Frederick V, Landgrave of Hesse-Homburg
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

BudapestIbu kotaIbu Kota HungariaMagyarország fővárosaDari atas, kiri ke kanan: Parlemen Hungaria, Halászbástya, Patung Kebebasan di Bukit Gellért, Alun-Alun Pahlawan di Taman Kota, Teater Nasional, Basilika Santo István dan Belváros dengan Jembatan Rantai Széchenyi pada malam hari BenderaLambang kebesaranJulukan: Jantung Eropa, Ratu Donau, Mutiara Donau, Ibu Kota Kebebasan, Ibu Kota Spa dan Pemandian Air Panas, Ibu Kota FestivalBudapestBudapest di HungariaTampilkan peta Hungari...

Naresh Chandra Duta Besar India untuk Amerika SerikatMasa jabatan1996–2001PresidenShankar Dayal Sharma (1997–2001)Kocheril Raman Narayanan (1996–1997) PendahuluSiddhartha Shankar RayPenggantiLalit MansinghGubernur Gujarat ke-13Masa jabatan1 Juli 1995 – 1 Maret 1996 PendahuluSarup SinghPenggantiKrishna Pal SinghSekretaris Kabinet India ke-20Masa jabatan11 Desember 1990 – 31 Juli 1992PresidenRamaswamy Venkataraman PendahuluV. C. PandePenggantiS. RajagopalMenteri Dala...

International Monument to the Reformation The Reformation Wall stretches for 100 m, depicting numerous Protestant figures from across Europe. At its heart are statues to William Farel, John Calvin, Theodore Beza, and John Knox. The Christogram can be seen below the statues. The International Monument to the Reformation, aerial view The International Monument to the Reformation (French: Monument international de la Réformation; German: Internationales Reformationsdenkmal), usually known as th...

Communist ideology This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Titoism – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Josip Broz Tito meeting with Bolesław Bierut and Michał Żymierski from the Polish People's Republic in 1946. Part of a series...

NGC 1300 La galaxie spirale barrée NGC 1300 Données d’observation(Époque J2000.0) Constellation Éridan Ascension droite (α) 03h 19m 41,1s[1] Déclinaison (δ) −19° 24′ 41″ [1] Magnitude apparente (V) 10,4[2] 11,1 dans la Bande B [2] Brillance de surface 13,91 mag/am2[2] Dimensions apparentes (V) 6,2′ × 4,1′[2] Décalage vers le rouge +0,005264 ± 0,000005[1] Angle de position 106°[2] Localisation dans la constellation : Éridan Astrom...
Khải hoàn môn Constantinus {{{tekst1}}} Vị trí Forum Xây dựng vào 315 CN Xây dựng bởi Constantinus I Loại công trình Khải hoàn môn Khải hoàn môn Constantinus Khải hoàn môn Constantinus (tiếng Latinh: Arcus Constantini, tiếng Ý: Arco di Costantino) là một Cổng chào chiến thắng tại Roma, nằm giữa Đấu trường La Mã và đồi Palatine. Cổng được lập nên bởi Viện Nguyên lão La Mã để kỷ niệm chiế...

Kyōdōstazione ferroviaria経堂 Vista dei binari della stazione LocalizzazioneStato Giappone LocalitàSetagaya, Tokyo Coordinate35°39′04.55″N 139°38′11.36″E / 35.651264°N 139.636489°E35.651264; 139.636489Coordinate: 35°39′04.55″N 139°38′11.36″E / 35.651264°N 139.636489°E35.651264; 139.636489 LineeFerrovie Odakyū ● Linea Odakyū Odawara StoriaStato attualeIn uso Attivazione1927 CaratteristicheTipoStazione su viadotto passante Bi...
Proton MailTangkapan layar situs web Proton Mail.URL protonmail.com TipeWebmailBersifat komersial?YaPendaftaranDiperlukanBahasaInggris, Spanyol, Jerman, Prancis, Italia, Jepang, Belanda, Polandia, Portugis, Romania, Rusia, Turki, UkrainaPengguna10 juta[1]Lisensilisensi MIT dan GPL-3.0 Bahasa pemrogramanPHP dan Javascript PemilikProton Technologies AG, Jenewa, SwissPembuatAndy Yen Web DeveloperProton Berdiri sejak16 Mei 2014; 9 tahun lalu (2014-05-16)NegaraSwiss Peringkat Alexa1,7...

此條目可能包含不适用或被曲解的引用资料,部分内容的准确性无法被证實。 (2023年1月5日)请协助校核其中的错误以改善这篇条目。详情请参见条目的讨论页。 各国相关 主題列表 索引 国内生产总值 石油储量 国防预算 武装部队(军事) 官方语言 人口統計 人口密度 生育率 出生率 死亡率 自杀率 谋杀率 失业率 储蓄率 识字率 出口额 进口额 煤产量 发电量 监禁率 死刑 国债 ...

29e cérémonie des Lumières Lumières de la presse internationale Organisée par l'Académie des Lumières Détails Date 22 janvier 2024 Lieu Forum des images Site web academiedeslumieres.com Résumé Meilleur film Anatomie d'une chute Meilleure mise en scène Thomas Cailley Film le plus nommé Anatomie d'une chute (6) Film le plus récompensé Anatomie d'une chute (3) Chronologie 28e cérémonie des Lumières 30e cérémonie des Lumières modifier La 29e cérémo...

