Entheogenic drugs and the archaeological record
|
Read other articles:

In Greek mythology, Hippolochus (Ancient Greek: Ἱππολόχoς Hippolokhos) may refer to two distinct characters: Hippolochus, a Lycian prince as son of Bellerophon[1] and father of Glaucus, one of the Trojan Leaders.[2] Hippolochus, a Trojan soldier and son of Antimachus.[3] Notes ^ Homer, Iliad 6.196–197; Apollodorus, 2.3.1 ^ Homer, Iliad 6.119, 144 & 206, 7.13, 12.309 & 387, 14.140; Apollodorus, Epitome 3.35 ^ Homer, Iliad 11.122 References Apollodorus...

Contextual design (CD) is a user-centered design process developed by Hugh Beyer and Karen Holtzblatt. It incorporates ethnographic methods for gathering data relevant to the product via field studies, rationalizing workflows, and designing human–computer interfaces. In practice, this means that researchers aggregate data from customers in the field where people are living and applying these findings into a final product.[1] Contextual design can be seen as an alternative to enginee...

English footballer Albert Pearson Personal informationFull name Albert Victor Pearson[1]Date of birth (1892-09-02)2 September 1892[1]Place of birth Tynemouth, England[1]Date of death 24 January 1975(1975-01-24) (aged 82)[1]Place of death Newcastle-under-Lyme, England[1]Height 5 ft 9+1⁄2 in (1.77 m)[2]Position(s) ForwardYouth career1910–1912 Hebburn ArgyleSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1912–1914 Sheffield United ...
BalaiKecamatanNegara IndonesiaProvinsiKalimantan BaratKabupatenSanggauPemerintahan • CamatPoheng Gew, S. Pd., M. A.Populasi • Total32,129 (2.019) jiwaKode Kemendagri61.03.12 Kode BPS6105160 Luas395,60 km²Desa/kelurahan12/51 Balai adalah salah satu kecamatan di Kabupaten Sanggau, Kalimantan Barat, Indonesia. Pusat pemerintahannya berada di Batang Tarang. Kecamatan Balai berbatasan dengan Kecamatan Tayan Hilir, Meliau dan Tayan Hulu di Kabupaten Sanggau. Selain itu...

Sports car launched into space in 2018 SpaceX Roadster redirects here. For a planned SpaceX option package using cold gas thrusters, see Tesla Roadster (second generation). Elon Musk's Tesla RoadsterElon Musk's Tesla Roadster; Earth in backgroundNamesSpaceX Roadster[1] Starman[1]Mission typeTest flightOperatorSpaceXCOSPAR ID2018-017ASATCAT no.43205Mission durationActive: 1 Day In Orbit: 6 years, 2 months and 1 day Spacecraft propertiesSpacecraft type2010 Tesla R...

العلاقات البلغارية الهندوراسية بلغاريا هندوراس بلغاريا هندوراس تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات البلغارية الهندوراسية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين بلغاريا وهندوراس.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: و�...

PerteguhenDesaGapura selamat datang di Desa PerteguhenNegara IndonesiaProvinsiSumatera UtaraKabupatenKaroKecamatanSimpang EmpatKode pos22153Kode Kemendagri12.06.12.2030 Luas... km²Jumlah penduduk... jiwaKepadatan... jiwa/km² Perteguhen merupakan salah satu desa yang ada di kecamatan Simpang Empat, Kabupaten Karo, provinsi Sumatera Utara, Indonesia.[1] Referensi ^ Pasaribu, Marianti Rosanna (2023). Kecamatan Simpang Empat Dalam Angka 2023. BPS Kabupaten Karo. hlm. 7. ...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando le voci specifiche per i documenti di Paesi precisi, vedi Categoria:Passaporti. Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando l'album di Gatto Panceri, vedi Passaporto (album). Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento diritto internazionale non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Il passaporto italiano biometrico, modello ...

GazzuoloKomuneComune di GazzuoloNegaraItaliaWilayahLombardyProvinsiMantua (MN)FrazioniBelforte, Bocca Chiavica, Pomara, Nocegrossa, La MarchesaPemerintahan • Wali kotaLoris ContesiniLuas • Total22,3 km2 (86 sq mi)Ketinggian25 m (82 ft)Populasi (1 January 2009) • Total2.435 • Kepadatan11/km2 (28/sq mi)Zona waktuUTC+1 (CET) • Musim panas (DST)UTC+2 (CEST)Kode pos46010Kode area telepon0376Situs webSitu...

Defunct U.S. hotel chain The Statler Hotel company was one of the United States' early chains of hotels catering to traveling businessmen and tourists. It was founded by Ellsworth Milton (E. M.) Statler in Buffalo, New York. Early ventures In 1901, Buffalo hosted the Pan-American Exposition. Statler built a hotel on the Exposition grounds and called it Statler's Hotel. It was a temporary wooden structure intended to last the duration of the Exposition. With 2,084 rooms, it could accommodate 5...

2008 Italian movie You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Italian. (May 2017) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the Italian article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into t...

