Halmyris
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini memberikan informasi dasar tentang topik kesehatan. Informasi dalam artikel ini hanya boleh digunakan untuk penjelasan ilmiah; bukan untuk diagnosis diri dan tidak dapat menggantikan diagnosis medis. Wikipedia tidak memberikan konsultasi medis. Jika Anda perlu bantuan atau hendak berobat, berkonsultasilah dengan tenaga kesehatan profesional. Tumor atau barah (Inggris: tumor, tumour) adalah sebutan untuk neoplasma atau lesi padat yang terbentuk akibat pertumbuhan sel tubuh yang...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Selasih (disambiguasi). Selasih Selasih Eropa (Ocimum basilicum) Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Plantae (tanpa takson): Angiospermae (tanpa takson): Eudikotil (tanpa takson): Asterids Ordo: Lamiales Famili: Lamiaceae Genus: Ocimum Spesies Terdapat 35 jenis, di antaranya Ocimum americanum Ocimum basilicum Ocimum campechianum Ocimum gratissimum Ocimum kilimandscharicum Ocimum tenuiflorum Selasih, tlasih, basil, atau basilikum (Ocimum) adalah segolongan terna yang dimanf...

Public monument in Philadelphia General Galusha Pennypacker MemorialThe monument in 200739°57′30.5″N 75°10′10.5″W / 39.958472°N 75.169583°W / 39.958472; -75.169583LocationLogan Circle, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United StatesDesignerCharles GraflyAlbert LaessleFabricatorRoman Bronze WorksTypeStatueMaterialBronzeLimestoneLength8 feet 2 inches (2.49 m)Width8 feet 2 inches (2.49 m)Height17 feet (5.2 m)Completion date19...

Questa voce sull'argomento scrittori statunitensi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Joseph Loeb III Joseph Loeb III, detto Jeph (Stamford, 29 gennaio 1958), è un fumettista, produttore televisivo e sceneggiatore statunitense. Stimato autore di fumetti, vincitore di 4 Eisner Award e 5 Wizard Fan Awards, ha partecipato in veste di sceneggiatore e produttore esecutivo a serie televisive com...

Car of TomorrowCar of Tomorrow dari Chevrolet Impala yang dipakai Jimmie Johnson.Konstruktor Chevrolet Dodge Ford ToyotaPenerusGeneration 6 (NASCAR)Spesifikasi teknisPanjang206 in (523,2 cm)Lebar785 in (1.993,9 cm)Tinggi53 in (134,6 cm)Wheelbase110 in (279,4 cm)Mesin358 cubic inci (5.870 cc) FR layoutTransmisi4-speed manualBerat3450 lbs (1565 kg) (Gen 5) 3,250 lbs (Gen 6 Sprint Cup) 3,200 lbs (Xfinity)Bahan bakarSunoco Unleaded: 2007–2011Sunoco G...

Regional airline based out of Appleton, Wisconsin Air Wisconsin Airlines IATA ICAO Callsign ZW AWI WISCONSIN Founded1965 (1965)[1]Commenced operationsAugust 23, 1965; 58 years ago (1965-08-23)[1]AOC #A6WA683W[2]Hubs Chicago–O'Hare Philadelphia Frequent-flyer program AAdvantage Alliance Oneworld (Affiliate) Fleet size63Parent companyHarbor Diversified Inc.Traded asOTC Pink Current: HRBR[3]HeadquartersAppleton, WisconsinKey...

Pino DanielePino Daniele in concerto nel 2009 Nazionalità Italia GenerePop[1]Canzone napoletana[1]Pop rock[1]Blues[2][3][4]World music[5] Periodo di attività musicale1975 – 2015 Strumentovoce, chitarra, basso EtichettaEMI Italiana, CGD, BMG, Blue Drag Album pubblicati47 Studio24 Live5 Raccolte18 Sito ufficiale Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Giuseppe Daniele, detto Pino (Napoli, 19 marzo 1955 – Rom...

Albert Abraham Michelson Albert Abraham Michelson (19 Desember 1852 – 9 Mei 1931) ialah seorang fisikawan yang hasil penemuannya secara akurat menentukan laju cahaya menyokong teori relativitas Albert Einstein. Dianggap sebagai penemuan kunci dalam sejarah ilmiah, penemuan itu dibuat pada alat yang ditemukannya dan kini digunakan pada kadar panjang gelombang spektrum. Ia pindah ke Amerika Serikat dan ialah orang pertama Amerika yang memenangkan Hadiah Nobel Fisika (1907). Pran...

This partial list of city nicknames in Pennsylvania compiles the aliases, sobriquets and slogans that cities, boroughs, and towns in Pennsylvania are known by (or have been known by historically), officially and unofficially, to municipal governments, local people, outsiders or their tourism boards or chambers of commerce. City nicknames can help in establishing a civic identity, helping outsiders recognize a community or attracting people to a community because of its nickname; promote civi...

2013 Android-based smartphone by HTC HTC Desire 500ManufacturerHTCSeriesHTC Desire seriesModel500Compatible networks2G 3G (Only one SIM card can be used at 3G at a time on the Dual SIM model)First releasedSeptember 1, 2013; 10 years ago (2013-09-01)TypeSmartphoneForm factorSlateDimensions131.8 mm (5.19 in) H 66.9 mm (2.63 in) W 9.9 mm (0.39 in) D [1]Mass123 g (4.3 oz)[1]Operating systemAndroid 4.1.2 Jelly Bean, Sense UI...

