Gambling Commission
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Canadian Museum of NatureGedung Victoria Memorial MuseumInformasi umumJenisMuseum sejarah alamGaya arsitekturKebangkitan Gotik Kanada, Baronial SkotlandiaLokasiOttawa, Ontario, KanadaKoordinat45°24′46″N 75°41′20″W / 45.41266°N 75.68875°W / 45.41266; -75.68875Koordinat: 45°24′46″N 75°41′20″W / 45.41266°N 75.68875°W / 45.41266; -75.68875Penyewa sekarangCanadian Museum of NatureMulai dibangun1905Rampung1912PemilikPemerintah ...

Robert Lewandowski Lewandowski pada 2019Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Robert LewandowskiTanggal lahir 13 Agustus 1988 (umur 35)Tempat lahir Warsawa, PolandiaTinggi 185 cm (6 ft 1 in)[1]Posisi bermain PenyerangInformasi klubKlub saat ini FC BarcelonaNomor 9Karier junior1996 - 1997 Partyzant Leszno1997 - 2004 MKS Varsovia WarsawKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2006–2008 Znicz Pruszków 59 (36)2008–2010 Lech Poznań 82 (41)2010–2014 Borussia Dortmund 187 (10...

هاغامان الإحداثيات 42°58′39″N 74°09′02″W / 42.9775°N 74.1506°W / 42.9775; -74.1506 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة مونتغومري خصائص جغرافية المساحة 3.999599 كيلومتر مربع3.998553 كيلومتر مربع (1 أبريل 2010) ارتفاع 219 متر عدد السكان...

Pemandangan Graslei dengan Sungai Leie di depannya. Graslei (pelafalan dalam bahasa Belanda: [ˈɣrɑslɛi̯], Indonesia: dermaga rumputcode: id is deprecated ) adalah sebuah dermaga yang terletak di pusat kota Gent, Belgia. Dermaga ini terletak di sisi kanan Sungai Leie dan berada di seberang Korenlei. Dermaga ini merupakan sebuah pelabuhan pada Abad Pertengahan, dan kini menjadi tujuan wisata yang populer.[1] Di dermaga ini berjajar gedung-gedung bersejarah, sehingga Graslei...

Oldenico commune di Italia Tempat Negara berdaulatItaliaRegion di ItaliaPiedmontProvinsi di ItaliaProvinsi Vercelli NegaraItalia Ibu kotaOldenico PendudukTotal226 (2023 )GeografiLuas wilayah6,53 km² [convert: unit tak dikenal]Ketinggian143 m Berbatasan denganCaresanablot Quinto Vercellese San Nazzaro Sesia Villata Albano Vercellese Collobiano SejarahSanto pelindungLaurensius Informasi tambahanKode pos13030 Zona waktuUTC+1 UTC+2 Kode telepon0161 ID ISTAT002089 Kode kadaster ItaliaG...

Welsh rugby union player (1945–2024) For the artist, see Barry John (artist). For the English-born Indian director, see Barry John (theatre director). Not to be confused with John Barry. Rugby playerBarry JohnJohn in 2011Date of birth(1945-01-06)6 January 1945Place of birthCefneithin, WalesDate of death4 February 2024(2024-02-04) (aged 79)Place of deathCardiff, WalesHeight5 ft 10 in (1.78 m)Weight11 st 11 lb (165 lb; 75 kg)UniversityTrinity College, C...

Европейская сардина Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеГруппа:Костные рыбыКласс:Лучепёрые рыбыПодкласс:Новопёры...

Evangelical Church in Brazil Marginal at first, news reports and political analysts have pointed the important weight that the Evangelical Christian community has and its impact in electoral politics in Latin America, even helping in the electoral victories of conservative candidates.[1][2][3] Evangelical political parties are a particular type of political parties in Latin America generally linked or known to advocate for the interests of the Evangelical Christian co...

Voce principale: Associazione Calcio Verona. Associazione Calcio VeronaStagione 1954-1955Sport calcio Squadra Verona Allenatore Luigi Ferrero (fino alla 9ª) Angelo Piccioli (dalla 10ª alla 17ª) Federico Allasio (dalla 18ª in poi) Direttore TecnicoGiulio Cappelli (dalla 5ª alla 17ª) Serie B15º 1953-1954 1955-1956 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti l'Associazione Calcio Verona nelle competizioni ufficiali della stagione 1954-195...

16th-century Mughal Empire document The Court of Akbar, an illustration from a manuscript of the Akbarnama The Ain-i-Akbari (Persian: آئینِ اکبری) or the Administration of Akbar, is a 16th-century detailed document regarding the administration of the Mughal Empire under Emperor Akbar, written by his court historian, Abu'l Fazl in the Persian language.[1] It forms Volume III and the final part of the much larger document, the Akbarnama (Account of Akbar), also by Abu'l-Fazl, ...

Anti-caste social movement This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article contains content that is written like an advertisement. Please help improve it by removing promotional content and inappropriate external links, and by adding encyclopedic content written from a neutral point of view. (April 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) This article needs additiona...

