Alexander Maconochie (penal reformer)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Liste der Filmjahre ◄◄ | ◄ | 1962 | 1963 | 1964 | 1965 | Filmjahr 1966 | 1967 | 1968 | 1969 | 1970 | ► | ►► Weitere Ereignisse Filmjahr 1966 Am 15. Dezember 1966 starb der US-amerikanische Filmproduzent und Trickfilmzeichner Walt Disney. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Ereignisse 2 Erfolgreichste Filme 2.1 Top 10 in Deutschland 2.2 Top 10 in den USA 2.3 Erfolgreichste Filme in Asien 3 Filmpreise 3.1 Golden Globe Award 3.2 Academy A...

Italia Selatan Italia Selatan (bahasa Italia: Italia meridionale atau sebatas Sud Italia) adalah satu dari lima wilayah statistik resmi di Italia yang digunakan oleh Institut Nasional Statistik (ISTAT), sebuah wilayah NUTS tingkat pertama di Italia, dan sebuah konstituensi Parlemen Eropa. Ia mencakup enam dari dua puluh daerah (regioni) di Italia, meliputi: Abruzzo Apulia Basilicata Calabria Campania Molise Italia Selatan hanya disebut dalam konteks statistik dan elektoral. Ia termasuk da...

For primaries in other races, see 2020 United States House of Representatives elections in Minnesota and 2020 United States Senate election in Minnesota. 2020 Minnesota Republican presidential primary ← 2016 March 3, 2020 2024 → ← MANC →39 Republican National Convention delegates Candidate Donald Trump Bill Weld(write-in) Home state Florida[1] Massachusetts Delegate count 39 0 Popular vote 137,275 443 Percentage 97.67%...

Mestaruussarja 1940-1941 Competizione Mestaruussarja Sport Calcio Edizione 33ª Organizzatore SPL/FBF Date dal agosto 1940al giugno 1941 Luogo Finlandia Partecipanti 8 Formula Girone all'italiana Risultati Vincitore TPS(3º titolo) Secondo VPS Retrocessioni HT HelsinkiHPS Statistiche Miglior marcatore Jussi Valtonen (14) Incontri disputati 52 Gol segnati 242 (4,65 per incontro) Cronologia della competizione 1940 1942 Manuale La Mestaruussarja 1940-1941 fu la trentatre...

County of the Kingdom of Hungary Győr CountyComitatus Jauriensis (Latin)Győr vármegye (Hungarian)Komitat Raab (German) County of the Kingdom of Hungary(12th century-1785, 1790-1923) Coat of arms CapitalGyőrArea • Coordinates47°41′N 17°38′E / 47.683°N 17.633°E / 47.683; 17.633 • 19101,534 km2 (592 sq mi)Population • 1910 136,300 History • Established 12th century• Merged in...

Family of Canadian-designed sounding rockets Black Brant sounding rockets The Black Brant is a family of Canadian-designed sounding rockets originally built by Bristol Aerospace, since absorbed by Magellan Aerospace in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Over 800 Black Brants of various versions have been launched since they were first produced in 1961, and the type remains one of the most popular sounding rockets.[1] They have been repeatedly used by the Canadian Space Agency and NASA. History Black...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Maret 2023. Samsung Galaxy S23Samsung Galaxy S23+Samsung Galaxy S23 UltraS23 (kiri), S23+ (tengah), S23 Ultra (kanan)MerekSamsung GalaxyPembuatSamsung ElectronicsSeriGalaxy S seriesJaringan2G / 3G / 4G LTE / 5G NRRilis pertama1 Februari 2023; 14 bulan lalu (202...

Indian multinational technology company Tech MahindraCompany typePublicTraded asBSE: 532755NSE: TECHMBSE SENSEX ConstituentNSE NIFTY 50 ConstituentISININE669C01036IndustryInformation technologyConsultingOutsourcingFounded24 October 1986; 37 years ago (24 October 1986)FounderAnand MahindraHeadquartersPune, Maharashtra, India[1]Area servedWorldwideKey peopleAnand Mahindra (Chairman)Mohit Joshi[2] (MD & CEO)Revenue ₹52,912 crore (US$6.6 billion) ...