这是马来族人名,“阿末”是父名,不是姓氏,提及此人时应以其自身的名“祖基菲里”为主。 尊敬的拿督斯里哈芝祖基菲里·阿末Dzulkefly bin Ahmad国会议员、DGSM博士 马来西亚卫生部部长现任就任日期2023年12月12日君主最高元首苏丹阿都拉最高元首苏丹依布拉欣·依斯迈首相安华·依布拉欣副职卡尼斯曼(英语:Lukanisman Awang Sauni)前任扎丽哈·慕斯达法任期2018年5月21日—2...

Holy Sepulchre CemeteryThe main entrance to Holy Sepulchre CemeteryDetailsEstablished1886 (1886)LocationNew Rochelle, New York, United StatesCoordinates40°54′13″N 73°47′51″W / 40.9037105°N 73.7976331°W / 40.9037105; -73.7976331TypeCatholicOwned byBlessed Sacrament ChurchFind a GraveHoly Sepulchre Cemetery Foy family headstone Holy Sepulchre Cemetery is a Catholic cemetery in New Rochelle in Westchester County, New York, United States. The cemetery is m...

Research body for universities The International Alliance of Research Universities (IARU) was launched on 14 January 2006 as a co-operative network of 10 leading, international research-intensive universities who share similar visions for higher education, in particular the education of future leaders. The IARU Chair is elected from among the IARU Presidents for a period of 2 years. Past IARU Chairpersons: At the launch the presidents elected Professor Ian Chubb, 2005 - 2008 (Australian Natio...

American politician (born 1947) Tom DaschleOfficial portrait, 2003Senate Majority LeaderIn officeJune 6, 2001 – January 3, 2003DeputyHarry ReidPreceded byTrent LottSucceeded byBill FristIn officeJanuary 3, 2001 – January 20, 2001DeputyHarry ReidPreceded byTrent LottSucceeded byTrent LottSenate Minority LeaderIn officeJanuary 3, 2003 – January 3, 2005DeputyHarry ReidPreceded byTrent LottSucceeded byHarry ReidIn officeJanuary 20, 2001 – June 6, 2001De...

Laurel Highlands CouncilOwnerBoy Scouts of AmericaHeadquartersPittsburgh, PennsylvaniaCountryUnited StatesFoundedJuly 1, 2011PresidentScott HardyCouncil CommissionerJack BoydeScout ExecutiveTodd McGregor Websitehttp://www.lhcscouting.org Scouting portal Laurel Highlands Council serves youth in Allegheny, Beaver, Bedford, Blair, Cambria, Greene, Indiana, Somerset, and Washington counties in Pennsylvania; Grant, Hampshire, Hardy, and Mineral counties in West Virginia; and Allegany and Gar...

Surat Cinta untuk Starla the SeriesGenre Roman Drama Cerita Pabrik Fiksi Tim Screenplay SutradaraOdy HarahapPemeran Jefri Nichol Caitlin Halderman Penggubah lagu temaVirgounLagu pembukaSurat Cinta untuk Starla oleh VirgounLagu penutupSurat Cinta untuk Starla oleh VirgounPenata musikJoseph S. DjafarNegara asalIndonesiaBahasa asliBahasa IndonesiaJmlh. musim1Jmlh. episode8ProduksiProduser eksekutif Monika Rudijono Daphne Yang Anthony Buncio Produser Wicky V. Olindo Dian Lasvita Shao-Yi Ch...
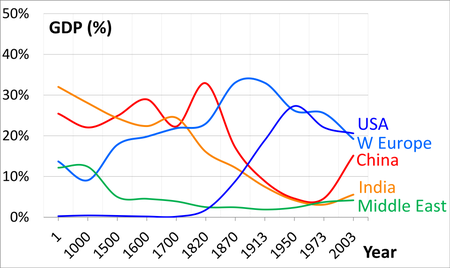
British economist The examples and perspective in this article may not include all significant viewpoints. Please improve the article or discuss the issue. (July 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Angus MaddisonBorn(1926-12-06)6 December 1926Newcastle upon Tyne, EnglandDied24 April 2010(2010-04-24) (aged 83)Neuilly-sur-Seine, FranceNationalityBritishAlma materUniversity of Cambridge University of Aix-MarseilleScientific careerFieldsEconomic HistoryInstitutionsUniversi...

U.S. federal agency Space Development AgencySpace Development AgencyAgency overviewFormedMarch 12, 2019; 5 years ago (2019-03-12)TypeDirect reporting unitHeadquartersThe Pentagon, Arlington County, Virginia, U.S.38°52′16″N 77°03′22″W / 38.871°N 77.056°W / 38.871; -77.056MottoSemper Citius(Latin: Always Faster)Agency executivesDerek Tournear, DirectorRyan C. Frigm, Deputy DirectorParent departmentUnited States Department of the Air ForcePar...

ماريوس لاكاتوش معلومات شخصية الاسم الكامل ماريوس ميهاي لاكاتوش الميلاد 5 أبريل 1964 (العمر 60 سنة)براشوف ، رومانيا الطول 1.81 م (5 قدم 11 بوصة) مركز اللعب مهاجم الجنسية رومانيا مسيرة الشباب سنوات فريق 1977–1981 فرق براشوف للشباب 0000–1981 براشوف تحت 19 المسيرة الاحترافية1 �...