Article principal : Chemins de fer dans la Guerre de Sécession. Premier conflit total de l'ère moderne[1],[2], la guerre de Sécession met en exergue le rôle déterminant que les chemins de fer joueront dans les conflits à venir, en particulier dans le domaine de la logistique et du transport de troupes. Mais si le réseau particulièrement bien développé du Nord et une gestion rigoureuse et sans compromis de ses moyens ferroviaires eurent un effet déterminant sur la victoire de l...
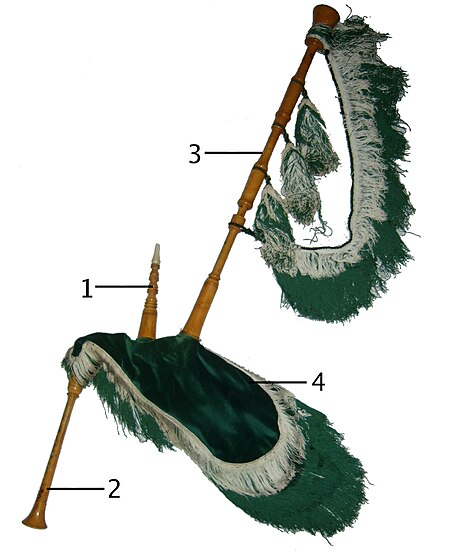
Gaitera Cantabrian band at Comillas festival Asturian bagpipers and drummers The gaita asturiana is a type of bagpipe native to the autonomous communities of Principality of Asturias and Cantabria on the northern coast of Spain. Differences from other Iberian gaitas The gaita asturiana is of larger size than the Galician gaita of the same key; that is to say, its pipes are of longer dimensions. The reed of the chanter (payuela) is of smaller size than the galician reed. Compared to the galici...

Về khái niệm không chắc chắn trong nhiều lĩnh vực, xem Không chắc chắn. Các tình huống thường phát sinh trong đó một quyết định phải được đưa ra khi kết quả của mỗi lựa chọn có thể không chắc chắn. Sự không chắc chắn đề cập đến các tình huống tri thức liên quan đến thông tin không hoàn hảo hoặc không xác định. Điều này áp dụng cho các dự đoán về các sự kiện trong tương la...

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Muhammad Said. Artikel biografi ini ditulis menyerupai resume atau daftar riwayat hidup (Curriculum Vitae). Tolong bantu perbaiki agar netral dan ensiklopedis. Artikel ini membutuhkan penyuntingan lebih lanjut mengenai tata bahasa, gaya penulisan, hubungan antarparagraf, nada penulisan, atau ejaan. Anda dapat membantu untuk menyuntingnya. Mohammad Said H. Mohammad Said (17 Agustus 1905 – 26 April 1995) adalah seorang wartawan, politikus, sejarawan da...
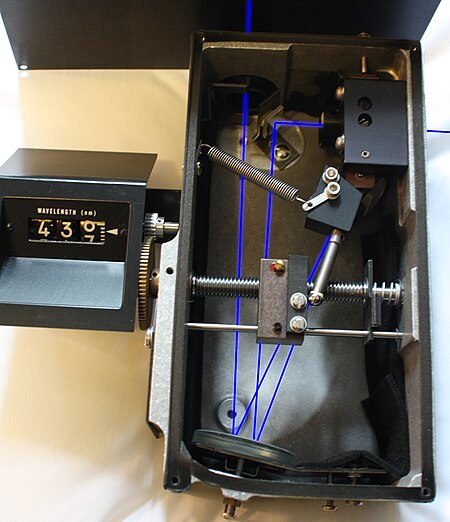
Монохроматор — спектральный оптико-механический прибор, предназначенный для выделения монохроматического излучения. Принцип работы основан на дисперсии света. Содержание 1 Устройство 2 Примечания 3 Литература 4 Ссылки Устройство Схема монохроматора Черни[англ.] — Т�...

مايكل أيبشير معلومات شخصية الميلاد 6 يناير 1997 (العمر 27 سنة)سويسرا الطول 1.83 م (6 قدم 0 بوصة) مركز اللعب وسط الجنسية سويسرا معلومات النادي النادي الحالي بولونيا الرقم 20 مسيرة الشباب سنوات فريق 0000–2016 يانغ بويز المسيرة الاحترافية1 سنوات فريق م. (هـ.) 2016–2022 يانغ بويز...

Renault R24 bersama Fernando Alonso. Renault R24 merupakan sebuah mobil Formula Satu yang dirancang oleh tim Renault F1 untuk musim balap F1 2004. Mobil ini dirancang oleh Mike Gascoyne dan sukses menjuarai satu balapan yaitu di Monako 2004 lewat Jarno Trulli. Total ada tiga pembalap yang balapan dengan mobil ini: Jarno Trulli, Fernando Alonso, dan Jacques Villeneuve. Wikimedia Commons memiliki media mengenai Renault R24. Artikel bertopik Formula Satu ini adalah sebuah rintisan. Anda dapat me...

Gold and uranium mine in South Africa Driefontein mineNo 5 or Hlanganani shaft of Driefonteinmine, in the Westrand DM, GautengLocationDriefontein mineLocationCarletonvilleProvinceGautengCountrySouth AfricaCoordinates26°23′26.16″S 27°29′24″E / 26.3906000°S 27.49000°E / -26.3906000; 27.49000ProductionProductsgold, uraniumOwnerCompanySibanye-StillwaterWebsitewww.sibanyestillwater.com/our-business/southern-africa/gold/driefontein/overviewYear of acquisition2002...

O futebol americano fez sua primeira aparição nos Jogos Olímpicos de 1904 e nos Jogos de Olímpicos de 1932 como esporte de demonstração. Entretanto, o futebol americano não foi reconhecido pelo COI e nunca estreou oficialmente nos Jogos Olímpicos de Verão.[1] Tentativas A IFAF, a instituição internacional que dirige as associações do futebol americano, já fez tentativas para ser aceitos no COI e, principalmente ter participação nos Jogos Olímpicos. Até agora ainda estão ten...

