Benton Harbor BASIC
| |||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

2008 American filmPedroTheatrical release posterDirected byNick OceanoWritten byDustin Lance BlackStory byDustin Lance Black Paris BarclayProduced byRichard Glatzer Wash Westmoreland Paris Barclay Anne Clements Scott Freeman Gil Goldschein Jonathan Murray Chris PanizzonStarringAlex Loynaz Justina Machado Hale Appleman Matt BarrCinematographyMark PutnamEdited byJonathan AlbertsMusic byBarbara CohenDistributed byWolfe VideoRelease date September 7, 2008 (2008-09-07) (TIFF) Ru...

French general Alexandre Camille TaponierTaponier is the third name on Column 5.Born2 February 1749 (1749-02-02)Valence, FranceDied13 April 1831 (1831-04-14) (aged 82)Vanves, Paris, FranceAllegiance FranceService/branchInfantryYears of service1767–1811RankGeneral of DivisionBattles/wars War of the First Coalition Battle of Kaiserslautern (1793) Battle of Froeschwiller (1793) Second Battle of Wissembourg (1793) Siege of Luxembourg (1794–1795) Battle of Ettlingen (17...

OLX Group (OnLine Exchange)URLhttps://www.olx.com/, https://www.olx.pl/ dan https://www.olx.ua/uk/ TipeInkorporasiPemilikOLX Group PembuatAlec Oxenford dan Fabrice Berdiri sejak2006 Lokasi kantor pusatAmsterdam OLX Group adalah pasar daring global yang berkantor pusat di Amsterdam, dan dimiliki oleh kelompok media dan teknologi di Afrika Selatan, Naspers.[1] Perusahaan ini didirikan pada 2006 dan beroperasi di 45 negara.[2] OLX Indonesia Perubahan nama dari Tokobagus menjadi O...

Pelarangan penyiksaan adalah salah satu contoh norma jus cogens Jus cogens atau ius cogens (dalam bahasa Inggris juga disebut peremptory norms) adalah asas dasar hukum internasional yang diakui oleh komunitas internasional sebagai norma yang tidak boleh dilanggar dalam keadaan apapun. Tidak ada konsensus resmi mengenai norma mana yang merupakan jus cogens dan bagaimana suatu norma mencapai status tersebut. Walaupun begitu, beberapa norma yang biasanya dianggap sebagai jus cogens adalah pelara...

Copa América 2004 diadakan di Peru dari 6 Juli hingga 25 Juli 2004. Sebanyak 12 tim terlibat dalam kejuaraan sepak bola bergengsi ini. Dalam kejuaraan ini, Brasil tampil sebagai juara setelah mengalahkan Argentina dengan skor 4-2 melalui adu penalti. Sedangkan Uruguay dan Kolombia berhasil menembus masuk babak semifinal. Venue Arequipa ArequipaChiclayoCuzcoLimaPiuraTacnaTrujillo Chiclayo Estadio Arequipa Estadio Elías Aguirre Kapasitas: 40,000 Kapasitas: 25,000 Cuzco Lima Estadio Garcilaso ...

Joint U.S.-Canadian military unit in WWII Not to be confused with 1st Special Service Brigade. Devil's Brigade and The Black Devils redirect here. For other uses, see Devil's Brigade (disambiguation) and Black Devil (disambiguation). 1st Special Service Force1st Special Service Force shoulder patchActive9 July 1942 – 5 December 1944Country United States CanadaAllegianceAllies (United Nations)BranchArmyTypeCommandoRoleSpecial operationsSize1,800Garrison/HQFort William Henry Harriso...

سيفكابين الاسم النظامي (6R,7R)-3-{[(Aminocarbonyl)oxy]methyl}-7-{(Z)-[2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-1-oxo-2-pentenyl]amino}-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid اعتبارات علاجية ASHPDrugs.com أسماء الدواء الدولية طرق إعطاء الدواء Oral معرّفات CAS 135889-00-8 Y ك ع ت J01J01DD17 DD17 تصنيف منظمة الصحة العالمية المراقبة [لغات أخرى][1]&...
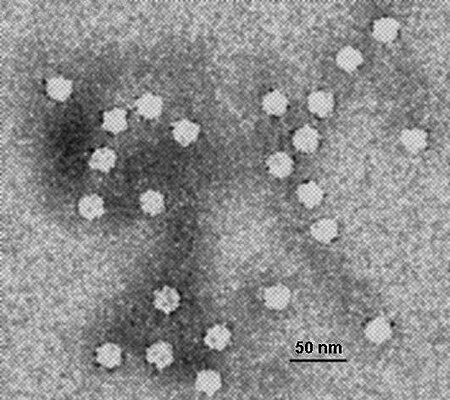
Virus that has DNA as its genetic material Orthopoxvirus particles A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: Duplodnaviria and Varidnaviria, and ssDNA vi...

Species of butterfly Tawny coster Upperside, West Bengal, India Underside, Komodo, Indonesia Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Insecta Order: Lepidoptera Family: Nymphalidae Genus: Acraea Species: A. terpsicore Binomial name Acraea terpsicore(Linnaeus, 1758) Synonyms Acraea violae (Fabricius, 1775) Acraea terpsicore, the tawny coster,[1] is a small, 53–64 millimetres (2.1–2.5 in), leathery-winged butterfly common in g...

