Differential Emotions Scale
|
Read other articles:

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Kugel (disambiguasi). KugelKugel miJenisPuding atau kaserolTempat asalYahudi dari Eropa Tengah. Sekarang sebagian besar di Israel dan AS.Bahan utamaTelur mi atau kentangSunting kotak info • L • BBantuan penggunaan templat ini Media: Kugel Kugel (קוגל kug(e)l, dibaca IPA: [ˈkʊɡl̩]) adalah sebuah puding atau kaserol panggang, yang paling umum terbuat dari mi telur (Lokshen kugel) atau kentang. Hidangan tersebut merupakan sebuah hid...

Dad rock dan stadium rock dialihkan ke halaman ini. Untuk format radio yang terkait dengan demografi baby boomer, lihat Classic rock. Untuk the 1985 Alexander Gradsky rock opera, lihat Stadion (rock opera). Arena rockKonser Queen + Paul Rodgers di Freedom Square Kharkiv, Ukraina, 12 September 2008Nama lain Anthem rock corporate rock dad rock melodic rock pomp rock stadium rock Sumber aliran Hard rock pop rock heavy metal progressive rock Sumber kebudayaan1960an ke pertengahan-1970anTopik lain...

Hiasan-Kepala HewanAjaw TikalGlif Hiasan-Kepala HewanBerkuasaTidak diketahuiPendahuluJaguar BerdaunanPenerusSihyaj Chan K'awiil IPasanganPutri TengkorakAnakSihyaj Chan K'awiil IAgamaAgama Maya Hiasan-Kepala Hewan adalah seorang ajaw (penguasa) kota Tikal, salah satu kota terbesar di peradaban Maya. Ia adalah ayah kandung penerusnya, Sihyaj Chan K'awiil I, serta istri dari Putri Skull.[1] Nama penguasa ini dapat ditranskripsikan menjadi ? K'INICH-E:B-?.[2] Catatan kaki ^ Martin...

Paladium pada karbon Nama Nama IUPAC Paladium Nama lain Paladium pada karbon, Pd/C, Pd-C Penanda Nomor CAS 7440-05-3 Model 3D (JSmol) Gambar interaktif 3DMet {{{3DMet}}} Nomor EC PubChem CID 23938 Nomor RTECS {{{value}}} UNII 5TWQ1V240M InChI InChI=1S/PdKey: KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N SMILES [Pd] Sifat Rumus kimia Pd Massa molar 106,42 Penampilan Bubuk hitam Kelarutan Air raja Kecuali dinyatakan lain, data di atas berlaku pada suhu dan tekanan standar (25 °C [7...

Wakil Wali Kota TualLambang Kota TualPetahanaUsman Tamngesejak 31 Oktober 2018Masa jabatan5 tahunPejabat perdanaAdam RahayaanDibentuk7 Oktober 2008Nama takresmiWawali TualWawako TualSitus webtualkota.go.id Berikut adalah daftar wakil wali kota Tual sejak awal dibentuk hingga sekarang. No Wakil Wali Kota Mulai Menjabat Akhir Menjabat Periode Wali Kota Ket. 1 Adam Rahayaan 7 Oktober 2008 7 Oktober 2013 1(2008) Mahmud Muhammad Tamher [Ket. 1] — lowong 7 Oktober 2013 31 Oktober 201...

Turkish footballer Alihan Kubalas Personal informationDate of birth (1991-10-26) 26 October 1991 (age 32)Place of birth Şişli, TurkeyHeight 1.85 m (6 ft 1 in)Position(s) MidfielderTeam informationCurrent team KocaelisporNumber 2Youth career2004–2007 Maltepespor2007–2009 Fenerbahçe2009–2010 BulvarsporSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2010–2012 Bağcılar 60 (6)2012–2013 Sivasspor 0 (0)2012–2013 → Tokatspor (loan) 25 (4)2013–2014 Altay 26 (4)2015 Karagüm...

Anti-cult organization FACTNetLogo up through 2016Formation1993Type501(c)(3) non-profitHeadquartersColorado, United StatesOfficial language EnglishKey peopleLawrence Wollersheim, Robert PennyWebsitefactnet.org FACTnet, also known as Fight Against Coercive Tactics Network, co-founded by Robert Penny and Lawrence Wollersheim, was a Colorado-based anti-cult organization with the stated aim of educating and facilitating communication about destructive mind control. Coercive tactics, or coercive p...

U.S. Senate election in West Virginia This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: 1964 United States Senate election in West Virginia – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) 1964 United States Senate election in West Virginia ← 1...

Former state Sultanate of Lower YafaArabic: يافع السفلى Yāfi‘ as-SufláState of the Federation of South Arabiaca. 1800–1967 Flag Coat of arms Map of the Federation of South ArabiaCapitalJaʿār • TypeSultanate Historical era20th century• Established ca. 1800• Disestablished 1967 Succeeded by South Yemen Lower Yafa, Lower Yafa'i (Arabic: يافع السفلى Yāfi‘ as-Suflá), or the Sultanate of Lower Yafa (Arabic: سلطنة يافع السفلى S...

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁�...

