De Quervain syndrome
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

العلاقات المكسيكية المالطية المكسيك مالطا المكسيك مالطا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات المكسيكية المالطية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين المكسيك ومالطا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة ا�...

Remains of Apollonia Excavations at Apollonia Apollonia (Greek: Ἀπολλωνία) was an ancient city of Magna Graecia in Sicily, which, according to Stephanus of Byzantium, was situated in the neighbourhood of Aluntium and Calacte. The city was founded by Dionysius I of Syracuse as an outpost against the Carthaginians. Cicero also mentions it[1] in conjunction with Haluntium, Capitium, and Enguium, in a manner that seems to imply that it was situated in the same part of Sicily wit...

Júlio Sérgio Júlio Sérgio nel 2010 Nazionalità Brasile Altezza 184 cm Peso 82 kg Calcio Ruolo Allenatore (ex portiere) Termine carriera 2014 - giocatore Carriera Giovanili 1995-1998 Botafogo-SP Squadre di club1 1998-1999 Botafogo-SP2 (-?)1999-2000 Sertãozinho13 (-?)2000 Inter de Bebedouro18 (-?)2000-2001 Francana21 (-80)2001 Malutrom15 (-?)2001-2002 Comercial-SP16 (-?)2002-2004 Santos41 (-?)2004-2005 Juventude7 (-?)2005-2006 Amér...

Television series NBA on ABCGenreNBA game telecastsPresented byMike BreenDoris BurkeJJ RedickLisa SaltersRyan RuoccoRichard JeffersonMark JonesDave PaschHubie BrownMalika AndrewsStephen A. SmithMichael WilbonBob MyersAdrian WojnarowskiCountry of originUnited StatesOriginal languagesEnglishSpanishProductionCamera setupMulti-cameraRunning time150 minutes or until the game endsProduction companiesABC Sports (1965–1973, 2002–2006)ESPN (2006–present)Original releaseNetworkABCReleaseJanuary 3...

Complexity class used to classify decision problems This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (October 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Unsolved problem in computer science: P = ? N P {\displaystyle {\mathsf {P\ {\overset {?}{=}}\ NP}}} (more unsolved problems in computer science) Euler diagram for P, NP, NP-complete, and N...

Questa voce sull'argomento politici statunitensi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Ralph Bunche Premio Nobel per la pace 1950 Raphael Johnson Bunche (Detroit, 7 agosto 1903 – New York, 9 dicembre 1971) è stato un politologo e diplomatico statunitense. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Onorificenze 3 Bibliografia 4 Altri progetti 5 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Fu Premio Nobel per la pace nel 1...

Airport in Pevek, RussiaPevek AirportАэропорт ПевекIATA: PWEICAO: UHMPLID: ПЕВSummaryAirport typePublicOperatorPevek branch of ChukotaviaServesPevekLocationPevek, RussiaElevation AMSL10 ft / 3 mCoordinates69°47′0″N 170°35′48″E / 69.78333°N 170.59667°E / 69.78333; 170.59667Runways Direction Length Surface ft m 17/35 8,202 2,500 Concrete Pevek Airport (Russian: Аэропорт Певек) (IATA: PWE, ICAO: UHMP) is a civilian a...

Haveluycomune Haveluy – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Francia RegioneAlta Francia Dipartimento Nord ArrondissementValenciennes CantoneAulnoy-lez-Valenciennes TerritorioCoordinate50°21′N 3°24′E / 50.35°N 3.4°E50.35; 3.4 (Haveluy)Coordinate: 50°21′N 3°24′E / 50.35°N 3.4°E50.35; 3.4 (Haveluy) Superficie4,7 km² Abitanti3 150[1] (2009) Densità670,21 ab./km² Altre informazioniCod. postale59255 Fuso orarioUTC+1 Codice ...

Lukaku celebrating his first goal against Tunisia at the 2018 FIFA World Cup Romelu Lukaku is a Belgian professional footballer who represents the Belgium national football team as a striker. Aged 17, he made his debut for his country in a 1–0 defeat to Croatia in Brussels in March 2010. His first and second international goals came on his eighth appearance for Belgium, in a 2–0 friendly victory over Russia. As of 26 March 2024[update], Lukaku is his country's top score...

2016年美國總統選舉 ← 2012 2016年11月8日 2020 → 538個選舉人團席位獲勝需270票民意調查投票率55.7%[1][2] ▲ 0.8 % 获提名人 唐納·川普 希拉莉·克林頓 政党 共和黨 民主党 家鄉州 紐約州 紐約州 竞选搭档 迈克·彭斯 蒂姆·凱恩 选举人票 304[3][4][註 1] 227[5] 胜出州/省 30 + 緬-2 20 + DC 民選得票 62,984,828[6] 65,853,514[6]...

