Giorgio Basta
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: I Supermodel season 2 – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Season of television series I SupermodelSeason 2Season 2 castCountry of originChinaNo. of episodes12ReleaseOriginal networkiQiyiOriginal releaseOctober 22, ...
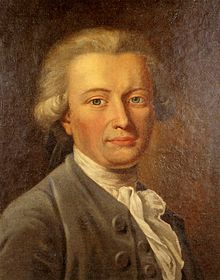
Untuk penggubah dan dokter Renaisans Jerman, lihat Georg Forster (penggubah). Georg ForsterGeorg Forster pada umur 26, oleh J. H. W. Tischbein, 1781 (juga dianggap dari Anton Graff)[1]LahirNovember 27, 1754 (1754-11-27)Nassenhuben (Mokry Dwór), Royal Prussia, Crown of the Kingdom of PolandMeninggal10 Januari 1794(1794-01-10) (umur 39)ParisKebangsaanJermanWarga negaraPrusia Polandia (Danziger)Karier ilmiahBidangsejarah alam, etnologiSingkatan penulis (botani)G.Forst. Jo...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. Hutan Hijau Subtropis Taiwanhutan di Cagar Alam ChatianshanWilayah ekoregion (warna ungu)EkologiWilayahAlam IndomalayaBiomaHutan tropis dan subtropis basah berdaun lebarBatasHutan hujan monsun Taiwan SelatanGeografiArea33,192 km2 (12,816 sq&...

Voce principale: Virtus Entella. AC Entella BacezzaStagione 1985-1986 Sport calcio Squadra Entella Bacezza Allenatore Gian Piero Ventura Presidente Sergio Barbieri Serie C25º nel girone A Coppa Italia Serie CFase eliminatoria a gironi Maggiori presenzeCampionato: D'Agostino (34) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: D'Agostino (11) 1984-1985 1986-1987 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti l'Associazione Calcio Entella Bacezza nelle competiz...

618–628 province of the Sasanian Empire Sasanian province of EgyptAgiptusProvince of the Sasanian EmpireMap of the Diocese of Egypt, which was controlled by the Sasanians.CapitalAlexandriaHistorical eraLate Antiquity• Established 618• Status quo ante bellum 628 Preceded by Succeeded by Egypt (Roman province) Egypt (Roman province) Today part ofEgyptLibya Part of a series on the History of Egypt Prehistoric Egypt Predynastic Period6000–3000 BC Ancient Egypt Early Dynastic Per...

Шалфей обыкновенный Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:РастенияКлада:Цветковые растенияКлада:ЭвдикотыКлада:СуперастеридыКлада:АстеридыКлада:ЛамиидыПорядок:ЯсноткоцветныеСемейство:ЯснотковыеРод:ШалфейВид:Шалфей обыкновенный Международное научное наз...

An area of a building or object whose existence or access is not immediately obvious A hidden compartment at the back of a lap desk, with two small drawers concealed beneath the pen and inkwell compartments A hidden door between the library and changing rooms at Mottisfont Abbey in England. A hidden compartment or secret compartment is a compartment whose existence or access is not obvious at first glance, and can be used as a hiding place for objects or sometimes even for people. A hidden co...

Petit Luxembourg Petit Luxembourg adalah hôtel particulier Prancis dan kediaman presiden Senat Prancis. Itu terletak di 17–17 bis, rue de Vaugirard, tepat di sebelah barat Istana Luxembourg, yang berfungsi sebagai kursi Senat, di arondisemen ke-6 Paris. Awalnya dibangun sekitar tahun 1550 dengan desain seorang arsitek yang tidak dikenal, bangunan ini terkenal karena interior Rokoko yang bertahan yang dirancang pada tahun 1710–1713 oleh arsitek Prancis Germain Boffrand.[1] Catatan...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: PS Keluarga USU – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Artikel ini perlu dikembangkan agar dapat memenuhi kriteria sebagai entri Wikipedia.Bantulah untuk mengembangkan artikel ini. Jika tida...

الناعمة الناعمة تهجى أيضاً الناعمة قضاء صفد إحداثيات 33°11′17″N 35°35′42″E / 33.18806°N 35.59500°E / 33.18806; 35.59500 السكان 1195 (1948) المساحة 7155 دونم تاريخ التهجير 14 مايو 1948 سبب التهجير تأثير سقوط المدن القريبة المستعمرات الحالية نيوت مردخاي، بيت هيلل [الإنجليزية]، كفار بلوم قري...

