Eye development
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2023. A.M. Tambunan dapat mengacu pada beberapa hal berikut: Albert Mangaratua Tambunan (1912 – 1970) politikus Parkindo, mantan Menteri Sosial Indonesia Albertus Maruli Tambunan (1925 – 2019) perwira tinggi angkatan darat Indo...
Kotak rangkap generik Kotak rangkap adalah gawit (atau kontrol) antarmuka pengguna grafis yang umum digunakan. Secara tradisional, ini adalah kombinasi daftar naik-turun atau kotak daftar dan kotak teks satu baris yang dapat disuntin, memungkinkan pengguna mengetikkan nilai secara langsung atau memilih nilai dari daftar. Istilah kotak rangkap kadang-kadang digunakan untuk mengartikan daftar naik-turun. [1] Baik di Java maupun . NET, kotak rangkap bukan sinonim untuk daftar naik-turun....

9°41′41″S 124°42′11″E / 9.69472°S 124.70306°E / -9.69472; 124.70306 Amanatun UtaraKecamatanNegara IndonesiaProvinsiNusa Tenggara TimurKabupatenTimor Tengah SelatanPemerintahan • Camat-Populasi • Total- jiwaKode Kemendagri53.02.09 Kode BPS5304110 Luas- km²Desa/kelurahan- Savana berbukit dekat Ayotupas Amanatun Utara adalah sebuah kecamatan di Kabupaten Timor Tengah Selatan, Nusa Tenggara Timur, Indonesia. Kecamatan ini beribu ko...

Strada statale 513di Val d'EnzaLocalizzazioneStato Italia Regioni Emilia-Romagna DatiClassificazioneStrada statale InizioParma FineCastelnovo ne' Monti Lunghezza56,270[1] km Provvedimento di istituzioneD.M. 27/12/1966 - G.U. 34 dell'8/02/1967[2] GestoreTratte ANAS: nessuna (dal 2001 la gestione è passata alla Provincia di Parma e alla Provincia di Reggio Emilia) Manuale La ex strada statale 513 di Val d'Enza (SS 513), ora strada provinciale 513 R di Val d'Enza (SP 5...

Universitas Prasetiya MulyaMotoA COLLABORATIVE LEARNING BY ENTERPRISINGJenisUniversitas swastaDidirikan1982RektorProf. Dr. Djisman S. Simandjuntak DekanDr. Fathony Rahman Dr. N. Hassan Wirajuda Stevanus Wisnu Wijaya, Ph.D.AlamatKavling Edutown I.1 Jl. BSD Raya Utama, BSD City, Tangerang, IndonesiaWarnaBiru TuaNama julukanPrasmulyanSitus webwww.prasetiyamulya.ac.id Universitas Prasetiya Mulya adalah institusi pendidikan di Indonesia yang berbasis di BSD City, Banten. Universitas ini memiliki k...
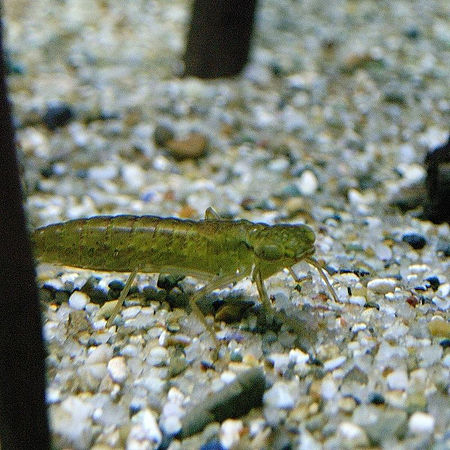

Capung Anisoptera Yellow-winged darter (en) TaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumArthropodaKelasInsectaOrdoOdonataUpaordoAnisoptera Selys, 1854 lbs Capung atau sibar-sibar adalah kelompok serangga yang tergolong ke dalam bangsa Odonata. Kedua macam serangga ini jarang berada jauh-jauh dari air, tempat mereka bertelur dan menghabiskan masa pra-dewasa anak-anaknya. Namanya dalam bahasa daerah adalah papatong (Sd.), kinjeng (Jw.), coblang (Jw.), kasasiur (bjn), tjapung, Sansibur (DykNgj) Bungkoloko (Si...