Poorly attested body of myths and religious practices of Baltic population of Old Prussians Part of a series onBaltic religion Mythology Prussian Lithuanian Latvian Indo-European Deities Panbaltic Perkūnas Velnias Dievas Saulė Mėnulis Prussian Patollo Peckols Potrimpo Swayxtix Autrimps Aušlavis Bardoayts Kurka Pilnytis Puszajtis Latvian Ūsiņš Ceroklis Jumis Auseklis Laima Dēkla Kārta Lauma Māra Mahte Lithuanian Gabija Žemyna Laima Medeina/Žvorūna Laumė/Ragana Aušrinė Bangpūty...

Virbhadra Singh Ketua Menteri Himachal Pradesh ke–4Masa jabatan25 Desember 2012 – 27 Desember 2017PendahuluPrem Kumar DhumalPenggantiJai Ram ThakurDaerah pemilihanPedesaan ShimlaMasa jabatan6 Maret 2003 – 30 Desember 2007PendahuluPrem Kumar DhumalPenggantiPrem Kumar DhumalDaerah pemilihanRohruMasa jabatan3 Desember 1993 – 24 Maret 1998PendahuluShanta KumarPenggantiPrem Kumar DhumalDaerah pemilihanRohruMasa jabatan8 April 1983 – 5 Maret 1990Pendahu...

此條目之中立性有争议。其內容、語調可能帶有明顯的個人觀點或地方色彩。 (2017年12月22日)加上此模板的編輯者需在討論頁說明此文中立性有爭議的原因,以便讓各編輯者討論和改善。在編輯之前請務必察看讨论页。 玛丽一世Mary I of Scots苏格兰女王統治1542年12月14日-1567年7月24日(24年222天)加冕1543年9月9日前任詹姆斯五世繼任詹姆斯六世摄政沙泰勒羅公爵詹姆斯·漢密爾�...

Mammalian protein found in Homo sapiens MC2RIdentifiersAliasesMC2R, ACTHR, melanocortin 2 receptorExternal IDsOMIM: 607397; MGI: 96928; HomoloGene: 444; GeneCards: MC2R; OMA:MC2R - orthologsGene location (Human)Chr.Chromosome 18 (human)[1]Band18p11.21Start13,882,044 bp[1]End13,915,707 bp[1]Gene location (Mouse)Chr.Chromosome 18 (mouse)[2]Band18 E2|18 41.89 cMStart68,539,978 bp[2]End68,562,391 bp[2]RNA expression patternBgeeHumanMouse (ortho...

Die Sprachphilosophie ist die Disziplin der Philosophie, die sich mit Sprache und Bedeutung beschäftigt, vor allem mit dem Verhältnis von Sprache und Wirklichkeit und dem Verhältnis von Sprache und Bewusstsein (bzw. Denken). Sie ist auch eine Teildisziplin der allgemeinen Linguistik. Sie kann weiter auch als ein Teilbereich der Semiotik angesehen werden, d. h. der allgemeinen Zeichenlehre.[1] Die Sprachphilosophie ist eng verwandt mit der Logik, indem zur Sprachphilosophie auc...
كأس الدوري الياباني 2011 تفاصيل الموسم كأس الدوري الياباني النسخة 19 البلد اليابان المنظم اتحاد اليابان لكرة القدم البطل كاشيما أنتلرز مباريات ملعوبة 27 عدد المشاركين 18 أهداف مسجلة 81 كأس الدوري الياباني 2010 كأس الدوري الياباني 2012 تعديل مصدري...

この項目では、中国料理における拉麺について説明しています。日本におけるラーメン(拉麺)については「ラーメン」をご覧ください。 この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 この項目には、JIS X 0213:2004 で規定されている文字が含まれています(詳細)。 拉麺繁体字 拉麵 簡体字 拉面 発音記号標準中国語�...

In computing, restricting data to be accessible by one thread at a time For the concept in logic and probability theory, see Mutual exclusivity. Two nodes, i and i + 1, being removed simultaneously results in node i + 1 not being removed. In computer science, mutual exclusion is a property of concurrency control, which is instituted for the purpose of preventing race conditions. It is the requirement that one thread of execution never enters a critical section while a concurrent thread of exe...

15/16th-century military campaigns by the Old Swiss Confederacy to expand south of the Alps You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (January 2021) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the German article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation ...

In this Dutch name, the surname is van Leuven, not Leuven. Darts playerNoa-Lynn van Leuvenvan Leuven in 2024Personal informationBorn (1996-09-27) 27 September 1996 (age 28)[1]Beverwijk, NetherlandsHome townHeemskerk, NetherlandsDarts informationLateralityRight-handedWalk-on musicEuphoria by LoreenOrganisation (see split in darts)Current world ranking(PDC) NR (3 October 2024)[2] (WDF W) NR (5 September 2022)[3]WDF major events – best performancesDutch OpenS...
Playing two strings at once on an instrument Audio playback is not supported in your browser. You can download the audio file.Cello triple and quadruple stops from the opening of Jean-Baptiste Bréval's Sonata in C major for cello and piano The beginning of Mozart's Eine kleine Nachtmusik (1787). The first and second violins have a triple stop notated. The low D is to be bowed only briefly and left to ring. Shortly afterwards, B and G are played normally. In music, a double stop is the techni...