Effects of economic liberalisation on education in Tajikistan
|
Read other articles:

Mountain-climbing cog railway in New Hampshire, United States For the defunct railway in Los Angeles, see Los Angeles and Mount Washington Railway. Mount Washington Cog RailwayTrack with rackOverviewLocaleCoos County, New Hampshire, U.S.HistoryOpened1868TechnicalLine length3 miles (4.8 km)[1]Rack systemMarsh rack systemTrack gauge4 ft 8 in (1,422 mm) Route map Legend Mount Washington summit Appalachian Trail Skyline siding(removed) Waumbek station and pa...

Model proposing regional biodiversity is increased by a moderate level of ecological disturbance The intermediate disturbance hypothesis (IDH) suggests that local species diversity is maximized when ecological disturbance is neither too rare nor too frequent. At low levels of disturbance, more competitive organisms will push subordinate species to extinction and dominate the ecosystem.[1] At high levels of disturbance, due to frequent forest fires or human impacts like deforestation, ...

Éphémérides Chronologie du Canada 1693 1694 1695 1696 1697 1698 1699Décennies au Canada :1660 1670 1680 1690 1700 1710 1720 Chronologie dans le monde 1693 1694 1695 1696 1697 1698 1699Décennies :1660 1670 1680 1690 1700 1710 1720Siècles :XVe XVIe XVIIe XVIIIe XIXeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies thématiques Art Architecture, Arts plastiques (Dessin, Gravure, Peinture et Sculpture), ...

Pangkalan Angkatan Udara.Lambang LanudNegaraIndonesiaCabang TNI Angkatan UdaraTipe unitPangkalan Udara MiliterPeranPangkalan Angkatan UdaraBagian dari Komando Operasi Udara NasionalLanudSeluruh WilayahJulukanLanudPelindungTentara Nasional IndonesiaMotoPrayatna Kerta GeganaBaret B I R U Pangkalan Angkatan Udara (disingkat Lanud) adalah kawasan di daratan dan/atau di perairan dengan batas-batas tertentu dalam wilayah suatu negara yang digunakan untuk kegiatan lepas landas dan penda...

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Stasiun Buluh. Stasiun Butuh Tampak depan Stasiun Butuh, 2022LokasiButuh, Butuh, Purworejo, Jawa Tengah 54264IndonesiaKoordinat7°43′27″S 109°51′31″E / 7.7242812°S 109.8585445°E / -7.7242812; 109.8585445Koordinat: 7°43′27″S 109°51′31″E / 7.7242812°S 109.8585445°E / -7.7242812; 109.8585445Ketinggian+10 mOperator Kereta Api IndonesiaDaerah Operasi V Purwokerto Letakkm 473+460 lintas Bogor–Bandung...

For the London theatre, see Victoria Palace Theatre. Governmental in Bucharest, RomaniaVictory PalacePalatul VictoriaGeneral informationTypeGovernmentalArchitectural styleStripped ClassicismAddress1 Victory Square, Sector 1Town or cityBucharestCountryRomaniaCurrent tenantsGovernment of Romania, Cabinet officesConstruction started1937Completed1944Inaugurated1952ClientMinistry of Foreign AffairsOwnerGovernment of RomaniaTechnical detailsFloor count3Design and constructionArchitect(s)Duiliu Marc...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento sparatutto non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. SingularityvideogiocoLogo del giocoPiattaformaMicrosoft Windows, Xbox 360, PlayStation 3 Data di pubblicazione 19 gennaio 2010 19 luglio 2010 GenereSparatutto in prima persona TemaFantascienza, guerra f...

Val CerondaLa Val Ceronda vista dalla cresta Colombano-LeraStati Italia Regioni Piemonte Province Torino Località principalila Cassa, Fiano, Vallo Torinese e Varisella Comunità montanaComunità Montana Valli di Lanzo, Ceronda e Casternone Fiumetorrente Ceronda CartografiaMappa della Valle Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale La Val Ceronda è una vallata alpina situata nelle Alpi Graie nella città metropolitana di Torino. Il torrente Ceronda è tributario della Stura di...

Cercola Airfield Part of Twelfth Air ForceCoordinates40°51′41.75″N 014°20′57.82″E / 40.8615972°N 14.3493944°E / 40.8615972; 14.3493944 (Approximate)TypeMilitary AirfieldSite informationControlled byUnited States Army Air ForcesSite historyBuilt1943In use1943-1944 Cercola Airfieldclass=notpageimage| Location of Cercola Airfield, Italy Cercola Airfield is an abandoned World War II military airfield in Italy, located approximately 2 km nort...
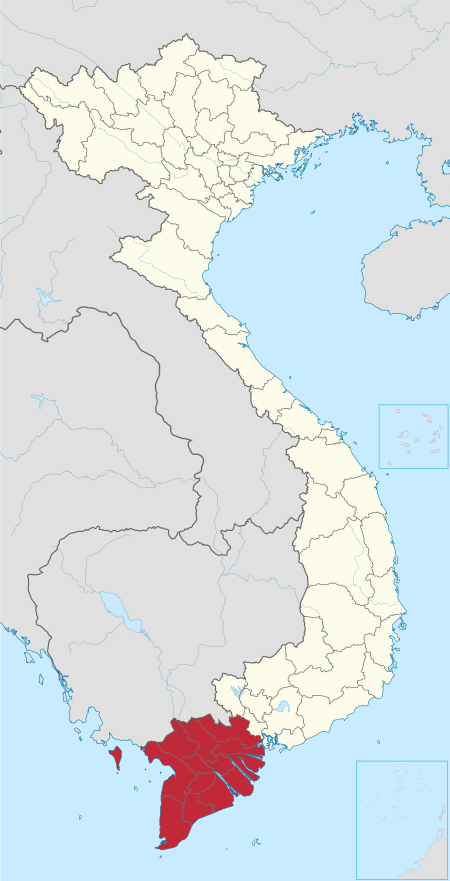
City in An Giang, Vietnam You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Vietnamese. (April 2024) Click [show] for important translation instructions. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia. Consider adding a topic ...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