此條目可能包含不适用或被曲解的引用资料,部分内容的准确性无法被证實。 (2023年1月5日)请协助校核其中的错误以改善这篇条目。详情请参见条目的讨论页。 各国相关 主題列表 索引 国内生产总值 石油储量 国防预算 武装部队(军事) 官方语言 人口統計 人口密度 生育率 出生率 死亡率 自杀率 谋杀率 失业率 储蓄率 识字率 出口额 进口额 煤产量 发电量 监禁率 死刑 国债 ...
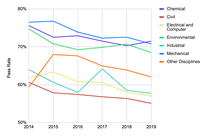
امتحان أساسيات الهندسة (FE)، كما يشار إليه بامتحان المهندس المتدرب (EIT)، وسابقا في بعض الدول امتحان الهندسة للمتدربين (EI)، هو أول اثنين من الامتحانات التي يجب على المهندسين اجتيازها من أجل أن يكونوا مرخصين كمهندسين محترفين في الولايات المتحدة وغيرها من الدول. الامتحان الثاني...

TroubleSutradaraKevin JohnsonProduserJohn H. WilliamsDanielle SterlingSkenarioRob MuirJohn Paul MurphyHarland WilliamsPemeranSean Big Sean AndersenPamela AdlonLucy HalePenata musikJessica WeissPenyuntingJudith AllenRob NealKevin PavlovicDistributor3QU MediaVanguard AnimationWV EnterprisesCinesite StudiosFocus Features (USA)Tanggal rilis 8 Agustus 2019 (2019-08-08) (Thailand) Durasi87 menitNegaraAmerika SerikatBahasaInggrisPendapatankotor$10,798,635[1] Trouble adalah fil...

For other people named Elisabeth of Austria, see Elisabeth of Austria (disambiguation). Duchess consort of Lorraine Elisabeth of AustriaImage of Elisabeth from the 15th centuryDuchess consort of LorraineTenure1307–1329Bornc. 1285Vienna, Duchy of Austria,Holy Roman EmpireDied19 May 1353Nancy, Duchy of Lorraine, Holy Roman EmpireBurialKönigsfelden Monastery, County of Tyrol, Holy Roman EmpireSpouseFrederick IV, Duke of LorraineIssueAmong others...Rudolph, Duke of LorraineMargaret, Countess o...

H. S. Bedi Hakim Mahkamah Agung IndiaMasa jabatan12-01-2007–04-09-2011 Informasi pribadiKebangsaanIndiaProfesiHakimSunting kotak info • L • B H. S. Bedi adalah hakim Mahkamah Agung India. Ia mulai menjabat sebagai hakim di mahkamah tersebut pada 12-01-2007. Masa baktinya sebagai hakim berakhir pada 04-09-2011.[1] Referensi ^ Daftar Hakim di Mahkamah Agung India. Mahkamah Agung India. Diarsipkan dari versi asli tanggal 2021-02-22. Diakses tanggal 10 Juni 2021. Art...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento singoli discografici non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Questa voce sull'argomento singoli pop è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Big Mistakesingolo dis...

Xylotrechus clarinus Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Arthropoda Kelas: Insecta Ordo: Coleoptera Famili: Cerambycidae Subfamili: Cerambycinae Tribus: Clytini Genus: Xylotrechus Spesies: Xylotrechus clarinus Xylotrechus clarinus adalah spesies kumbang tanduk panjang yang berasal dari famili Cerambycidae. Spesies ini juga merupakan bagian dari genus Xylotrechus, ordo Coleoptera, kelas Insecta, filum Arthropoda, dan kingdom Animalia. Larva kumbang ini biasanya mengebor ke dalam kayu...

1950–1953 bombing during the Korean War You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in French. (February 2019) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the French article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting mach...

公使可以指: 特命全權公使(Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary,簡稱Envoy),為公使館的館長,以及外交官體系中僅次於大使、級別第二高的外交官銜。 公使(瑞典语:Minister (diplomat))(Minister),附派於大使館內的外交官,可作為副館長擔任大使館的二把手。 常駐公使(德语:Ministerresident)(Minister Resident,亦稱駐辦公使),為1818年亞琛會議後始設的外交官銜,1961�...
Questa voce sull'argomento giocatori di football americano statunitensi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Jeff QueryNazionalità Stati Uniti Altezza183 cm Peso75 kg Football americano RuoloWide receiver Termine carriera1995 CarrieraGiovanili -1989Millikin University Squadre di club 1989-1991 Green Bay Packers481992-1995 Cincinnati Bengals371995 Washington Redskins1 Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Jeff...