Voce principale: Supercopa de España. Supercopa de España 2004Supercoppa di Spagna 2004 Competizione Supercopa de España Sport Calcio Edizione 19ª Organizzatore RFEF Date 21 e 24 agosto 2004 Luogo Spagna Partecipanti 2 Risultati Vincitore Real Saragozza(1º titolo) Secondo Valencia Statistiche Incontri disputati 2 Gol segnati 5 (2,5 per incontro) Pubblico 60 000 (30 000 per incontro) Cronologia della competizione 2003 2005 Manuale La Supercopa de España 2004 è stat...

List of events in the year 1329 ← 1328 1327 1326 1325 1324 1329 in Ireland → 1330 1331 1332 1333 1334 Centuries: 12th 13th 14th 15th 16th Decades: 1300s 1310s 1320s 1330s 1340s See also:Other events of 1329 List of years in Ireland Events from the year 1329 in Ireland. Incumbent Lord: Edward III Events June 10 – Braganstown massacre, County Louth: over 160 killed. August 10 - The battle of Ardnocher took place near Horseleap between the forces of Thomas Butler and William Mac Ge...

此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2021年7月4日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:美国众议院 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 美國眾議院 United States House of Representatives第118届美国国会众议院徽章 众议院旗...
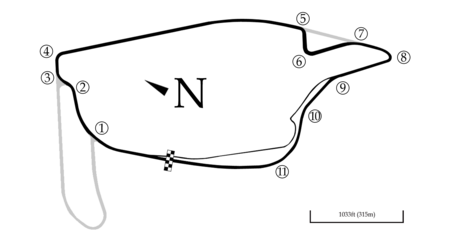
Motor race meeting 2015 ITM 500 AucklandEvent InformationRound 12 of 14 in the 2015 International V8 Supercars ChampionshipDate6–8 November 2015LocationPukekohe, New ZealandVenuePukekohe Park RacewayWeatherFineResultsRace 1Distance 21 laps 60 kmPole position Jamie WhincupTriple Eight Race Engineering 1:03.3203Winner Jamie WhincupTriple Eight Race Engineering 24:48.8376Race 2Distance 21 laps 60 kmPole position David ReynoldsRod Nash Racing 1:02.4690Winner David ReynoldsRod Nash Racing 26:37....

Micropolitan Statistical Area in Texas, United StatesGranbury micropolitan areaMicropolitan Statistical AreaGranbury, TX Micropolitan Statistical AreaHood County Courthouse in 2018Interactive Map of Granbury, TX μSA City of Granbury Granbury, TX μSA Other Counties in the Dallas–Fort Worth CSA CountryUnited StatesStateTexasTime zoneUTC-6 (CST) • Summer (DST)UTC-5 (CDT) The Granbury micropolitan statistical area, as defined by the Unite...

Toby TurnerTobuscus di VidCon pada tahun 2012.LahirToby Joe Turner3 Maret 1985 (umur 39)Osborn, MississippiTempat tinggalLos Angeles, CaliforniaKebangsaanAmerikaAlmamaterUniversitas FloridaPekerjaanAktor, komedian, musisi dan artis Internet.Tahun aktif2006–sekarangKarya terkenalLiteral Trailers, Tobuscus Adventures, I Can Swing My Sword, The Dramatic SongTelevisiThe High Fructose Adventures of Annoying Orange Toby Joe Turner (lahir 3 Maret 1985) adalah seorang aktor, komedian, mu...