2008 Italian general election ← 2006 13–14 April 2008 2013 → ← outgoing memberselected members →All 630 seats in the Chamber of Deputies316 seats needed for a majorityAll 315 elective seats in the Senate162 seats needed for a majority[a]Opinion pollsRegistered47,041,814 (C) · 42,358,775 (S)Turnout37,874,569 (C) · 80.5% (3.1 pp) 34,058,406 (S) · 80.4% (3.1 pp) First party Second party T...

Bear CountryPoster filmSutradaraJames AlgarProduserBen SharpsteenDitulis olehJames AlgarNaratorWinston HiblerPenyuntingLloyd L. RichardsonPerusahaanproduksiWalt Disney ProductionsDistributorRKO Radio PicturesTanggal rilis 5 Februari 1953 (1953-02-05) Durasi33 menitNegaraAmerika SerikatBahasaInggris Bear Country adalah sebuah film dokumenter pendek Amerika 1953 yang disutradarai oleh James Algar. Film tersebut memenangkan sebuah Academy Award di Academy Awards ke-26 pada 1954 untuk Subyek...

الصرفند الإحداثيات 33°27′27″N 35°17′45″E / 33.4575°N 35.295833333333°E / 33.4575; 35.295833333333 تقسيم إداري البلد لبنان التقسيم الأعلى قضاء صيدا تعديل مصدري - تعديل الصرفند[1] هي إحدى البلدات اللبنانية من بلدات قضاء صيدا في محافظة الجنوب. موقعها تقع الصرفند في �...

No debe confundirse con Emisión termoiónica. La ionización térmica, también conocida como ionización de superficie o ionización de contacto, es un proceso físico por el cual los átomos se desorben de una superficie caliente, y en el proceso se ionizan. La ionización térmica se utiliza para hacer fuentes de iones simples, para espectrometría de masas y para generar haces de iones.[1] La ionización térmica ha sido ampliamente utilizada para determinar los pesos atómicos, a...

The following highways are numbered 203: This list is incomplete; you can help by adding missing items. (August 2008) Canada Manitoba Provincial Road 203 Newfoundland and Labrador Route 203 Nova Scotia Route 203 Prince Edward Island Route 203 Quebec Route 203 Chile Route 203-CH in Los Ríos Region China China National Highway 203 Costa Rica National Route 203 India National Highway 203 (India) Japan Japan National Route 203 Belgium Belgium B203 Thailand Thailand Route 203 United States Alaba...

Commune and town in Sétif Province, AlgeriaGuelta ZerkaCommune and townCountry AlgeriaProvinceSétif ProvinceTime zoneUTC+1 (CET) Guelta Zerka is a town and commune in Sétif Province in north-eastern Algeria.[1] References Algeria portal ^ Communes of Algeria. Statoids. Retrieved December 12, 2010. vte Sétif ProvinceCapital: SétifDistricts Aïn Arnat Babor Béni Aziz Béni Ourtilane Bir El Arch Bouandas Bougaâ Djémila El Eulma Guenzet Guidjel Hammam Guergour Hammam Souhna M...

الدَّولةُ الحَمَدَانِيَّةُ الإِمَارَةُ الحَمَدَانِيَّةُ - دَوْلَةُ بَني حَمدَان 930 – 1003 خارطة تُظهر حُدود الدولة الحمدانيَّة ضمن الحُدود السياسيَّة المُعاصرة للوطن العربي سميت باسم حمدان بن حمدون التغلبي عاصمة الموصل (إمارة الموصل)حلب (إمارة حلب) نظام الحكم إم...
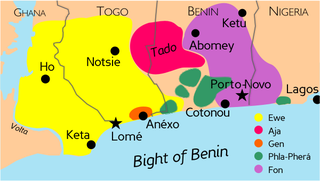
Gbe language Fonfɔ̀ngbèNative toBenin, Nigeria, Togo.EthnicityFon peopleNative speakers2.3 million (2019–2021)[1]Language familyNiger–Congo? Atlantic–CongoVolta-CongoVolta–NigerGbeFonDialects Agbome Arohun Gun Gbekon Kpase Writing systemLatin, GbékounOfficial statusOfficial language in BeninLanguage codesISO 639-2fonISO 639-3fonGlottologfonn1241 Fon languageGbe languages. Fon is purple.This article contains IPA phonetic symbols. Without proper ren...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Nages (homonymie). Pour l’article ayant un titre homophone, voir Nage. Nages-et-Solorgues Le village. Blason Administration Pays France Région Occitanie Département Gard Arrondissement Nîmes Intercommunalité Communauté de communes Rhôny Vistre Vidourle Maire Mandat Michel Chambelland 2020-2026 Code postal 30114 Code commune 30186 Démographie Gentilé Nageois Populationmunicipale 2 107 hab. (2021 ) Densité 341 hab./km2 Géographie Coo...

Municipality in the canton of Graubünden, Switzerland This article is about the city in Switzerland. For other uses, see Davos (disambiguation). Municipality in Graubünden, SwitzerlandDavosMunicipalityTop: View of the Sertig Valley, Middle left: World Economic Forum congress centre, Middle right: Lake Davos, Bottom: View over Davos FlagCoat of armsLocation of Davos DavosShow map of SwitzerlandDavosShow map of Canton of GraubündenCoordinates: 46°48′N 9°50′E / 46.800°N...

