Captaincy of Paraíba
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Negara-negara bagian dan Distrik Federal Brasil Brasil adalah sebuah republik federal yang terdiri dari 26 negara bagian (bahasa Portugis: estado, jamak - estados) dan sebuah Distrik Federal (Distrito Federal) yang merupakan tempat ibu kota negara ini, Brasília. Statistik Bendera Lambang Negara bagian Singkatan[1] Ibu kota Luas wilayah (km2) Penduduk (2014) Kepadatan penduduk per km2 (2014) Acre AC Rio Branco 152.581,4 790.101 4,47 Alagoas AL Maceió 27.767,7 3.321.730 112,3 Amapá A...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Jérôme Bignon et Bignon. Jérôme Bignon de BlanzyFonctionsConseiller d'État1743Maître de la Librairie et garde de la Bibliothèque du Roi1740-1743Intendant de la généralité de Soissons1737-1743Intendant de la généralité de La Rochelle1726-1737Intendant de la Marine de Rochefort1726-1737BiographieNaissance 26 février 1698ParisDécès 8 mars 1743 (à 45 ans)ParisActivité AdministrateurPère Armand Roland Bignon de Blanzy (d)Fratrie Armand-Jé...

Batalyon Infanteri 621/ManuntungLambang Yonif 621/ManuntungDibentuk18 Juni 1950NegaraIndonesiaCabangInfanteriTipe unitSatuan TempurPeranPasukan SenapanBagian dariKodam VI/MulawarmanMarkasBarabai, Kabupaten Hulu Sungai Tengah, Kalimantan SelatanJulukanYonif 621/MTGMotoManuntung (Awal Sampai Akhir)BaretHijauMaskotBeruang MaduUlang tahun18 JuniTokohKomandan saat iniLetkol Inf Deny Ahdiani Amir, M.Han. (2022 - Sekarang) Batalyon Infanteri 621/Manuntung atau Yonif 621/Manuntung adalah Batalyon Inf...

American political strategist (born 1976) Jen O'Malley DillonO'Malley Dillon in the White House Oval Office in 2023White House Deputy Chief of StaffIncumbentAssumed office January 20, 2021Serving with Bruce Reed and Natalie QuillianPresidentJoe BidenChief of StaffRon KlainJeff ZientsPreceded byEmma Doyle Personal detailsBornJennifer Brigid O'Malley (1976-09-28) September 28, 1976 (age 47)Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.Political partyDemocraticSpousePatrick DillonChildren3Relative...

1936 film by Sidney Lanfield Sing, Baby, SingPoster of the filmDirected bySidney LanfieldWritten byMilton SperlingHarry TugendJack YellenProduced byDarryl F. ZanuckStarringAlice FayeAdolphe MenjouGregory RatoffTed HealyPatsy KellyMichael WhalenThe Ritz BrothersMontagu LoveDixie DunbarDouglas FowleyPaul StantonTony MartinCinematographyJ. Peverell MarleyEdited byBarbara McLeanMusic byRichard A. WhitingWalter BullockCyril J. MockridgeProductioncompanyTwentieth Century FoxDistributed byTwentieth ...
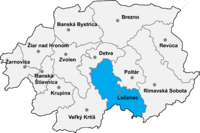
Roman Catholic church in Rapovce Location of Lučenec District in the Banská Bystrica Region Rapovce (Hungarian: Rapp) is a village and municipality in the Lučenec District in the Banská Bystrica Region of Slovakia. External links http://www.statistics.sk/mosmis/eng/run.html Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rapovce. vteMunicipalities of Lučenec District Lučenec Fiľakovo Ábelová Belina Biskupice Boľkovce Budiná Bulhary Buzitka Čakanovce Čamovce Divín Dobroč Fiľakovské Kov...

5-idrossitriptofano Nome IUPACacido 2S-ammino-3-(5-idrossi-1H-indol-3-il)propanoico Caratteristiche generaliFormula bruta o molecolareC11H12N2O3 Massa molecolare (u)220,225 Numero CAS56-69-9 Numero EINECS224-411-1 PubChem439280 DrugBankDB02959 SMILESC1=CC2=C(C=C1O)C(=CN2)CC(C(=O)O)N Indicazioni di sicurezzaSimboli di rischio chimico pericolo Frasi H301 Consigli P301+310 [1] Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Il 5-idrossitriptofano (5-HTP) è un amminoacido non pr...

Historically popular gauge of film 16 mm redirects here. For other uses, see 16 mm (disambiguation). 16 mm sound movie showing a variable-width sound track on single-perforation film stock 16 mm film is a historically popular and economical gauge of film. 16 mm refers to the width of the film (about 2⁄3 inch); other common film gauges include 8 mm and 35 mm. It is generally used for non-theatrical (e.g., industrial, educational, televisual) film-making, or for low-bu...

Colonial state within the Spanish Empire in South America (1776–1825) Not to be confused with United Provinces of the Río de la Plata or Governorate of the Río de la Plata. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (J...