Baldissero CanaveseKomuneComune di Baldissero CanaveseNegaraItaliaWilayahPiedmontProvinsiProvinsi Torino (TO)Luas • Total4,4 km2 (17 sq mi)Populasi (Desember 2004) • Total510 • Kepadatan12/km2 (30/sq mi)Zona waktuUTC+1 (CET) • Musim panas (DST)UTC+2 (CEST)Kode pos10080Kode area telepon0124 Baldissero Canavese adalah komune yang terletak di distrik Provinsi Torino, Italia. Kota Baldissero Canavese memiliki luas sebesar 4....

Bupati SukabumiLambang Kabupaten SukabumiPetahanaDrs. H. Marwan Hamami, MMsejak 17 Februari 2016KediamanKantor Bupati Sukabumi (Palabuhanratu)Masa jabatan5 TahunDibentuk21 April 1921 (pembentukan)1 Oktober 1945 (hari jadi)Pejabat pertamaR. A. A. SoerianatabrataSitus webhttp://sukabumikab.go.id/ Berikut ini adalah daftar Bupati Sukabumi. No Potret Bupati Mulai menjabat Akhir menjabat Prd. Ket. Wakil Bupati 1 R. A. A. Soerianatabrata 1921 1930 1 — 2 R. A. A. Soeriadanoeningrat 1930 1942 ...
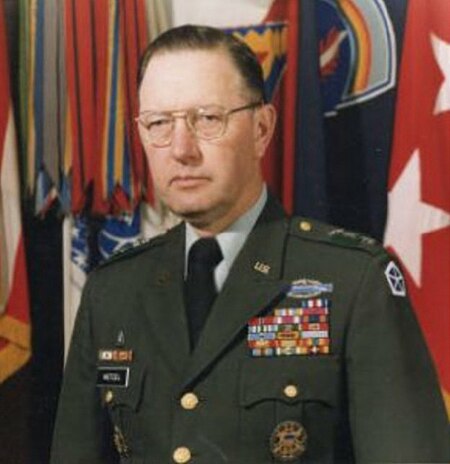

United States Army general (1930–2022) Robert Wetzel redirects here. For the American limnologist and ecologist, see Robert G. Wetzel. Robert L. WetzelWetzel in the 1980sNickname(s)SamBorn(1930-10-06)October 6, 1930Clarksburg, West Virginia, U.S.DiedJanuary 20, 2022(2022-01-20) (aged 91)Columbus, Georgia, U.S.BuriedFort Benning Main Post CemeteryAllegianceUnited StatesService/branchUnited States ArmyYears of service1952–1986RankLieutenant GeneralCommands held V Corps Fort Bennin...

US Navy Seawolf-class submarine Jimmy Carter returns to NSB Kitsap, 2017 Jimmy Carter's profile History United States NameUSS Jimmy Carter NamesakeJimmy Carter Ordered29 June 1996 BuilderGeneral Dynamics Electric Boat Laid down5 December 1998 Launched13 May 2004 Christened5 June 2004 Commissioned19 February 2005 HomeportBangor Annex of Naval Base Kitsap, Washington MottoSemper Optima (Always the Best) Statusin active service Badge General characteristics Class and typeModified Seawolf-class s...

令制国一覧 > 東海道 > 武蔵国 > 児玉郡 日本 > 関東地方 > 埼玉県 > 児玉郡 埼玉県児玉郡の範囲(1.美里町 2.神川町 3.上里町 薄緑・水色:後に他郡から編入した区域) 児玉郡(こだまぐん) は、埼玉県(武蔵国)の郡。 人口53,331人、面積109.99km²、人口密度485人/km²。(2024年8月1日、推計人口) 以下の3町を含む。 美里町(みさと...

Voce principale: Unione Sportiva Foggia. Unione Sportiva Foggia & InceditStagione 1962-1963Sport calcio Squadra Foggia & Incedit Allenatore Oronzo Pugliese All. in seconda Giuseppe Bortolotti Presidente Domenico Rosa Rosa Serie B5º posto Coppa ItaliaSecondo turno Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Lazzotti e Nocera (38)Totale: Lazzotti e Nocera (40) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Nocera (24)Totale: Nocera (24) 1961-1962 1963-1964 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa pagina rac...

