Apiogalacturonan
| |||||||||||
Read other articles:

Keuskupan ItabunaDioecesis ItabunensisCatedral São José (2015)LokasiNegara BrazilProvinsi gerejawiSão Salvador da BahiaStatistikLuas14.533 km2 (5.611 sq mi)Populasi- Total- Katolik(per 2006)650.000550,000 (84.6%)InformasiRitusRitus LatinPendirian7 November 1978 (45 tahun lalu)KatedralCatedral São JoséKepemimpinan kiniPausFransiskusUskupCzeslaw Stanula, C.Ss.R. Keuskupan Itabuna (Latin: Dioecesis Itabunensiscode: la is deprecated ) adalah sebuah keu...

PT Gojek IndonesiaNama dagangGojekJenisPerusahaan swastaIndustriTeknologi informasiTransportasiDidirikan5 Oktober 2010Pendiri Nadiem Makarim Kevin Aluwi Michaelangelo Moran KantorpusatJakarta, IndonesiaWilayah operasi Indonesia Thailand Vietnam[1] Singapura FilipinaTokohkunci Catherine Hindra Sutjahyo (CEO) Antoine de Carbonnel (CCO) Severan Rault (CTO) PemilikGoToSitus webwww.gojek.com Gojek (ditulis bergaya sebagai goȷek; sebelumnya ditulis GO-JEK) merupaka...

† Человек прямоходящий Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:Синапсиды�...

Discrimination of person because of sexual orientation Sexualism redirects here. Not to be confused with Sexism. This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. The specific problem is: Article contains a lot of broad and uncited information that could be rewritten and cleaned up into more comprehensible paragraphs. P...

Armed border guard of the Soviet Union This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Soviet Border Troops – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Soviet Border TroopsПограничные войска СССРPograníchnyye Voiská SSSRPatch...
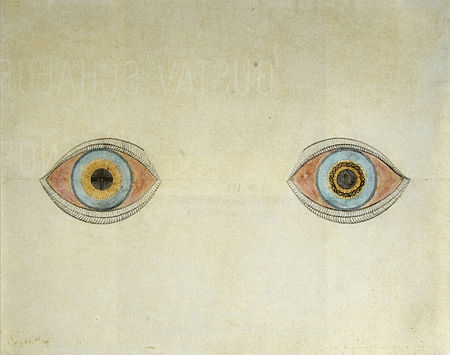
Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando il racconto di Asimov, vedi Allucinazione (racconto). Le informazioni riportate non sono consigli medici e potrebbero non essere accurate. I contenuti hanno solo fine illustrativo e non sostituiscono il parere medico: leggi le avvertenze. AllucinazioneMy eyes at the moment of the apparitions di August Natterer, un artista tedesco che ha dipinto diversi quadri seguendo le sue allucinazioni.Specialitàpsichiatria, psicologia medica e psicoterapia Classifica...

Human settlement in EnglandSands EndSands EndLocation within Greater LondonPopulation12,760 (2011 Census.Ward)[1]OS grid referenceTQ265765London boroughHammersmith & FulhamCeremonial countyGreater LondonRegionLondonCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townLONDONPostcode districtSW6Dialling code020PoliceMetropolitanFireLondonAmbulanceLondon UK ParliamentChelsea and FulhamLondon AssemblyWest Central List of places UK Engl...

莎拉·阿什頓-西里洛2023年8月,阿什頓-西里洛穿著軍服出生 (1977-07-09) 1977年7月9日(46歲) 美國佛羅里達州国籍 美國别名莎拉·阿什頓(Sarah Ashton)莎拉·西里洛(Sarah Cirillo)金髮女郎(Blonde)职业記者、活動家、政治活動家和候選人、軍醫活跃时期2020年—雇主內華達州共和黨候選人(2020年)《Political.tips》(2020年—)《LGBTQ國度》(2022年3月—2022年10月)烏克蘭媒�...

Comedy by Aristophanes This article is about Aristophanes' Ecclesiazusae (Ἐκκλησιάζουσαι). For women in parliament or government, see assembly and women in government. AssemblywomenAristophanes[1]Written byAristophanesChorusAthenian WomenSettingAn Athenian street Assemblywomen (Greek: Ἐκκλησιάζουσαι Ekklesiazousai; also translated as, Congresswomen, Women in Parliament, Women in Power, and A Parliament of Women) is a comedy written by the Greek playwright...

Premier of the Free StateIncumbentMxolisi Dukwanasince 24 February 2023StyleThe HonourableAppointerFree State LegislatureTerm lengthFive years, renewable onceInaugural holderMosiuoa LekotaFormation7 May 1994Websitewww.fs.gov.za/Premiers.htm This article is part of a series on thePolitics of Free State Executive Council Premier: Mxolisi Kaunda Members of the Executive Council Provincial Legislature Speaker: Zanele Sifuba Deputy Speaker: Lucy Mapena Members of the Provincial Legislature S...

Defunct flying squadron of the Royal Air Force This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (February 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) No. 53 Squadron RAFActive15 May 1916–25 October 1919 28 June 1937 – 15 June 1946 1 November 1946 – 28 June 19631 November 1965 - 14 September 1976Country United KingdomBranch Royal Air ForceMotto(s)Uni...