Canadian junior men's ice hockey championship 1980 Memorial CupTournament detailsVenue(s)Keystone Centre(Brandon, Manitoba)Agridome(Regina, Saskatchewan)DatesMay 4–11, 1980Teams3Final positionsChampionsCornwall Royals (QMJHL) (2nd title)← 19791981 → The Memorial Cup trophy The 1980 Memorial Cup occurred May 4–11 at the Keystone Centre in Brandon, Manitoba and at the Agridome in Regina, Saskatchewan. It was the 62nd annual Memorial Cup competition and determined the m...

Bay in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany Hohwacht Bay from the west near the Kleiner Binnensee Hohwacht Bay (German: Hohwachter Bucht) is a wide bay in the state of Schleswig-Holstein on Germany's Baltic Sea coastline. It is named after the village and seaside resort of Hohwacht. The nearest large town is Oldenburg in Holstein, about 5 kilometres inland. A number of nature reserves fringe the bay and there is a military training area along its eastern shore.[1] On the western shore, about 1...
NFL team season 1979 Philadelphia Eagles seasonOwnerLeonard ToseGeneral managerJim MurrayHead coachDick VermeilHome fieldVeterans StadiumResultsRecord11–5Division place2nd NFC EastPlayoff finishWon Wild Card Playoffs(vs. Bears) 27–17Lost Divisional Playoffs(at Buccaneers) 17–24 ← 1978 Eagles seasons 1980 → The Eagles playing against the Buccaneers in the 1979 NFC Divisional Playoff Game. The 1979 Philadelphia Eagles season was the franchise's 47th season in th...

L'Accademia dei Facchini della Val di Blenio è un'accademia fondata a Milano nel 1560. Indice 1 Storia 2 Note 3 Bibliografia 4 Voci correlate 5 Collegamenti esterni Storia Giovan Paolo Lomazzo, Autoritratto come Abate dell'Accademia della Val di Blenio, Milano, Brera Il frontespizio dei Rabìsch (la raccolta di poesie dialettali dell'accademia) Singolarissimo consesso di artisti, artigiani, musici, attori teatrali che si riunì a Milano nell'età dell'ultimo Manierismo, l'Accademia d...

此條目没有列出任何参考或来源。 (2012年2月7日)維基百科所有的內容都應該可供查證。请协助補充可靠来源以改善这篇条目。无法查证的內容可能會因為異議提出而被移除。 伊凡一世 伊凡一世·丹尼洛维奇(钱袋)(Ива́н I Дани́лович Калита́,1288年—1340年3月31日),是莫斯科大公(约1325年-1340年3月31日在位),亚历山大·涅夫斯基幼子丹尼尔·亚历山德罗维奇�...

ماهاراجافرع من عاهل النوع منصبلقب نبيل تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات الماهاراجا دوليب سانغ بريشة الفنان الألماني فرانز فينترهالتر ماهاراجا أو مهراجا (باللغة السنسكرينية: महाराज) ومعناها «ماهات» أي العظيم و«راجا» أي الملك، فيكون معنى الكلمة الملك العظيم.[1]...

1302 battle of the Franco-Flemish War Not to be confused with Battle of the Spurs. Battle of the Golden SpursPart of the Franco-Flemish WarDepiction from the Grandes Chroniques de FranceDate11 July 1302[1]LocationKortrijk, County of Flanders50°49′44″N 03°16′33″E / 50.82889°N 3.27583°E / 50.82889; 3.27583Result Flemish victoryBelligerents County of FlandersCounty of Namur Kingdom of FranceCommanders and leaders William of JülichGuy of NamurJohn I of...

Elezioni parlamentari negli Stati Uniti del 2012Stato Stati Uniti Data6 novembre AssembleeCamera dei rappresentanti degli Stati Uniti, Senato degli Stati Uniti Liste Partito Democratico Partito Repubblicano Camera dei rappresentanti degli Stati Uniti Seggi 201 / 435 224 / 435 Differenza seggi 8 8 Senato degli Stati Uniti Seggi 23 / 33 8 / 33 Differenza seggi 2 2 Distribuzione del voto alla Camera e al Senato 2010 2014 Le elezioni parlamentari negli Stati Uniti d'America del 2012 si tenn...
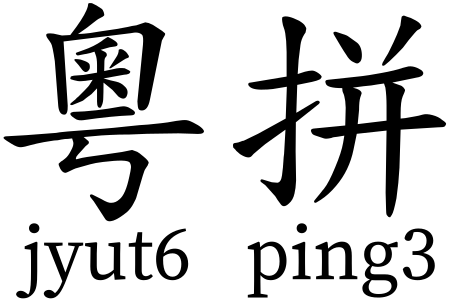
Romanization scheme for Cantonese This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Jyutping – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) JyutpingJyutping RomanizationTraditional Chinese粵拼Simplified Chinese粤拼Jyutpingjyut6 ping3Canton...

Ira LandrithPersonal detailsBorn(1865-03-23)March 23, 1865Milford, Texas, U.S.DiedOctober 11, 1941(1941-10-11) (aged 76)Altadena, California, U.S.Political partyProhibitionSpouse(s) Corinne Burney (m. 1889; died 1889) Harriett Canfield Grannis (m. 1891; died 1925) Sallie A. Alexander (m. 1936)ParentsMartin Luther Landrith (father)Mary Matilda Groves (moth...