Este artículo o sección necesita referencias que aparezcan en una publicación acreditada. Busca fuentes: «Banco Mundial» – noticias · libros · académico · imágenesEste aviso fue puesto el 8 de octubre de 2013. Banco Mundial Sede del Banco en Washington D. C.LocalizaciónPaís Estados UnidosInformación generalTipo Servicios financierosSede Washington D. C., Estados UnidosOrganizaciónDirección Ajay BangaComposición Banco Internacional de Reconstrucción ...

لينداو شعار الاسم الرسمي (بالألمانية: Lindau) الإحداثيات 47°32′45″N 9°41′02″E / 47.545833333333°N 9.6838888888889°E / 47.545833333333; 9.6838888888889 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد ألمانيا (1871–)[2][3] خصائص جغرافية المساحة 33.06 كيلومتر مربع (31 ديسمبر 2017)[4] ارتفا�...

Untuk pengertian lain, lihat Polewali. PolewaliPulau PolewaliPolewaliTampilkan peta Sulawesi SelatanPolewaliTampilkan peta SulawesiPolewaliTampilkan peta IndonesiaPolewaliTampilkan peta Asia TenggaraGeografiLokasiSelat MakassarAsia TenggaraSamudra HindiaKoordinat4°50′41.000″S 119°24′13.000″E / 4.84472222°S 119.40361111°E / -4.84472222; 119.40361111KepulauanKepulauan Spermonde, Kepulauan Sunda Besar (Pulau Sulawesi dan Pulau-pulau Kecil di Sekitarnya), Kepul...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant la généalogie. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Vécsey Armes de la famille. Période depuis le XVe siècle Pays ou province d’origine Hongrie modifier Vécsey (hernádvécsei és hajnácskeői nemes, báró és gróf Vécsey en hongrois) est le patronyme d'une ancienne famille noble hongroise originaire du comté de Abaúj en Haute-Hongrie. O...

Iain Pears di Festival Buku Internasional Edinburgh 2015 Iain George Pears (lahir 8 Agustus 1955)[1] adalah seorang sejarawan seni rupa, novelis dan wartawan asal Inggris.[2][3] Kehidupan pribadi Pears lahir pada 8 Agustus 1955 di Coventry, Inggris. Ia dididik di Warwick School, sebuah sekolah negeri khusus putra di Warwick. Ia dididik di Wadham College, Oxford, lulus dengan gelar sarjana, dan di Wolfson College, Oxford, lulus dengan gelar Doktor.[1][4]...

University in Indonesia Yogyakarta State Universityꦈꦤꦶꦮ꦳ꦼꦂꦱꦶꦠꦱ꧀ꦤꦒꦫꦶꦔꦪꦺꦴꦒꦾꦏꦂꦠEmblem of Yogyakarta State UniversityMottoLeading in Character EducationTypePublic universityEstablished21 May 1964RectorProf. Dr. Sumaryanto, M.Kes., AIFOLocationSleman Regency, Special Region of Yogyakarta, Indonesia7°46′17″S 110°22′39″E / 7.7713847°S 110.3774998°E / -7.7713847; 110.3774998CampusUrban, 432.613 square metres (...

Metro station in Incheon, South Korea 156 주안Juan Juan stationKorean nameHangul주안역Hanja朱安驛Revised RomanizationJuan-yeokMcCune–ReischauerChuan-yŏk General informationLocation125 Juan 5-dong, 95-19 Juanno, Nam-gu, Incheon[1][2]Operated byKorail, Incheon Transit CorporationLine(s) Line 1 Incheon Line 2Platforms4Tracks6ConstructionStructure typeAboveground/UndergroundKey dates18 Sep 1899[1][2&#...

Voce principale: Fussball-Club Rot-Weiß Erfurt. Fussball-Club Rot-Weiß ErfurtStagione 2004-2005Sport calcio Squadra Rot-Weiß Erfurt Allenatore René Müller (1ª-22ª) Ján Kocian (23ª-34ª) All. in seconda Alois Schwartz 2. Bundesliga18º posto Coppa di GermaniaPrimo turno Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Traub (32)Totale: Traub (33) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: David (6)Totale: David (6) StadioSteigerwaldstadion Maggior numero di spettatori19 500 vs. Erzgebirge Aue Minor numero d...
Lambang Peta Data dasar Bundesland: Schleswig-Holstein Ibu kota: Schleswig Wilayah: 2.071,59 km² Penduduk: 197.241 (30 Juni 2005) Kepadatan penduduk: 95 jiwa per km² Pelat nomor kendaraan bermotor: SL Pembagian administratif: 136 Gemeinden Alamat kantor bupati: Flensburger Straße 724837 Schleswig Situs web resmi: www.schleswig-flensburg.de Bupati: Bogislav-Tessen von Gerlach Peta Schleswig-Flensburg (bahasa Denmark: Slesvig-Flensborg) adalah sebuah distrik (Landkreis) yang terletak di Sch...