweeping floor-length sleeves to the revealing doublets and hose of Renaissance Italy. Hats, hoods, and other headdresses assumed increasin...

Italian-born American women's basketball coach Geno AuriemmaAuriemma in 2023Current positionTitleHead coachTeamUConnConferenceBig EastRecord1,213–162 (.882)Annual salary$2.4 million[1]Biographical detailsBorn (1954-03-23) March 23, 1954 (age 70)Montella, ItalyAlma materWest Chester UniversityCoaching career (HC unless noted)1977-1979Bishop McDevitt High School (Assistant Varsity Coach / Head Junior Varsity Coach)1978–1979Saint Joseph's (assistant)1979–1981Bishop Kenric...

Defunct American motor vehicle manufacturer This article is about the Imperial marque manufactured by U.S. automaker Chrysler between 1955 and 1983. For Imperial cars manufactured under the Chrysler marque, see Chrysler Imperial. For the early British manufacturer, see Imperial (British automobile). For the Imperial automobile from 1908 to 1916, see Imperial Automobile Company. ImperialCompany typeDivisionIndustryAutomotivePredecessorChrysler ImperialFounded1955FounderChryslerDefunct1983;...

Species of moth Marmara smilacisella Larva and leaf mines Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Insecta Order: Lepidoptera Family: Gracillariidae Genus: Marmara Species: M. smilacisella Binomial name Marmara smilacisella(Chambers, 1875) Synonyms Phyllocnistis smilacisella Chambers, 1875 Marmara similiacicella Dyar, [1903] Marmara smilaciella Meyrick, 1912 Marmara smilacisella is a species of moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known ...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Merkel (homonymie). Angela Merkel Angela Merkel en 2019. Fonctions Chancelière fédérale d'Allemagne 22 novembre 2005 – 8 décembre 2021(16 ans et 16 jours) Élection 22 novembre 2005 Réélection 28 octobre 200917 décembre 201314 mars 2018 Président fédéral Horst KöhlerJens Böhrnsen (intérim)Christian WulffHorst Seehofer (intérim)Joachim GauckFrank-Walter Steinmeier Gouvernement Merkel I, II, III et IV Législature 16e, 17e, 18e et 19e...

Voce principale: Football-Club Bulle. Football-Club BulleStagione 2021-2022Sport calcio Squadra Bulle Allenatore Lucien Dénervaud All. in seconda François Bonetti Prima Lega3º posto Coppa SvizzeraSecondo turno StadioStade de Bouleyres Maggior numero di spettatori480 vs. Vevey United Minor numero di spettatori287 vs. Lancy Media spettatori387 2020-2021 2022-2023 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti il Football-Club Bulle nelle compet...

Executive branch of the European Union European Commission Name in official languages Bulgarian: Европейска комисия Croatian: Europska komisija Czech: Evropská komise Danish: Europa-Kommissionen Dutch: Europese Commissie English: European Commission Estonian: Euroopa Komisjon Finnish: Euroopan komissio French: Commission européenne German: Europäische Kommission Greek: Ευρωπαϊκή Επιτροπή Hungarian: Európai Bizottság Irish: Coimisiún Eorpach Italian: Com...

OK-GLI OK-GLI actuellement exposé au musée des techniques de Spire. Caractéristiques Date de construction 1984 Performances Nombre de vols 25 Temps passé dans l'espace 0 modifier OK-GLI au Salon international aérospatial de Moscou en 1997. L'appareil OK-GLI (Bourane Analog BTS-02) est un véhicule d'essai soviétique (Bourane aerodynamic analogue) du programme de la navette spatiale Bourane. Il a été construit en 1984, et a été utilisé pour 25 vols tests entre 1985 et 1988 avant d'...