Langeland ialah pulau di Denmark yang terletak antara Sabuk Besar dan Teluk Kiel. Memiliki luas 285 km² (skt. 110 mil persegi), dan berpenduduk sekitar 15.000. Pulau ini memproduksi padi dan dikenal sebagai objek wisata. Sebuah jembatan menghubungkannya ke Taasinge dan Fyn. Secara administratif, pulau ini dibagi atas 3 kotamadya: Rudkøbing, Sydlangeland, dan Tranekær. Semuanya akan bergabung pada 1 Januari 2007 sebagai bagian dari reformasi skala nasional dan membentuk kotamadya Lange...

Административное деление Италии Топонимия Италии — совокупность географических названий, включающая наименования природных и культурных объектов на территории Италии. Структура и состав топонимии страны обусловлены её географическим положением, богатой историей...

ColumbiformesRentang fosil: Miosen Awal - Sekarang Tekukur Biasa Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Kelas: Aves Infrakelas: Neognathae Ordo: ColumbiformesLatham, 1790 Famili Columbidae Raphidae Ordo burung Columbiformes mencakup dara dan merpati yang tersebar luas di seluruh penjuru dunia dan diklasifikasikan ke dalam famili Columbidae, dan Dodo & Solitaire Rodrigues yang telah punah dan telah lama diklasifikasikan ke dalam famili kedua, Raphidae.[1] 313 spesie...

2006 protest This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Great American Boycott – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) The Great American BoycottDateMay 1, 2006 (2006-05-01)LocationUnited States, nationwideTypeDemonstra...
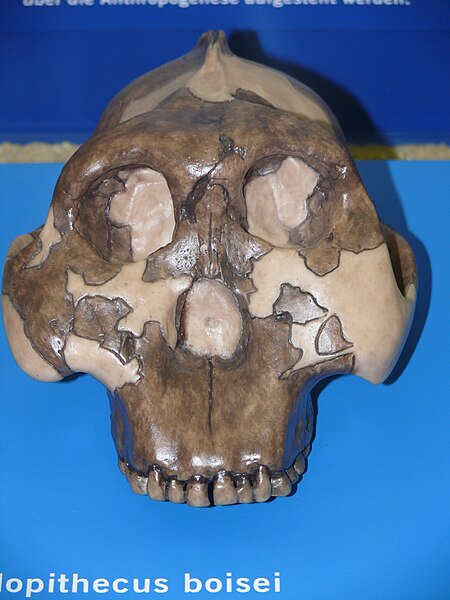
Robust australopithecinesRentang fosil: Pleistosen Skull of Paranthropus boisei Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Kelas: Mammalia Ordo: Primates Famili: Hominidae Subfamili: Homininae Tribus: Hominini Subtribus: Hominina Genus: ParanthropusBroom, 1938 Species †Paranthropus aethiopicus †Paranthropus boisei †Paranthropus robustus Robust australopithecines, anggota genus hominin Paranthropus yang telah punah, adalah hominin bipedal yang merupakan keturunan dari hominin...

Muhammad Taufiq Arasj Waasops Panglima TNIPetahanaMulai menjabat 1 April 2024PendahuluFebriel Buyung SikumbangPenggantiPetahanaKomandan Lanud Atang SendjajaMasa jabatan29 Maret 2023 – 1 April 2024PendahuluSulionoPenggantiJuli Heryanto Ginting Informasi pribadiLahir6 Agustus 1973 (umur 50)Ujung Pandang, Sulawesi SelatanKebangsaanIndonesiaAlma materAkademi Angkatan Udara (1995)Karier militerPihak IndonesiaDinas/cabang TNI Angkatan UdaraMasa dinas1995—sekarangPang...