Baseball stadium in Clearwater, Florida, U.S. Jack Russell Memorial StadiumJack Russell Stadium in 1950sFormer namesJack Russell Stadium (1955–1990)Location800 Phillies Drive, Clearwater, Florida 33755, United StatesCoordinates27°58′28″N 82°47′21″W / 27.97444°N 82.78917°W / 27.97444; -82.78917OwnerCity of ClearwaterCapacity4,744 (1955)4,808 (1967)5,368 (1985)6,942 (2003)1,200 (2018)Field sizeLeft – 340 ft.Center – 400 ft.Right – 340 ft.SurfacegrassC...

National Football League rivalry Chargers–Raiders rivalry Los Angeles Chargers Las Vegas Raiders First meetingNovember 27, 1960Chargers 52, Raiders 28Latest meetingDecember 14, 2023Raiders 63, Chargers 21Next meetingSeptember 8, 2024StatisticsMeetings total129All-time seriesRaiders, 69–58–2Postseason resultsRaiders, 1–0 January 11, 1981:Raiders 34, Chargers 27Largest victoryChargers: 44–0 (1961);Raiders: 63–21 (2023)Longest win streakChargers, 13 (2003–09);Raiders: 10 (1972–77...

Esta página cita fontes, mas que não cobrem todo o conteúdo. Ajude a inserir referências. Conteúdo não verificável pode ser removido.—Encontre fontes: ABW • CAPES • Google (N • L • A) (Junho de 2018) Identidade cultural é o sentimento de identidade de um grupo, cultura ou indivíduo, na medida em que este é influenciado pela cultura do grupo a que pertença.[1] Descrição Identidade é algo único, distinto e completo...

Suasana permainan gateball. Gateball (Jepang: ゲートボールcode: ja is deprecated , Hepburn: gētobōru) adalah olahraga modifikasi permainan croquet, yang menggunakan palu untuk memukul bola. Olahraga ini tidak mengenal batas tertentu sehingga tergolong sebagai barrier-free sport (olahraga tanpa batas).[1] Olahraga ini pertama kali dikenalkan di Jepang, kemudian menyebar ke seluruh dunia. Seiring dengan perkembangan waktu, permainan gateball menyebar ke berbagai negara lain, ter...

This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: List of museums in North Macedonia – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) National Gallery Museum of the City of Skopje This is a list of museums in North Macedonia. This list is incomplete; you can help by adding mi...

Conferenza internazionale dei meridianiIl meridiano fondamentale attraverso Greenwich TemaDefinizione del meridiano fondamentale Partecipanti41 delegati (25 nazioni) Apertura1 ottobre 1884 Chiusura1 novembre 1884 Stato Stati Uniti LocalitàWashington La Conferenza internazionale dei meridiani si tenne a Washington nell'ottobre 1884 per decidere il meridiano fondamentale sia per il calcolo della latitudine sia per il calcolo dei fusi orari.[1] Indice 1 I partecipanti 2 Le conclusi...
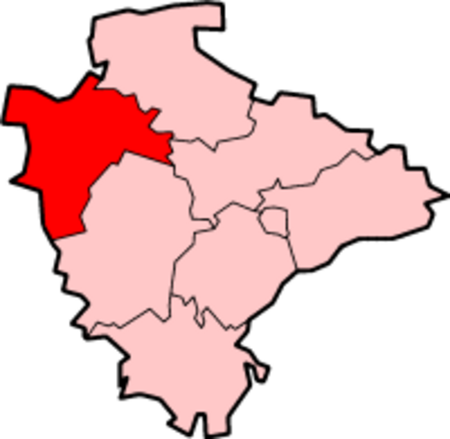
Village in Devon, England Human settlement in EnglandPyworthySt Swithuns churchPyworthyLocation within DevonPopulation689 OS grid referenceSS313028DistrictTorridgeShire countyDevonRegionSouth WestCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townHolsworthyPostcode districtEX22Dialling code01409PoliceDevon and CornwallFireDevon and SomersetAmbulanceSouth Western UK ParliamentTorridge and West Devon List of places UK England Devon 50°48′21″N 4°23�...

Comic strip The LockhornsThe LockhornsAuthor(s)Bill Hoest (1968–1988)Bunny Hoest (1988–present)Illustrator(s)Bill Hoest (1968–1988)John Reiner (1988–present)WebsiteThe LockhornsCurrent status/scheduleRunningLaunch dateSeptember 9, 1968; 55 years ago (September 9, 1968)Syndicate(s)King Features Syndicate (1968-2023)Andrews McMeel Syndication (2024-present) The Lockhorns is a United States single-panel cartoon created September 9, 1968 by Bill Hoest and originally distribut...

Broth obtained from clams A shot glass of clam juice Clam juice is a broth derived from steamed clams,[1] which can be consumed on its own or used as an ingredient in various dishes and beverages. Preparation Clam juice is typically prepared from the liquid obtained from steamed clams.[1] Clam juice may be prepared fresh for consumption,[2] or purchased in prepared bottled form.[1][3] Some companies mass-produce prepared clam juice, which is made by ste...

Uel Walter LamkinPresident of Northwest Missouri State UniversityIn office1921–1945Preceded byIra RichardsonSucceeded byJ. W. Jones Personal detailsBorn(1877-01-18)January 18, 1877California, Missouri, U.S.DiedSeptember 16, 1956(1956-09-16) (aged 79) Uel Walter Lamkin (January 18, 1877 – September 16, 1956) was president of Northwest Missouri State University from 1921 to 1945. Lamkin was born in California, Missouri. He attended the private Clinton, Missouri Academy run by his fathe...