关于与「友谊勋章 (俄罗斯)」標題相近或相同的条目页,請見「友谊勋章 (消歧义)」。 友谊勋章类型单级勋章(仅设有一个等级)授予原因加强各民族友谊、交流与合作国家/地区俄罗斯 颁发单位 俄羅斯颁授资格俄罗斯国民及世界各民族人民設立時間1994年3月2日[1]首次颁发康斯坦丁·蒂托夫(萨马拉州州长)绶带 优先顺序上等荣誉勋章下等光荣父母�...

NATCOIndustryTransportFounded1974HeadquartersGilgit, PakistanKey peopleTahir Hussain (Chairman) Muhammad Saeedullah Yousafzai (Managing Director)Websitewww.natco.gov.pk NATCO bus at Balakot, Mansehra NATCO bus at bus stand in Rawalpindi Northern Areas Transport Corporation or NATCO (Urdu: ٹرانسپورٹ کارپوریشن برائے شمالی علاقہ جات) is the largest transport company in Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan and throughout the Karakoram Highway. NATCO is providing its serv...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada November 2022. Seder-MasochismSutradaraNina PaleyProduserNina PaleyDitulis olehNina PaleyTanggal rilis 11 Juni 2018 (2018-06-11) (Festival Film Animasi Internasional Annecy[1]) Durasi78 menitNegaraAmerika SerikatBahasaInggrisAnggaran$20.000[2 ...

American judge (born 1987) Kathryn Kimball MizelleJudge of the United States District Court for the Middle District of FloridaIncumbentAssumed office November 20, 2020Appointed byDonald TrumpPreceded byVirginia M. Hernandez Covington Personal detailsBornKathryn Anne Kimball (1987-08-14) August 14, 1987 (age 36)Lakeland, Florida, U.S.SpouseChad MizelleEducationCovenant College (BA)University of Florida (JD) Kathryn Kimball Mizelle[1] (née Kathryn Anne Kimball; born August 14,...

5th President of Iran from 1997 to 2005 For other persons with this surname, see Khatami (surname). SayyidAmirHujjat al-IslamMuhammad Khatamiمحمد خاتمیKhatami in 20075th President of IranIn office3 August 1997 – 3 August 2005Supreme LeaderAli KhameneiVice PresidentHassan HabibiMohammad Reza ArefPreceded byAkbar Hashemi RafsanjaniSucceeded byMahmoud AhmadinejadMinister of Culture and Islamic GuidanceIn office9 November 1982 – 24 May 1992PresidentAli Khamenei...

Sports season2019 Pac-12 Conference men's soccer seasonLeagueNCAA Division ISportSoccerDurationAugust 2019 – November 2019Number of teams62020 MLS SuperDraftRegular SeasonChampionsWashington Runners-upStanfordPac-12 Conference men's soccer seasons← 20182020 → 2019 Pac-12 Conference men's soccer standings vte Conf Overall Team W L T W L T No. 6 Washington † 9 – 2 – 0 16 – 4 – 0 No. 4 Stanford + 6 – 2 –...

The practice of removing a portion of an animal's ears or tail For ear cropping, see Cropping (animal). Docking is the intentional removal of part of an animal's tail or, sometimes, ears. The term cropping is more commonly used in reference to the cropping of ears, while docking more commonly—but not exclusively—refers to the tail; the term tailing is used, also. The term has its origins in the living flesh of the tail, commonly known as the dock, from which the animal's tail hairs grow. ...

瓜因贝Guaimbê市镇瓜因贝在巴西的位置坐标:21°54′36″S 49°53′48″W / 21.91°S 49.896666666667°W / -21.91; -49.896666666667国家巴西州圣保罗州面积 • 总计217.448 平方公里(83.957 平方英里)海拔469 公尺(1,539 英尺)人口(2006) • 總計5,258人 • 密度24.2人/平方公里(62.6人/平方英里) 瓜因贝(葡萄牙语:Guaimbê)是巴西圣保罗州�...

For the Band of Brothers episode, see Carentan (Band of Brothers). For the Sanctuary episode, see Carentan (Sanctuary). Delegated commune of Carentan-les-Marais in Normandy, FranceCarentanDelegated commune of Carentan-les-Marais PortLocation of Carentan CarentanShow map of FranceCarentanShow map of NormandyCoordinates: 49°18′N 1°15′W / 49.30°N 1.25°W / 49.30; -1.25CountryFranceRegionNormandyDepartmentMancheArrondissementSaint-LôCantonCarentanCommuneCarentan-le...

Policy on permits required to enter Seychelles Politics of Seychelles Constitution Human rights LGBT rights Cabinet President Wavel Ramkalawan Vice-President Ahmed Afif Legislature National Assembly Speaker: Roger Mancienne Leader of the Opposition: Sebastien Pillay Judiciary Supreme Court Chief Justice: Mathilda Twomey Elections Political parties Recent elections Presidential: 20202025 Parliamentary: 20202025 Administrative divisions Districts Outer Islands Foreign relations Ministry of Fore...

Horror fiction podcast This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Alice Isn't Dead – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) PodcastAlice Isn't DeadPresentationGenreMysterySupernatural horrorDramaHorror podcastCreated byJoseph FinkWritt...