土库曼斯坦总统土库曼斯坦国徽土库曼斯坦总统旗現任谢尔达尔·别尔德穆哈梅多夫自2022年3月19日官邸阿什哈巴德总统府(Oguzkhan Presidential Palace)機關所在地阿什哈巴德任命者直接选举任期7年,可连选连任首任萨帕尔穆拉特·尼亚佐夫设立1991年10月27日 土库曼斯坦土库曼斯坦政府与政治 国家政府 土库曼斯坦宪法 国旗 国徽 国歌 立法機關(英语:National Council of Turkmenistan) ...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Jurong West Sports and Recreation Centre – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Jurong West Sports and Recreational Centre裕廊西体育场Full nameJurong West ActiveSG StadiumAddress20 Jurong...

Bilateral relationsBritish – Portuguese relations United Kingdom Portugal Diplomatic missionEmbassy of the United Kingdom, LisbonEmbassy of Portugal, London British–Portuguese relations are foreign relations between Portugal and the United Kingdom. The relationship, largely driven by the nations' common interests as maritime countries on the edge of Europe and close to larger continental neighbours, dates back to the Middle Ages in 1373 with the Anglo-Portuguese Alliance. The two countrie...
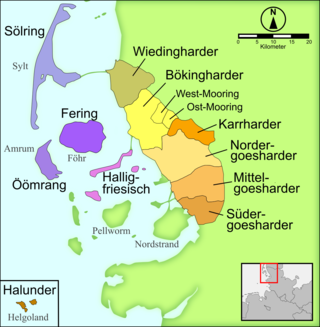
Minority language of Germany, spoken mostly by people in North Frisia North FrisianSylt: NuurđfriiskFöhr/Amrum: nuurdfreskHeligoland: NoorfriiskWiedingharde/Halligen: nordfreeskMooring: nordfraschKarrharde: nordfräischCentral Goesharde: noordfreeschBilingual sign in German and North Frisian, respectively, in Husum, GermanyNative toGermanyRegionNorth FrisiaEthnicityNorth FrisiansNative speakers(10,000 cited 1976)[1]Language familyIndo-European GermanicWest GermanicNorth Sea Ger...

У Вікіпедії є статті про інші значення цього терміна: Четвер (значення). Римська копія статуї Зевса, бога, від якого йде традиція називання «четверга» на честь небесного божества грому і його планети в багатьох мовах Четвер (також діал. четверг[1]) — четвертий день т�...

American politician John W. MoonFrom 1893's The House of Representatives of the Fifty Third Congress by The Graphic Chicago.Member of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom Michigan's 9th districtIn officeMarch 4, 1893 – March 3, 1895Preceded byHarrison H. WheelerSucceeded byRoswell P. Bishop Personal detailsBorn(1836-01-18)January 18, 1836Wayne County, Michigan, U.S.DiedApril 5, 1898(1898-04-05) (aged 62)Muskegon, Michigan, U.S.Political partyRepublican John Wesley...

Australian Customs and Border Protection ServiceAustralian Customs FlagAgency overviewFormed22 May 2009[1]Preceding AgencyAustralian Customs ServiceDissolved1 July 2015Superseding agencyAustralian Border ForceTypeStatutory authorityJurisdictionGovernment of AustraliaHeadquartersCustoms HouseCanberra35°17′1″S 149°7′55″E / 35.28361°S 149.13194°E / -35.28361; 149.13194Employees5,424 (at June 2014)[2]Annual budgetA$1.09 billion (2011)Parent Age...

Passband modulation Analog modulation AM FM PM QAM SM SSB Digital modulation ASK APSK CPM FSK MFSK MSK OOK PPM PSK QAM SC-FDE TCM WDM Hierarchical modulation QAM WDM Spread spectrum CSS DSSS FHSS THSS See also Capacity-approaching codes Demodulation Line coding Modem AnM PoM PAM PCM PDM PWM ΔΣM OFDM FDM Multiplexing vte Angle modulation is a class of carrier modulation that is used in telecommunications transmission systems. The class comprises frequency modulation (FM) and phase modulation...

Madurai R. MuralidaranOccupations Dance Guru (teacher) Composer choreographer dancer playwright director Years active1978–present Kalaimamani Shri Guru Madurai R. Muralidaran is an acclaimed dance Guru (teacher), composer, dancer, choreographer, lyricist, playwright and director best known for his large body of modern compositions for Bharatanatyam dancers and his many elaborate dance musical productions. His works explore the complexities of Bharathanatyam theory and rhythms while rem...

关于与「光 (宇多田光單曲)」標題相近或相同的条目页,請見「光_(消歧義)」。 光宇多田光的歌曲收录于专辑《DEEP RIVER》B面光 - PLANITb Remix光 - Godson Mix发行日期2002年3月20日格式CD, Regular Single录制时间文化村錄音室类型J-Pop时长20:28唱片公司東芝EMI词曲宇多田光制作人三宅彰, 宇多田光 and 宇多田 Skingg 照實(1.)Russell McNamara(2.)Alex “Godson” Richbourg(3.)排行榜最高...