提示:此条目页的主题不是萧。 簫琴簫與洞簫木管樂器樂器別名豎吹、豎篴、通洞分類管樂器相關樂器 尺八 东汉时期的陶制箫奏者人像,出土於彭山江口汉崖墓,藏於南京博物院 箫又稱洞簫、簫管,是中國古老的吹管樂器,特徵為單管、豎吹、開管、邊稜音發聲[1]。「簫」字在唐代以前本指排簫,唐宋以來,由於單管豎吹的簫日漸流行,便稱編管簫爲排簫�...
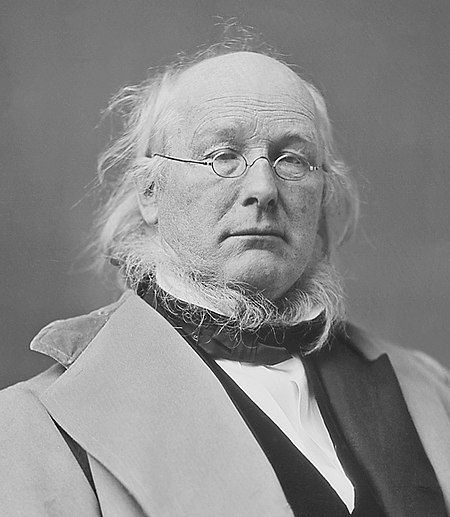

Election in Virginia Main article: 1872 United States presidential election 1872 United States presidential election in Virginia ← 1860 November 5, 1872 1876 → Nominee Ulysses S. Grant Horace Greeley Party Republican Liberal Republican Home state Illinois New York Running mate Henry Wilson Benjamin G. Brown Electoral vote 11 0 Popular vote 93,463 91,647 Percentage 50.47% 49.49% County Results Grant 50-60% 60-70% &#...

Leader of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 Khrushchev redirects here. For the surname and other people with the surname, see Khrushchev (surname). Nikita KhrushchevНикита ХрущёвKhrushchev in 1962First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet UnionIn office7 September 1953 – 14 October 1964Preceded byJoseph Stalin (as General Secretary)Succeeded byLeonid Brezhnev7th Premier of the Soviet UnionIn office27 March 1958 – 14 October 1964PresidentKliment Vor...

جواز سفر جورجيمعلومات عامةنوع المستند جواز سفرالغرض التعريف (هوية شخصية)صادر عن جورجياصالح في جورجيامتطلبات الاستحقاق الجنسية الجورجيةالانتهاء البالغ (18 عامًا أو أكبر): 10 سنوات الطفل (أقل من 18 عامًا): 3 سنوات[1]تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات تصدر جوازات السفر الج...

Sub-prefecture and town in Mbomou, Central African RepublicBakoumaSub-prefecture and townBakoumaCoordinates: 5°41′55″N 22°47′0″E / 5.69861°N 22.78333°E / 5.69861; 22.78333Country Central African RepublicPrefectureMbomouGovernment • Sub-PrefectSerge Didier Kamegba Makimba[1]Elevation500 m (1,640 ft)Population (2003) • Total17,599 Bakouma is a sub-prefecture in the prefecture of Mbomou in Central African Re...

Мікросхема (EPROM) з прозорим віконцем, через яке видно кристал напівпровідника Мікропроцесор Intel Pentium з тепловідводом Мікросхе́ма (інтегральна мікросхема, інтегральна схема(ІС), чип, мікрочип, англ. integrated circuit) — напівпровідниковий електронний пристрій, який являє собою ...

加拿大 加拿大政府与政治系列条目 王室 君主(歷任名單):查爾斯三世 總督(歷任名單):瑪麗·梅·西蒙 各省君主制(英语:Monarchy in the Canadian provinces) 省督 皇家特權 行政部門(國王會同樞密院) 樞密院 總理(歷任名單):賈斯汀·杜魯多 內閣(閣員名單(英语:List of Canadian ministries)):第29屆內閣 樞密院院長(英语:President of the King's Privy Council for Canada) 樞密�...

Gymnastik vid olympiska sommarspelen 2004 Artistisk Kval herrar damer Mångkamp, lag herrar damer Mångkamp, ind. herrar damer Hopp herrar damer Fristående herrar damer Bygelhäst herrar Ringar herrar Barr herrar damer Räck herrar Bom damer Rytmisk Trupp damer Individuellt damer Trampolin Individuellt herrar damer Herrarnas barr i gymnastik vid olympiska sommarspelen 2004 avgjordes den 14 och 23 augusti i O.A.C.A. Olympic Indoor Hall. Medaljörer Gren Guld Silve...

كاس من القهوة الأيرلندية القهوة الأيرلندية (بالإيرلندية Caife Gaelach) عبارة عن كوكتيل مكون من خليط القهوة الساخنة، الويسكي الإيرلندي والسكر مع الكريمة.[1][2][3] بحسب الوصفة الأصلية الكريمة غير مخفوقة مع أن البعض يستعمل الكريمة المخفوقة. ينسب اختراع هذا المشروب إلى جو�...