Galaxy containing well-studied supermassive black hole IRAS 13224-3809Observation data (J2000[1] epoch)ConstellationCentaurus[2]Right ascension13h 25m 19.38s[1]Declination−38° 24′ 52.61″[1]Redshift0.06580 ± 0.00018Distance1 billion light-years[3]Apparent magnitude (V)13.80[4]Other designations2MASX J13251937-3824524; 2MASS J13251937-3824526; GSC 07787-00931; IRAS F13224-3809; 1RXS J132519.4-382445; WISE J132519...

Atlanta BravesBaseball Campione della NL East division in carica Segni distintivi Uniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Terza Colori sociali Blu marino, rosso scarlatto, bianco Dati societari Città Atlanta Nazione Stati Uniti Lega National League Division East Fondazione 1871 Denominazione Boston Red Stockings(1871-1876)Boston Red Caps(1876-1882)Boston Beaneaters(1883-1906)Boston Doves(1907-1910)Boston Rustlers(1911)B...

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang kabupaten di Indonesia. Untuk kota bernama sama, lihat Kota Serang. Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Serang (disambiguasi). Kabupaten SerangKabupatenTranskripsi bahasa daerah • Aksara Sundaᮞᮦᮛᮀ • Cacarakanꦱꦺꦫꦁ • PegonسيراڠPemandangan di Pantai Anyer. LambangMotto: Sepi ing pamrih, rame ing gawe(Jawa) Bekerja tanpa mengharap imbalan apa punPetaKabupaten SerangPetaTampilkan peta JawaKabupaten SerangK...

Disused railway station in North Yorkshire, England BeckholeBeckhole station site 1988General informationLocationBeck Hole, ScarboroughEnglandCoordinates54°24′28″N 0°44′11″W / 54.407889°N 0.736475°W / 54.407889; -0.736475Grid referenceNZ821020Other informationStatusDisusedHistoryOriginal companyWhitby and Pickering RailwayPre-groupingNorth Eastern RailwayKey dates1836OpenedClosed to passengers1 July 1865Reopened for passengers (summers only)19081914Closed f...

This article is about the administrative county. For the Riksdag constituency, see Uppsala County (Riksdag constituency). County (län) of Sweden County of SwedenUppsala County Uppsala län (Swedish)County of Sweden FlagCoat of armsUppsala County in SwedenLocation map of Uppsala County in SwedenCoordinates: 59°51′30″N 17°39′00″E / 59.85833°N 17.65000°E / 59.85833; 17.65000CountrySwedenFormed1634CapitalUppsalaMunicipalities 8 ÄlvkarlebyEnköpingHåboHe...

Study and practice to minimize the occurrence and consequences of motor vehicle accidents Passive safety and ETSC redirect here. For nuclear safety, see Passive nuclear safety. For the former East Texas State College, see Texas A&M University–Commerce. Passive restraint redirects here. For the Clutch EP, see Passive Restraints. Crash testing is one of the components of automotive safety. Automotive safety is the study and practice of automotive design, construction, equipment and regula...

لويس الحادي عشر ملك فرنسا (بالفرنسية: Louis XI) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 3 يوليو 1423(1423-07-03)بورجيز الوفاة 30 أغسطس 1483 (60 سنة) سبب الوفاة سكتة دماغية مواطنة فرنسا الديانة الكنيسة الرومانية الكاثوليكية الزوجة مارغريت ستيوارت (24 يونيو 1436–16 أغسطس 1445)شارلوت من سافوي (9 مارس 1451–...

Filmfare Award for Best Actor2022 winner: Biju Menon for Ayyappanum KoshiyumAwarded forBest Performance by an Actor in a Leading Role in Malayalam FilmsCountryIndiaPresented byFilmfareFirst awardedMadhu,Swayamvaram (1972)Currently held byBiju Menon, Ayyappanum Koshiyum (2022)HighlightsMost awardsMammootty (12)Total awarded48First winnerMadhuWebsitefilmfare.com The Filmfare Award for Best Actor – Malayalam is an award instituted in 1972, presently annually at the Filmfare Awards South to an...